Get started using Python on Windows for beginners
The following is a step-by-step guide for beginners interested in learning Python using Windows 10.
Set up your development environment
For beginners who are new to Python, we recommend you install Python from the Microsoft Store. Installing via the Microsoft Store uses the basic Python3 interpreter, but handles set up of your PATH settings for the current user (avoiding the need for admin access), in addition to providing automatic updates. This is especially helpful if you are in an educational environment or a part of an organization that restricts permissions or administrative access on your machine.
If you are using Python on Windows for web development, we recommend a different set up for your development environment. Rather than installing directly on Windows, we recommend installing and using Python via the Windows Subsystem for Linux. For help, see: Get started using Python for web development on Windows. If you’re interested in automating common tasks on your operating system, see our guide: Get started using Python on Windows for scripting and automation. For some advanced scenarios (like needing to access/modify Python’s installed files, make copies of binaries, or use Python DLLs directly), you may want to consider downloading a specific Python release directly from python.org or consider installing an alternative, such as Anaconda, Jython, PyPy, WinPython, IronPython, etc. We only recommend this if you are a more advanced Python programmer with a specific reason for choosing an alternative implementation.
Install Python
To install Python using the Microsoft Store:
Go to your Start menu (lower left Windows icon), type «Microsoft Store», select the link to open the store.
Once the store is open, select Search from the upper-right menu and enter «Python». Open «Python 3.7» from the results under Apps. Select Get.
Once Python has completed the downloading and installation process, open Windows PowerShell using the Start menu (lower left Windows icon). Once PowerShell is open, enter Python —version to confirm that Python3 has installed on your machine.
The Microsoft Store installation of Python includes pip, the standard package manager. Pip allows you to install and manage additional packages that are not part of the Python standard library. To confirm that you also have pip available to install and manage packages, enter pip —version .
Install Visual Studio Code
By using VS Code as your text editor / integrated development environment (IDE), you can take advantage of IntelliSense (a code completion aid), Linting (helps avoid making errors in your code), Debug support (helps you find errors in your code after you run it), Code snippets (templates for small reusable code blocks), and Unit testing (testing your code’s interface with different types of input).
VS Code also contains a built-in terminal that enables you to open a Python command line with Windows Command prompt, PowerShell, or whatever you prefer, establishing a seamless workflow between your code editor and command line.
To install VS Code, download VS Code for Windows: https://code.visualstudio.com.
Once VS Code has been installed, you must also install the Python extension. To install the Python extension, you can select the VS Code Marketplace link or open VS Code and search for Python in the extensions menu (Ctrl+Shift+X).
Python is an interpreted language, and in order to run Python code, you must tell VS Code which interpreter to use. We recommend sticking with Python 3.7 unless you have a specific reason for choosing something different. Once you’ve installed the Python extension, select a Python 3 interpreter by opening the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), start typing the command Python: Select Interpreter to search, then select the command. You can also use the Select Python Environment option on the bottom Status Bar if available (it may already show a selected interpreter). The command presents a list of available interpreters that VS Code can find automatically, including virtual environments. If you don’t see the desired interpreter, see Configuring Python environments.
To open the terminal in VS Code, select View > Terminal, or alternatively use the shortcut Ctrl+` (using the backtick character). The default terminal is PowerShell.
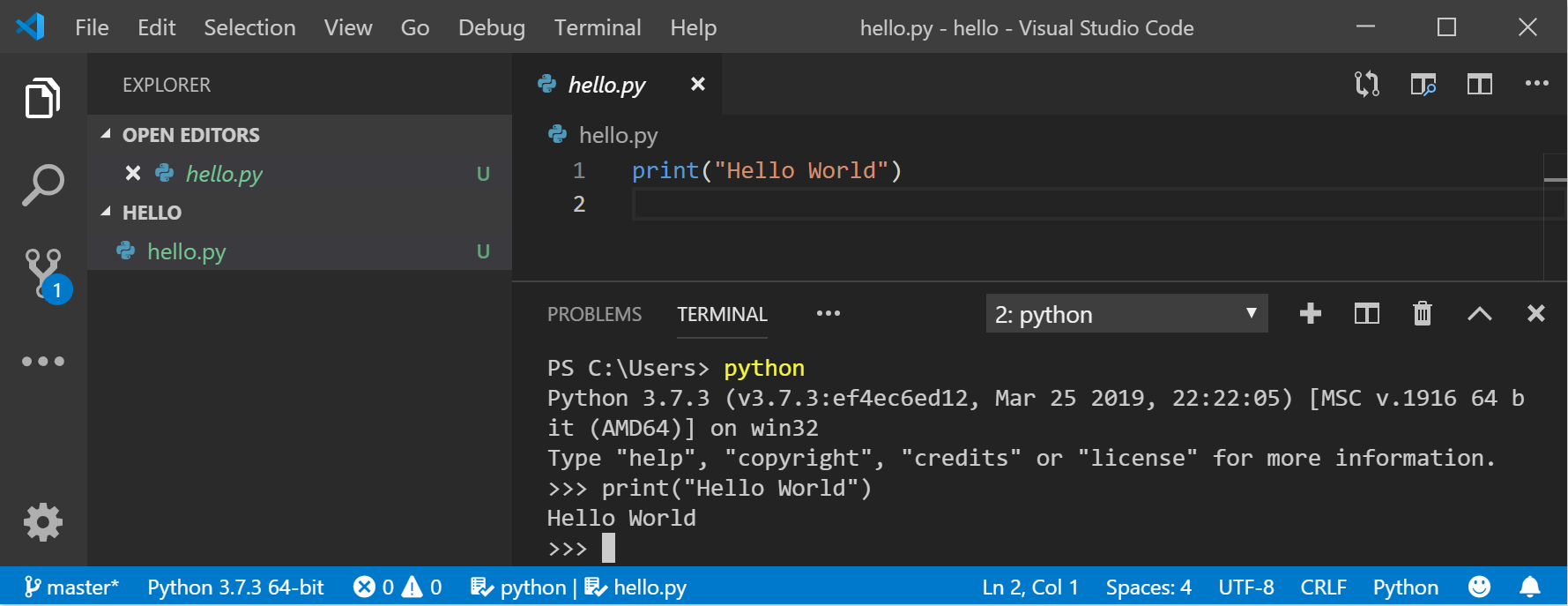
Inside your VS Code terminal, open Python by simply entering the command: python
Try the Python interpreter out by entering: print(«Hello World») . Python will return your statement «Hello World».
Install Git (optional)
If you plan to collaborate with others on your Python code, or host your project on an open-source site (like GitHub), VS Code supports version control with Git. The Source Control tab in VS Code tracks all of your changes and has common Git commands (add, commit, push, pull) built right into the UI. You first need to install Git to power the Source Control panel.
Download and install Git for Windows from the git-scm website.
An Install Wizard is included that will ask you a series of questions about settings for your Git installation. We recommend using all of the default settings, unless you have a specific reason for changing something.
If you’ve never worked with Git before, GitHub Guides can help you get started.
Hello World tutorial for some Python basics
Python, according to its creator Guido van Rossum, is a “high-level programming language, and its core design philosophy is all about code readability and a syntax which allows programmers to express concepts in a few lines of code.”
Python is an interpreted language. In contrast to compiled languages, in which the code you write needs to be translated into machine code in order to be run by your computer’s processor, Python code is passed straight to an interpreter and run directly. You just type in your code and run it. Let’s try it!
With your PowerShell command line open, enter python to run the Python 3 interpreter. (Some instructions prefer to use the command py or python3 , these should also work). You will know that you’re successful because a >>> prompt with three greater-than symbols will display.
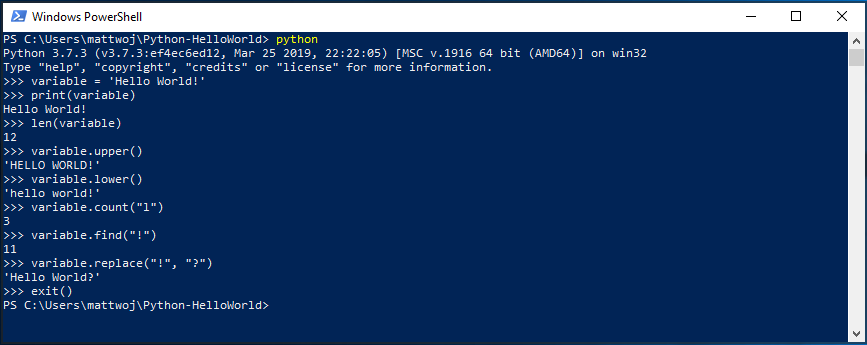
There are several built-in methods that allow you to make modifications to strings in Python. Create a variable, with: variable = ‘Hello World!’ . Press Enter for a new line.
Print your variable with: print(variable) . This will display the text «Hello World!».
Find out the length, how many characters are used, of your string variable with: len(variable) . This will display that there are 12 characters used. (Note that the blank space it counted as a character in the total length.)
Convert your string variable to upper-case letters: variable.upper() . Now convert your string variable to lower-case letters: variable.lower() .
Count how many times the letter «l» is used in your string variable: variable.count(«l») .
Search for a specific character in your string variable, let’s find the exclamation point, with: variable.find(«!») . This will display that the exclamation point is found in the 11th position character of the string.
Replace the exclamation point with a question mark: variable.replace(«!», «?») .
To exit Python, you can enter exit() , quit() , or select Ctrl-Z.
Hope you had fun using some of Python’s built-in string modification methods. Now try creating a Python program file and running it with VS Code.
Hello World tutorial for using Python with VS Code
The VS Code team has put together a great Getting Started with Python tutorial walking through how to create a Hello World program with Python, run the program file, configure and run the debugger, and install packages like matplotlib and numpy to create a graphical plot inside a virtual environment.
Open PowerShell and create an empty folder called «hello», navigate into this folder, and open it in VS Code:
Once VS Code opens, displaying your new hello folder in the left-side Explorer window, open a command line window in the bottom panel of VS Code by pressing Ctrl+` (using the backtick character) or selecting View > Terminal. By starting VS Code in a folder, that folder becomes your «workspace». VS Code stores settings that are specific to that workspace in .vscode/settings.json, which are separate from user settings that are stored globally.
Continue the tutorial in the VS Code docs: Create a Python Hello World source code file.
Create a simple game with Pygame
Pygame is a popular Python package for writing games — encouraging students to learn programming while creating something fun. Pygame displays graphics in a new window, and so it will not work under the command-line-only approach of WSL. However, if you installed Python via the Microsoft Store as detailed in this tutorial, it will work fine.
Once you have Python installed, install pygame from the command line (or the terminal from within VS Code) by typing python -m pip install -U pygame —user .
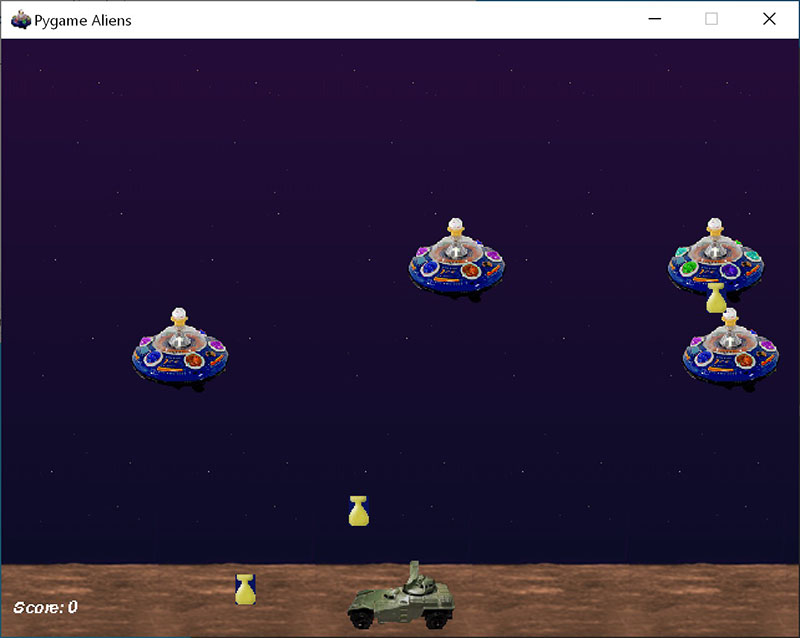
Test the installation by running a sample game : python -m pygame.examples.aliens
All being well, the game will open a window. Close the window when you are done playing.
Here’s how to start writing your own game.
Open PowerShell (or Windows Command Prompt) and create an empty folder called «bounce». Navigate to this folder and create a file named «bounce.py». Open the folder in VS Code:
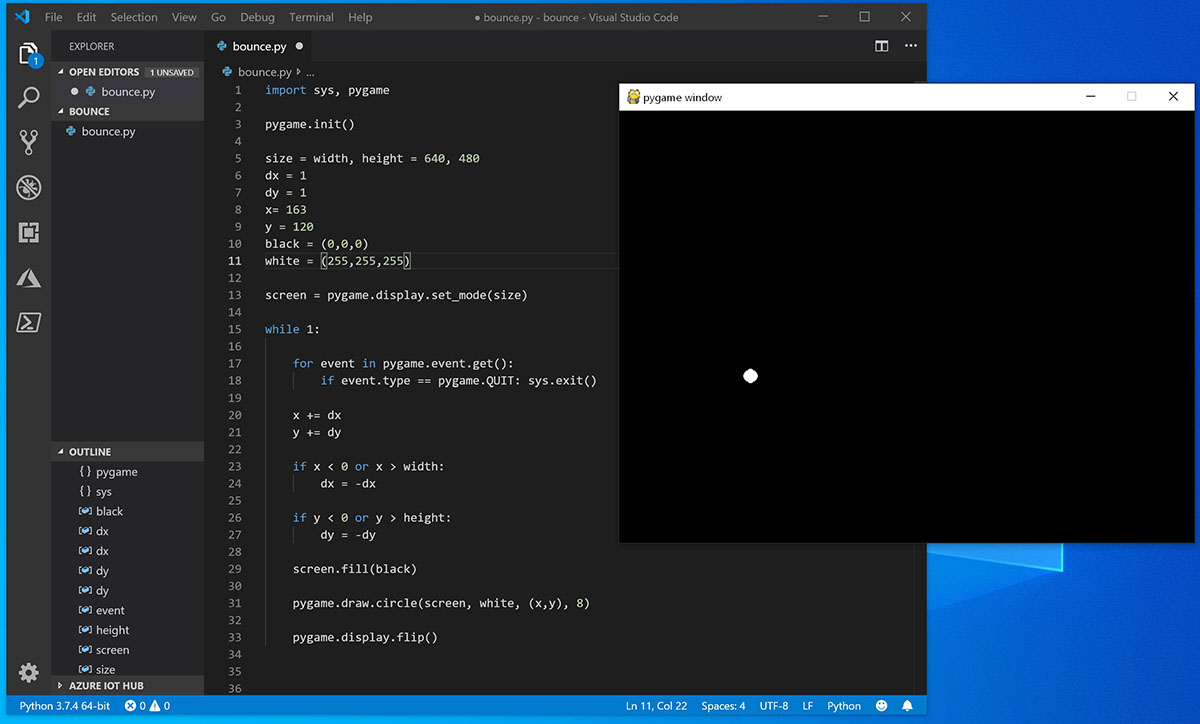
Using VS Code, enter the following Python code (or copy and paste it):
Save it as: bounce.py .
From the PowerShell terminal, run it by entering: python bounce.py .
Try adjusting some of the numbers to see what effect they have on your bouncing ball.
Read more about writing games with pygame at pygame.org.
Resources for continued learning
We recommend the following resources to support you in continuing to learn about Python development on Windows.
Online courses for learning Python
Introduction to Python on Microsoft Learn: Try the interactive Microsoft Learn platform and earn experience points for completing this module covering the basics on how to write basic Python code, declare variables, and work with console input and output. The interactive sandbox environment makes this a great place to start for folks who don’t have their Python development environment set up yet.
Python on Pluralsight: 8 Courses, 29 Hours: The Python learning path on Pluralsight offers online courses covering a variety of topics related to Python, including a tool to measure your skill and find your gaps.
LearnPython.org Tutorials: Get started on learning Python without needing to install or set anything up with these free interactive Python tutorials from the folks at DataCamp.
The Python.org Tutorials: Introduces the reader informally to the basic concepts and features of the Python language and system.
Learning Python on Lynda.com: A basic introduction to Python.
Working with Python in VS Code
Editing Python in VS Code: Learn more about how to take advantage of VS Code’s autocomplete and IntelliSense support for Python, including how to customize their behavior. or just turn them off.
Linting Python: Linting is the process of running a program that will analyse code for potential errors. Learn about the different forms of linting support VS Code provides for Python and how to set it up.
Debugging Python: Debugging is the process of identifying and removing errors from a computer program. This article covers how to initialize and configure debugging for Python with VS Code, how to set and validate breakpoints, attach a local script, perform debugging for different app types or on a remote computer, and some basic troubleshooting.
Unit testing Python: Covers some background explaining what unit testing means, an example walkthrough, enabling a test framework, creating and running your tests, debugging tests, and test configuration settings.
Python 3 Installation & Setup Guide
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Installing Python on Windows, macOS, and Linux
Installing or updating Python on your computer is the first step to becoming a Python programmer. There are a multitude of installation methods: you can download official Python distributions from Python.org, install from a package manager, and even install specialized distributions for scientific computing, Internet of Things, and embedded systems.
This tutorial focuses on official distributions, as they’re generally the best option for getting started with learning to program in Python.
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to:
- Check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your machine
- Install or update Python on Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Use Python on mobile devices like phones or tablets
- Use Python on the Web with online interpreters
No matter what operating system you’re on, this tutorial has you covered. Find your operating system below and dive in!
Free Bonus: Click here to get a Python Cheat Sheet and learn the basics of Python 3, like working with data types, dictionaries, lists, and Python functions.
How to Install Python on Windows#
There are three installation methods on Windows:
- The Microsoft Store
- The full installer
- Windows Subsystem for Linux
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your Windows computer. You’ll also learn which of the three installation methods you should use.
How to Check Your Python Version on Windows#
To check if you already have Python on your Windows machine, first open a command-line application, such as PowerShell.
Tip: Here’s how you open PowerShell:
- Press the Win key.
- Type PowerShell .
- Press Enter .
Alternatively, you can right-click the Start button and select Windows PowerShell or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
You can also use cmd.exe or Windows Terminal.
With the command line open, type in the following command and press Enter :
Using the —version switch will show you the version that’s installed. Alternatively, you can use the -V switch:
In either case, if you see a version less than 3.8.4 , which was the most recent version at the time of writing, then you’ll want to upgrade your installation.
Note: If you don’t have a version of Python on your system, then both of the above commands will launch the Microsoft Store and redirect you to the Python application page. You’ll see how to complete the installation from the Microsoft Store in the next section.
If you’re interested in where the installation is located, then you can use the where.exe command in cmd.exe or PowerShell:
Note that the where.exe command will work only if Python has been installed for your user account.
What Your Options Are#
As mentioned earlier, there are three ways to install the official Python distribution on Windows:
Microsoft Store package: The most straightforward installation method on Windows involves installing from the Microsoft Store app. This is recommended for beginner Python users looking for an easy-to-set-up interactive experience.
Full Installer: This approach involves downloading Python directly from the Python.org website. This is recommended for intermediate and advanced developers who need more control during the setup process.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): The WSL allows you to run a Linux environment directly in Windows. You can learn how to enable the WSL by reading the Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide for Windows 10.
In this section, we’ll focus on only the first two options, which are the most popular installation methods in a Windows environment.
If you want to install in the WSL, then you can read the Linux section of this tutorial after you’ve installed the Linux distribution of your choice.
Note: You can also complete the installation on Windows using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on Windows, check out Setting Up Python for Machine Learning on Windows.
The two official Python installers for Windows aren’t identical. The Microsoft Store package has some important limitations.
Limitations of the Microsoft Store Package#
The official Python documentation has this to say about the Microsoft Store package:
The Microsoft Store package is an easily installable Python interpreter that is intended mainly for interactive use, for example, by students. (Source)
The key takeaway here is that the Microsoft Store package is “intended mainly for interactive use.” That is, the Microsoft Store package is designed to be used by students and people learning to use Python for the first time.
In addition to targeting beginning Pythonistas, the Microsoft Store package has limitations that make it ill-suited for a professional development environment. In particular, it does not have full write access to shared locations such as TEMP or the registry.
Windows Installer Recommendations#
If you’re new to Python and focused primarily on learning the language rather than building professional software, then you should install from the Microsoft Store package. This offers the shortest and easiest path to getting started with minimal hassle.
On the other hand, if you’re an experienced developer looking to develop professional software in a Windows environment, then the official Python.org installer is the right choice. Your installation won’t be limited by Microsoft Store policies, and you can control where the executable is installed and even add Python to PATH if necessary.
How to Install From the Microsoft Store#
If you’re new to Python and looking to get started quickly, then the Microsoft Store package is the best way to get up and running without any fuss. You can install from the Microsoft Store in two steps.
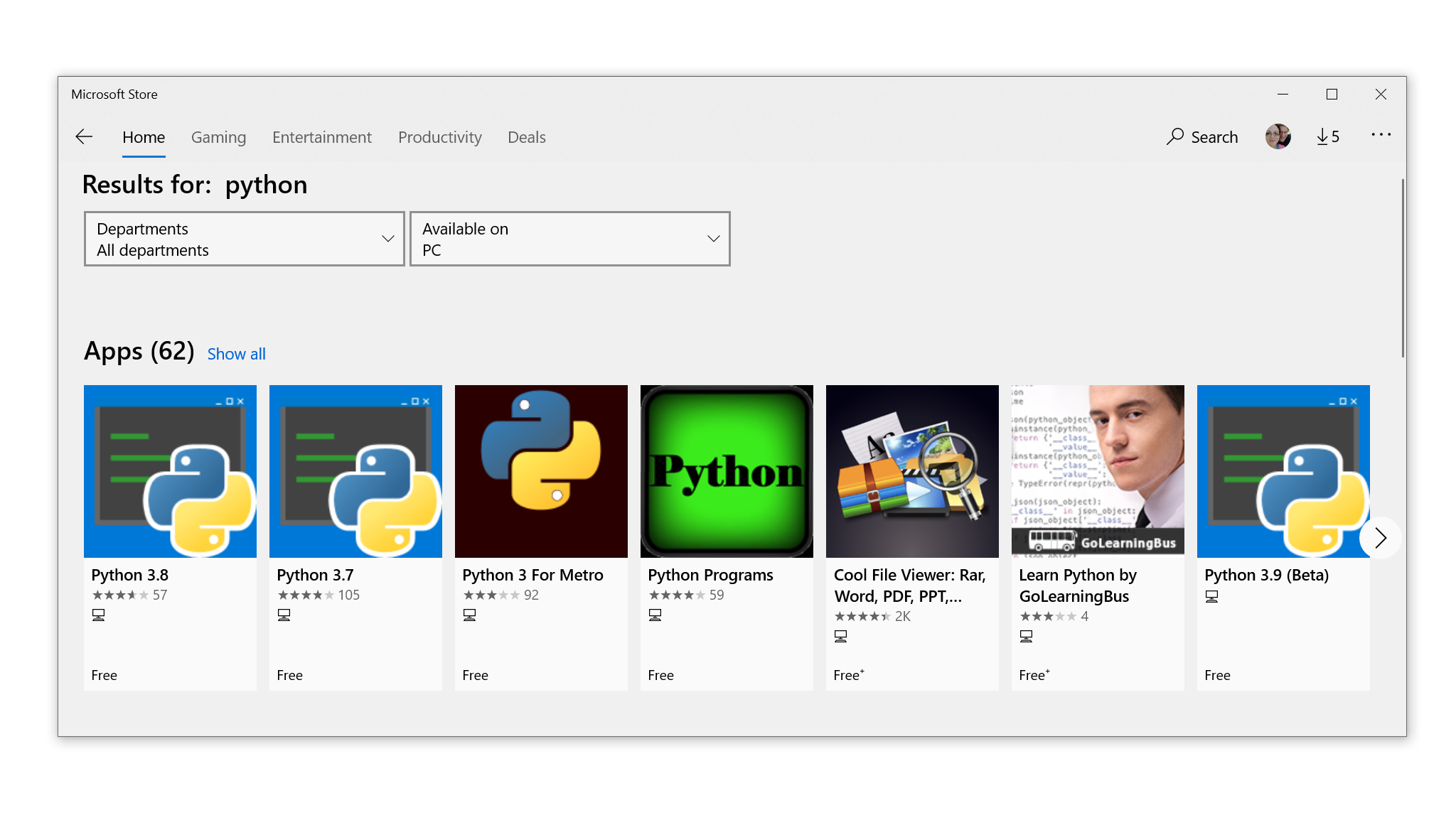
Step 1: Open the Python App Page in the Microsoft Store#
Open the Microsoft Store app and search for Python .
You’ll likely see multiple versions that you can choose to install:
Select Python 3.8, or the highest version number you see available in the app, to open the installation page.
Warning: Make sure that the Python application you’ve selected is created by the Python Software Foundation.
The official Microsoft Store package will always be free, so if the application costs money, then it’s the wrong application.
Alternatively, you can open PowerShell and type the following command:
If you don’t already have a version of Python on your system, then when you press Enter , the Microsoft Store will automatically launch and take you to the latest version of Python in the store.
Step 2: Install the Python App#
After you’ve selected the version to be installed, follow these steps to complete the installation:
Wait for the application to download. When it’s finished downloading, the Get button will be replaced with a button that says Install on my devices.
Click Install on my devices and select the devices on which you’d like to complete the installation.
Click Install Now and then OK to start the installation.
If the installation was successful, then you’ll see the message “This product is installed” at the top of the Microsoft Store page.
Congratulations! You now have access to Python, including pip and IDLE!
How to Install From the Full Installer#
For professional developers who need a full-featured Python development environment, installing from the full installer is the right choice. It offers more customization and control over the installation than installing from the Microsoft Store.
You can install from the full installer in two steps.
Step 1: Download the Full Installer#
Follow these steps to download the full installer:
Open a browser window and navigate to the Python.org Downloads page for Windows.
Under the “Python Releases for Windows” heading, click the link for the Latest Python 3 Release — Python 3.x.x. As of this writing, the latest version was Python 3.8.4.
Scroll to the bottom and select either Windows x86-64 executable installer for 64-bit or Windows x86 executable installer for 32-bit.
If you aren’t sure whether to select the 32-bit or the 64-bit installer, then you can expand the box below to help you decide.
32-bit or 64-bit Python? Show/Hide
For Windows, you can choose either the 32-bit or the 64-bit installer. Here’s the difference between the two:
If your system has a 32-bit processor, then you should choose the 32-bit installer. If you attempt to install the 64-bit version on a 32-bit processor, then you’ll get an error at the beginning and the install will fail.
On a 64-bit system, either installer will work for most purposes. The 32-bit version will generally use less memory, but the 64-bit version performs better for applications with intensive computation.
If you’re unsure which version to pick, go with the 64-bit version.
If you have a 64-bit system and would like to switch from 64-bit Python to 32-bit (or vice versa), then you can just uninstall Python and then reinstall it by downloading the other installer from Python.org.
When the installer is finished downloading, move on to the next step.
Step 2: Run the Installer#
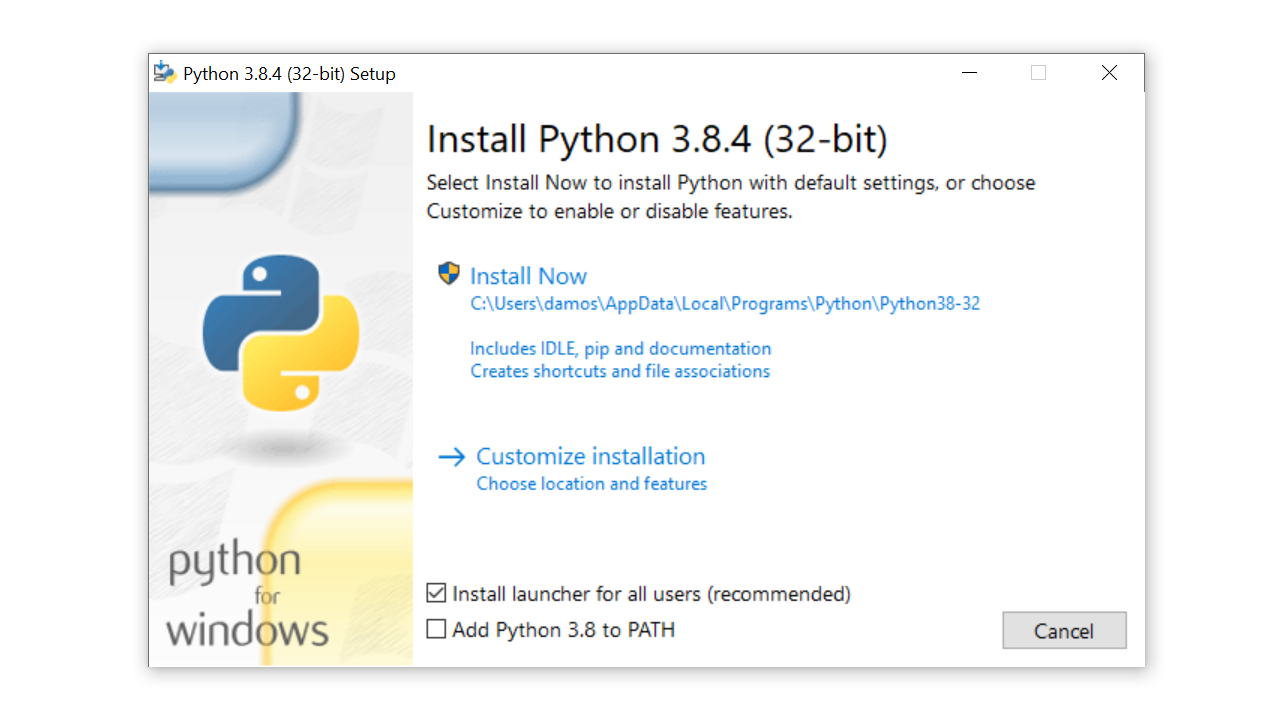
Once you’ve chosen and downloaded an installer, run it by double-clicking on the downloaded file. A dialog box like the one below will appear:
There are four things to notice about this dialog box:
The default install path is in the AppData/ directory of the current Windows user.
The Customize installation button can be used to customize the installation location and which additional features get installed, including pip and IDLE.
The Install launcher for all users (recommended) checkbox is checked default. This means every user on the machine will have access to the py.exe launcher. You can uncheck this box to restrict Python to the current Windows user.
The Add Python 3.8 to PATH checkbox is unchecked by default. There are several reasons that you might not want Python on PATH , so make sure you understand the implications before you check this box.
The full installer gives you total control over the installation process.
Warning: If you don’t know what PATH is, then it’s highly recommended that you do not install with the full installer. Use the Microsoft Store package instead.
Customize the installation to meet your needs using the options available on the dialog box. Then click Install Now. That’s all there is to it!
Congratulations—you now have the latest version of Python 3 on your Windows machine!
How to Install Python on macOS#
Python 2 comes preinstalled on older versions of macOS. This is no longer the case for current versions of macOS, starting with macOS Catalina.
There are two installation methods on macOS:
- The official installer
- The Homebrew package manager
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your macOS device. You’ll also learn which of the two installation methods you should use.
How to Check Your Python Version on a Mac#
To check which Python version you have on your Mac, first open a command-line application, such as Terminal.
Tip: Here’s how you open Terminal:
- Press the Cmd + Space keys.
- Type Terminal .
- Press Enter .
Alternatively, you can open Finder and navigate to Applications → Utilities → Terminal.
With the command line open, type in the following commands:
If you have Python on your system, then one or more of these commands should respond with a version number.
For example, if Python 3.6.10 were already set up on your computer, then the python3 command would display that version number:
- None of the above commands returns a version number.
- The only version you see displayed is in the Python 2.X series.
- You have a version of Python 3 that isn’t the latest available, which was version 3.8.4 as of this writing.
What Your Options Are#
There are two ways to install the official Python distribution on macOS:
The official installer: This method involves downloading the official installer from the Python.org website and running it on your machine.
The Homebrew package manager: This method involves downloading and installing the Homebrew package manager if you don’t already have it installed, and then typing a command into a terminal application.
Both the official installer and the Homebrew package manager will work, but only the official installer is maintained by the Python Software Foundation.
Note: You can also complete the installation on macOS using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on macOS, check out the macOS installation guide from the official Anaconda documentation.
The distributions installed by the official installer and the Homebrew package manager aren’t identical. Installing from Homebrew has some limitations.
Limitations of Installing From Homebrew#
The Python distribution for macOS available on Homebrew doesn’t include the Tcl/Tk dependency required by the Tkinter module. Tkinter is the standard library module for developing graphical user interfaces in Python and is in fact an interface for the Tk GUI toolkit, which isn’t part of Python.
Homebrew doesn’t install the Tk GUI toolkit dependency. Instead, it relies on an existing version installed on your system. The system version of Tcl/Tk may be outdated or missing entirely and could prevent you from importing the Tkinter module.
macOS Installer Recommendations#
The Homebrew package manager is a popular method for installing Python on macOS because it’s easy to manage from the command line and offers commands to upgrade Python without having to go to a website. Because Homebrew is a command-line utility, it can be automated with bash scripts.
However, the Python distribution offered by Homebrew isn’t controlled by the Python Software Foundation and could change at any time. The most reliable method on macOS is to use the official installer, especially if you plan on doing Python GUI programming with Tkinter.
How to Install From the Official Installer#
Installing Python from the official installer is the most reliable installation method on macOS. It includes all the system dependencies needed for developing applications with Python.
You can install from the official installer in two steps.
Step 1: Download the Official Installer#
Follow these steps to download the full installer:
Open a browser window and navigate to the Python.org Downloads page for macOS.
Under the “Python Releases for Mac OS X” heading, click the link for the Latest Python 3 Release — Python 3.x.x. As of this writing, the latest version was Python 3.8.4.
Scroll to the bottom and click macOS 64-bit installer to start the download.
When the installer is finished downloading, move on to the next step.
Step 2: Run the Installer#
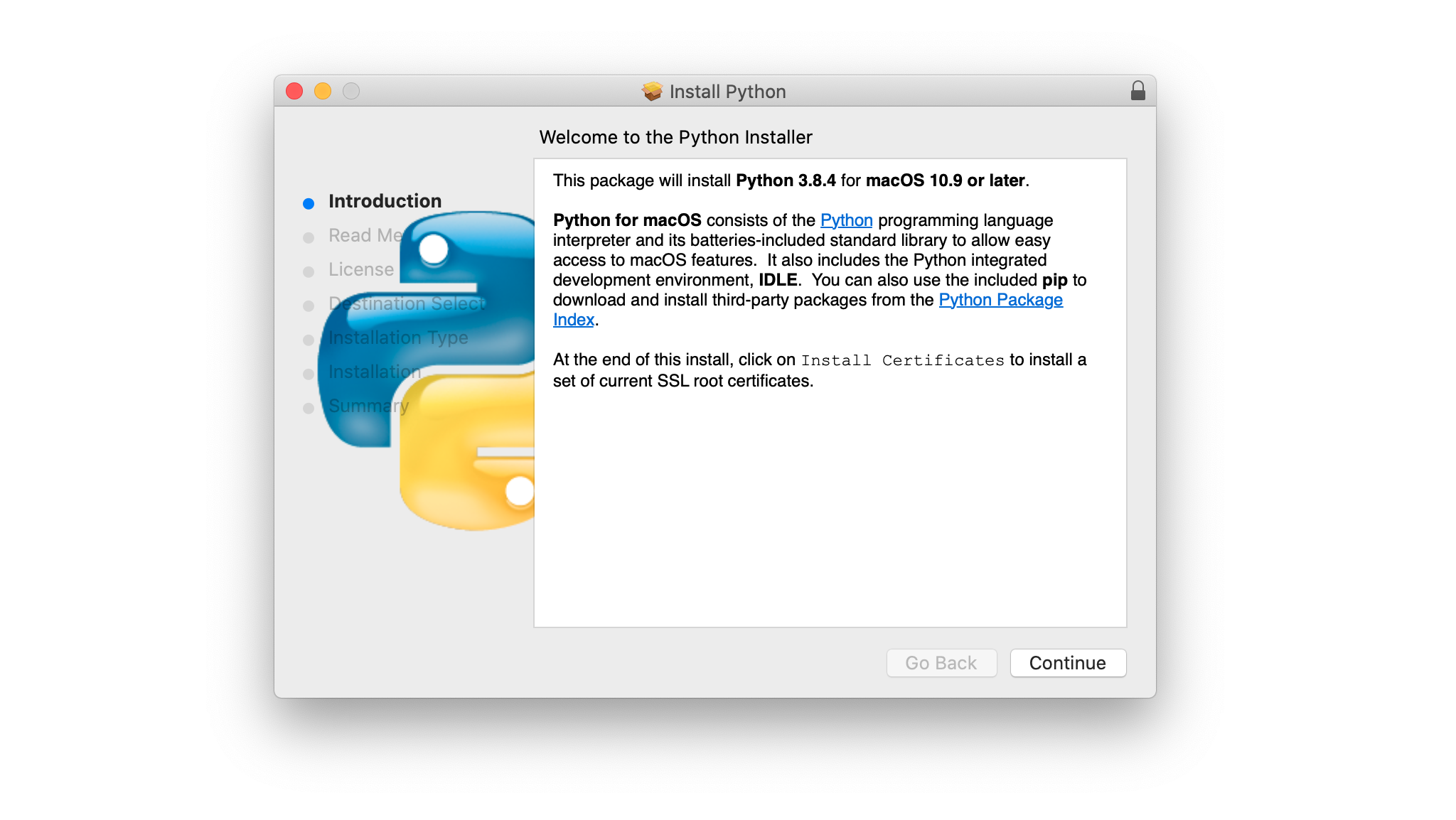
Run the installer by double-clicking the downloaded file. You should see the following window:
Follow these steps to complete the installation:
Press Continue a few times until you’re asked to agree to the software license agreement. Then click Agree.
You’ll be shown a window that tells you the install destination and how much space it will take. You most likely don’t want to change the default location, so go ahead and click Install to start the installation.
When the installer is finished copying files, click Close to close the installer window.
Congratulations—you now have the latest version of Python 3 on your macOS computer!
How to Install From Homebrew#
For users who need to install from the command line, especially those who won’t be using Python to develop graphical user interfaces with the Tkinter module, the Homebrew package manager is a good option. You can install from the Homebrew package manager in two steps.
Step 1: Install Homebrew#
If you already have Homebrew installed, then you can skip this step. If you don’t have Homebrew installed, then use the following procedure to install Homebrew:
Open a browser and navigate to http://brew.sh/.
You should see a command for installing Homebrew near the top of the page under the tile “Install Homebrew.” This command will be something like the following:
Highlight the command with your cursor and press Cmd + C to copy it to your clipboard.
Open a terminal window and paste the command, then press Enter . This will begin the Homebrew installation.
Enter your macOS user password when prompted.
Depending on your Internet connection, it may take a few minutes to download all of Homebrew’s required files. Once the installation is complete, you’ll end up back at the shell prompt in your terminal window.
Note: If you’re doing this on a fresh install of macOS, you may get a pop-up alert asking you to install Apple’s command line developer tools. These tools are necessary for installation, so you can confirm the dialog box by clicking Install.
After the developer tools are installed, you’ll need to press Enter to continue installation of Homebrew.
Now that Homebrew is installed, you’re ready to install Python.
Step 2: Install Python#
Follow these steps to complete the installation with Homebrew:
Open a terminal application.
Type in the following command to upgrade Homebrew:
Installing with Homebrew is now as straightforward as running the command brew install python3 . This will download and set up the latest version of Python on your machine.
You can make sure everything went correctly by testing if you can access Python from the terminal:
Type pip3 and press Enter .
You should see the help text from Python’s pip package manager. If you get an error message running pip3 , then go through the install steps again to make sure you have a working installation.
Congratulations—you now have Python on your macOS system!
How to Install Python on Linux#
There are two installation methods on Linux:
- Using your operating system’s package manager
- Building Python from source code
In this section, you’ll learn how to check which version of Python, if any, is on your Linux computer. You’ll also learn which of the two installation methods you should use.
How to Check Your Python Version on Linux#
Many Linux distributions come packaged with Python, but it probably won’t be the latest version and may even be Python 2 instead of Python 3. You should check the version to make sure.
To find out which version of Python you have, open a terminal window and try the following commands:
If you have Python on your machine, then one or more of these commands should respond with a version number.
For example, if you already had Python 3.6.10 on your computer, then the python3 —version command would display that version number:
You’ll want to get the latest version of Python if your current version is in the Python 2.X series or is not the latest version of Python 3 available, which was 3.8.4 as of this writing.
What Your Options Are#
There are two ways to install the official Python distribution on Linux:
Install from a package manager: This is the most common installation method on most Linux distributions. It involves running a command from the command line.
Build from source code: This method is more difficult than using a package manager. It involves running a series of commands from the command line as well as making sure you have the correct dependencies installed to compile the Python source code.
Not every Linux distribution has a package manager, and not every package manager has Python in its package repository. Depending on your operating system, building Python from source code might be your only option.
Note: You can also complete the installation on Linux using alternative distributions, such as Anaconda, but this tutorial covers only official distributions.
Anaconda is a popular platform for doing scientific computing and data science with Python. To learn how to install Anaconda on Linux, check out the Linux installation guide in the official Anaconda documentation.
Which installation method you use mainly boils down to whether your Linux OS has a package manager and whether you need to control the details of the installation.
Linux Installation Recommendations#
The most popular way to install Python on Linux is with your operating system’s package manager, which is a good choice for most users. However, depending on your Linux distribution, Python may not be available through a package manager. In this case, you’ll need to build Python from source code.
There are three main reasons that you might choose to build Python from source code:
You can’t download Python from your operating system’s package manager.
You need to control how Python gets compiled, such as when you want to lower the memory footprint on embedded systems.
You want to try out beta versions and release candidates of the latest and greatest version before it’s generally available.
To complete the installation on your Linux machine, find your Linux distribution below and follow the steps provided.
How to Install on Ubuntu and Linux Mint#
In this section, you’ll learn how to install Python using Ubuntu’s apt package manager. If you’d like to build Python from source code, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
Note: Linux Mint users can skip to the “Linux Mint and Ubuntu 17 and below” section.
Depending on the version of the Ubuntu distribution you run, the process for setting up Python on your system will vary. You can determine your local Ubuntu version by running the following command:
Follow the instructions below that match the version number you see under Release in the console output:
Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04 and above: Python 3.8 doesn’t come by default on Ubuntu 18.04 and above, but it is available in the Universe repository. To install version 3.8, open a terminal application and type the following commands:
Once the installation is complete, you can run Python 3.8 with the python3.8 command and pip with the pip3 command.
Linux Mint and Ubuntu 17 and below: Python 3.8 isn’t in the Universe repository, so you need to get it from a Personal Package Archive (PPA). For example, to install from the “deadsnakes” PPA, use the following commands:
Once the installation is complete, you can run Python 3.8 with the python3.8 command and run pip with the pip3 command.
Congratulations! You now have Python 3 set up on your machine!
How to Install on Debian Linux#
Before you can install Python 3.8 on Debian, you’ll need to install the sudo command. To install it, execute the following commands in a terminal:
After that, open the /etc/sudoers file using the sudo vim command or your favorite text editor. Add the following line of text to the end of the file, replacing your_username with your actual username:
Now you can skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section to finish installing Python.
How to Install on openSUSE#
Building from source is the most reliable way to set up Python on openSUSE. To do that, you’ll need to install the development tools, which can be done in YaST via the menus or by using zypper :
This might take a while to complete as it installs over 150 packages. Once it’s completed, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
How to Install on CentOS and Fedora#
Python 3.8 isn’t available in the CentOS and Fedora repositories, so you’ll have to build Python from source code. Before you compile Python, though, you need to make sure your system is prepared.
Once yum finishes updating, you can install the necessary build dependencies with the following commands:
When everything is finished installing, skip ahead to the How to Build Python From Source Code section.
How to Install on Arch Linux#
Arch Linux is fairly diligent about keeping up with Python releases. It’s likely you already have the latest version. If not, use the following command to update Python:
When Python is finished updating, you should be all set!
How to Build Python From Source Code#
Sometimes your Linux distribution doesn’t have the latest version of Python, or maybe you just want to be able to build the latest, greatest version yourself. Here are the steps you need to take to build Python from source:
Step 1: Download the Source Code#
To start, you need to get the Python source code. Python.org makes this fairly straightforward. If you go to the Downloads page, then you’ll see the latest source for Python 3 at the top. Just make sure you don’t grab Legacy Python, Python 2!
When you select the Python 3 version, you’ll see a “Files” section at the bottom of the page. Select Gzipped source tarball and download it to your machine. If you prefer a command-line method, you can use wget to download the file to your current directory:
When the tarball finishes downloading, there are a few things you’ll need to do to prepare your system for building Python.
Step 2: Prepare Your System#
There are a few distro-specific steps involved in building Python from scratch. The goal of each step is the same on all distros, but you might need to translate to your distribution if it doesn’t use apt-get :
First, update your package manager and upgrade your packages:
Next, make sure you have all of the build requirements installed:
It’s fine if you already have some of the requirements installed on your system. You can execute the above commands and any existing packages will not be overwritten.
Now that your system is ready to go, it’s time to start building Python!
Step 3: Build Python#
Once you have the prerequisites and the TAR file, you can unpack the source into a directory. Note that the following command will create a new directory called Python-3.8.3 under the one you’re in:
Now you need to run the ./configure tool to prepare the build:
The enable-optimizations flag will enable some optimizations within Python to make it run about 10 percent faster. Doing this may add twenty or thirty minutes to the compilation time. The with-ensurepip=install flag will install pip bundled with this installation.
Next, you build Python using make . The -j option simply tells make to split the building into parallel steps to speed up the compilation. Even with the parallel builds, this step can take several minutes:
Finally, you’ll want to install your new version of Python. You’ll use the altinstall target here to avoid overwriting the system Python. Since you’re installing into /usr/bin , you’ll need to run as root:
It might take a while to finish installation. Once it’s done, you can verify that Python is set up correctly.
Step 4: Verify Your Installation#
Test that the python3.8 —version command returns the latest version:
If you see Python 3.8.4 , then you’re all set!
If you have some extra time on your hands, you can also run the test suite to make sure everything is working properly on your system.
To run the test suite, type the following command:
You’ll probably want to find something else to do for a while, as your computer will be running tests for some time. If all the tests pass, then you can be confident that your brand-new Python build is working as expected!
How to Install Python on iOS#
The Pythonista app for iOS is a full-fledged Python development environment that you can run on your iPhone or iPad. It features a Python editor, technical documentation, and an interpreter all rolled into a single app.
Pythonista is surprisingly fun to use. It’s a great little tool when you’re stuck without a laptop and want to work on your Python skills on the go. It comes with the complete Python 3 standard library and even includes full documentation that you can browse offline.
To set up Pythonista, you need to download it from the iOS app store.
How to Install Python on Android#
If you have an Android tablet or phone and want to practice Python on the go, there are several options available. The one that we found most reliably supports Python 3.8 is Pydroid 3.
Pydroid 3 features an interpreter that you can use for REPL sessions, and it also allows you to edit, save, and execute Python code.
You can download and install Pydroid 3 from the Google Play store. There is a free version and also a paid Premium version that supports code prediction and code analysis.
Online Python Interpreters#
If you want to try out the examples in this tutorial without setting up Python on your machine, then there are several websites that offer an online Python interpreter:
These cloud-based Python interpreters may not be able to execute some of the more complex examples in this tutorial, but they’re adequate for running most of the code and may be a nice way to get started. More information on using these sites is presented in the next tutorial in this series.
Conclusion#
Congratulations! You now have access to the latest version of Python for your system. Your Python journey is just beginning.
In this tutorial you’ve learned how to:
- Check which version of Python, if any, is installed on your system
- Install the latest version of Python on Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Use Python on mobile devices like phones or tablets
- Use Python on the Web with online interpreters
You’re now ready to get started programming in Python! Be sure to share your progress and any questions you may have in the comments below.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Installing Python on Windows, macOS, and Linux
Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. No spam ever. Unsubscribe any time. Curated by the Real Python team.
Each tutorial at Real Python is created by a team of developers so that it meets our high quality standards. The team members who worked on this tutorial are:
Master Real-World Python Skills With Unlimited Access to Real Python
Join us and get access to hundreds of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
Master Real-World Python Skills
With Unlimited Access to Real Python
Join us and get access to hundreds of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
Real Python Comment Policy: The most useful comments are those written with the goal of learning from or helping out other readers—after reading the whole article and all the earlier comments. Complaints and insults generally won’t make the cut here.
What’s your #1 takeaway or favorite thing you learned? How are you going to put your newfound skills to use? Leave a comment below and let us know.