Installing Ruby
With package managers or third-party tools, you have plenty of options to install and manage Ruby.
You may already have Ruby installed on your computer. You can check inside a terminal emulator by typing:
This should output some information on the installed Ruby version.
Choose Your Installation Method
There are several ways to install Ruby:
- On a UNIX-like operating system, using your system’s package manager is easiest. However, the packaged Ruby version may not be the newest one.
- Installers can be used to install a specific or multiple Ruby versions. There is also an installer for Windows.
- Managers help you to switch between multiple Ruby versions on your system.
- Finally, you can also build Ruby from source.
On Windows 10, you can also use the Windows Subsystem for Linux to install one of the supported Linux distributions and use any of the installation methods available on that system.
Here are available installation methods:
Package Management Systems
If you cannot compile your own Ruby, and you do not want to use a third-party tool, you can use your system’s package manager to install Ruby.
Some members of the Ruby community feel that you should avoid package managers to install Ruby and that you should use dedicated tools instead.
It is possible that major package managers will install older Ruby versions instead of the latest release. To use the latest Ruby release, check that the package name matches its version number. Or use a dedicated installer.
apt (Debian or Ubuntu)
Debian GNU/Linux and Ubuntu use the apt package manager. You can use it like this:
yum (CentOS, Fedora, or RHEL)
CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL use the yum package manager. You can use it like this:
The installed version is typically the latest version of Ruby available at the release time of the specific distribution version.
snap (Ubuntu or other Linux distributions)
Snap is a package manager developed by Canonical. It is available out-of-the-box on Ubuntu, but snap also works on many other Linux distributions. You can use it like this:
We have several channels per Ruby minor series. For instance, the following commands switch to Ruby 2.3:
portage (Gentoo)
Gentoo uses the portage package manager.
To install a specific version, set RUBY_TARGETS in your make.conf . See the Gentoo Ruby Project website for details.
pacman (Arch Linux)
Arch Linux uses a package manager named pacman. To get Ruby, just do this:
This should install the latest stable Ruby version.
Homebrew (macOS)
Ruby versions 2.0 and above are included by default in macOS releases since at least El Capitan (10.11).
Homebrew is a commonly used package manager on macOS. Installing Ruby using Homebrew is easy:
This should install the latest Ruby version.
FreeBSD
FreeBSD offers both pre-packaged and source-based methods to install Ruby. Prebuilt packages can be installed via the pkg tool:
A source-based method can be used to install Ruby using the Ports Collection. This is useful if you want to customize the build configuration options.
More information about Ruby and its surrounding ecosystem on FreeBSD can be found on the FreeBSD Ruby Project website.
Ruby on OpenIndiana
To install Ruby on OpenIndiana, please use the Image Packaging System (IPS) client. This will install the Ruby binaries and RubyGems directly from the OpenIndiana repositories. It’s easy:
However, the third-party tools might be a good way to obtain the latest version of Ruby.
Other Distributions
On other systems, you can search the package repository of your Linux distribution’s manager for Ruby. Alternatively, you can use a third-party installer.
Installers
If the version of Ruby provided by your system or package manager is out of date, a newer one can be installed using a third-party installer.
Some installers allow you to install multiple versions on the same system; associated managers can help to switch between the different Rubies.
If you are planning to use RVM as a version manager you don’t need a separate installer, it comes with its own.
ruby-build
ruby-build is a plugin for rbenv that allows you to compile and install different versions of Ruby. ruby-build can also be used as a standalone program without rbenv. It is available for macOS, Linux, and other UNIX-like operating systems.
ruby-install
ruby-install allows you to compile and install different versions of Ruby into arbitrary directories. chruby is a complimentary tool used to switch between Ruby versions. It is available for macOS, Linux, and other UNIX-like operating systems.
RubyInstaller
On Windows, RubyInstaller gives you everything you need to set up a full Ruby development environment.
Just download it, run it, and you are done!
Ruby Stack
If you are installing Ruby in order to use Ruby on Rails, you can use the following installer:
- Bitnami Ruby Stack provides a complete development environment for Rails. It supports macOS, Linux, Windows, virtual machines, and cloud images.
Managers
Many Rubyists use Ruby managers to manage multiple Rubies. They allow easy or even automatic switching between Ruby versions depending on the project and other advantages but are not officially supported. You can however find support within their respective communities.
asdf-vm
asdf-vm is an extendable version manager that can manage multiple language runtime versions on a per-project basis. You will need the asdf-ruby plugin (which in turn uses ruby-build) to install Ruby.
chruby
chruby allows you to switch between multiple Rubies. It can manage Rubies installed by ruby-install or even built from source.
rbenv
rbenv allows you to manage multiple installations of Ruby. While it can’t install Ruby by default, its ruby-build plugin can. Both tools are available for macOS, Linux, or other UNIX-like operating systems.
RVM (“Ruby Version Manager”)
RVM allows you to install and manage multiple installations of Ruby on your system. It can also manage different gemsets. It is available for macOS, Linux, or other UNIX-like operating systems.
Uru is a lightweight, multi-platform command line tool that helps you to use multiple Rubies on macOS, Linux, or Windows systems.
Building from Source
Of course, you can install Ruby from source. Download and unpack a tarball, then just do this:
By default, this will install Ruby into /usr/local . To change, pass the —prefix=DIR option to the ./configure script.
You can find more information about building from source in the Ruby README file.
Using the third-party tools or package managers might be a better idea, though, because the installed Ruby won’t be managed by any tools.
Установка Ruby
Вы можете использовать различные инструменты для установки Ruby. Эта страница описывает, как использовать основные системы управления пакетами и сторонние инструменты для управления и установки Ruby, и как собрать Ruby из исходников.
Выберите ваш метод установки
Есть несколько способов установки Ruby:
- Когда вы на UNIX-подобных операционных системах, использование менеджера пакетов вашей системы — это самый простой способ. Однако, версия Ruby в пакетных менеджерах не самая последняя.
- Установщики могут быть использованы для установки конкретной версии или нескольких версий Ruby. Есть установщик для Windows.
- Менеджеры помогут вам переключаться между различными версиями Ruby, установленными на вашей системе.
- Ну и наконец, вы можете также собрать Ruby из исходников.
В следующем списке перечислены доступные способы установки для различных нужд и платформ.
Системы управления пакетами
Если вы не можете скомпилировать ваш собственный Ruby и не хотите использовать сторонний инструмент для установки – вы можете воспользоваться пакетным менеджером вашей операционной системы.
Некоторые участники сообщества Ruby убеждены, что никогда не стоит пользоваться пакетными менеджерами для установки Ruby. Вместо этого лучше воспользоваться другими инструментами. Оставим все плюсы и минусы данного подхода за границами данного текста, отметим лишь, что основной причиной данной убежденности является то, что в пакетных менеджерах зачастую содержится информация об устаревших версиях Ruby. Если вы хотите использовать новейшую версию Ruby, убедитесь, что вы используете верное имя пакета или воспользуйтесь инструментами описанными ниже вместо этого.
apt (Debian или Ubuntu)
Debian GNU/Linux и Ubuntu используют систему управления пакетами apt . Вы можете использовать ее следующим образом:
Пакет ruby-full установит Ruby версии 2.3.1, которая является последним стабильным релизом.
yum (CentOS, Fedora, или RHEL)
CentOS, Fedora, и RHEL используют систему управления пакетами yum . Вы можете использовать ее следующим образом:
Устанавливаемая версия обычно является последней версией Ruby, доступной на момент выхода конкретной версии дистрибутива.
portage (Gentoo)
Gentoo использует систему управления пакетами portage .
По умолчанию, будут установлены версии 1.9 и 2.0, но доступны и другие версии. Для установки конкретной версии, заполните RUBY_TARGETS в вашем make.conf . Подробнее смотрите на сайте проекта Gentoo Ruby.
pacman (Arch Linux)
Arch Linux использует систему управления пакетами pacman . Чтобы получить Ruby, просто напишите следующее:
Это должно установить последнюю стабильную версию Ruby.
Homebrew (macOS)
На OS X El Capitan, Yosemite и Mavericks, Ruby 2.0 уже включены. OS X Mountain Lion, Lion и Snow Leopard поставляются с версией Ruby 1.8.7.
Многие люди на macOS используют Homebrew как пакетный менеджер. И это действительно просто – установить Ruby:
Это установит последнюю версию Ruby.
Ruby на Solaris и OpenIndiana
Ruby 1.8.7 доступен для Solaris 8-10 на Sunfreeware и Blastwave. Ruby 1.9.2p0 также доступен на Sunfreeware, но это все уже устарело.
Чтобы установить Ruby на OpenIndiana, пожалуйста, используйте клиент Image Packaging System, или IPS. Это установит последние бинарники Ruby и RubyGems прямо из сетевого репозитория OpenSolaris для Ruby 1.9. Это просто:
Однако, сторонние инструменты могут быть хорошим способом получить последнюю версию Ruby.
Другие дистрибутивы
На других системах, вы можете поискать репозиторий пакета Ruby для пакетного менеджера вашего Linux дистрибутива, или же сторонние инструменты могут стать хорошим выбором для вас.
Установщики
Если версия Ruby, предоставляемая вашей операционной системой или пакетным менеджером, не актуальна, то вы можете установить новую версию при помощи сторонних установщиков. Некоторые из них также позволяют установить несколько версий Ruby в вашей системе и переключаться между ними. Если вы планируете использовать RVM как менеджер версий — то вам не нужен отдельный установщик, он идет со своим.
ruby-build
ruby-build — это плагин для rbenv, который позволяет вам скомпилировать и установить разные версии Ruby в произвольные каталоги. ruby-build может использоваться как отдельная программа без rbenv. Он доступен для macOS, Linux и других UNIX-подобных операционных систем.
ruby-install
ruby-install позволяет вам скомпилировать и установить различные версии Ruby в произвольные каталоги. Существует также родственник chruby, который управляет переключением между версиями Ruby. Он доступен для macOS, Linux и других UNIX-подобных операционных систем.
RubyInstaller
Для пользователей Windows существует отличный проект, помогающий установить Ruby: RubyInstaller. Он предоставляет вам все, что нужно для настройки полноценного окружения Ruby на Windows.
Просто скачайте его, запустите и все готово!
Ruby Stack
Если вы устанавливаете Ruby для того, чтобы воспользоваться Ruby on Rails, вы можете использовать следующий установщик:
- Bitnami Ruby Stack, которые предоставляет полное окружение для разработки на Rails. Поддерживает macOS, Linux, Windows, виртуальные машины и облачные сервисы.
Менеджеры
Многие рубисты используют менеджеры для управления несколькими версиями Ruby. Они предоставляют различные преимущества, но поддерживаются не официально. Однако их сообщество может оказать помощь.
asdf-vm
asdf-vm — это расширяемый менеджер версий, который может управлять несколькими исполняемыми версиями языка для каждого проекта. Вам понадобится плагин asdf-ruby (который, в свою очередь, использует ruby-build), чтобы установить Ruby.
chruby
chruby позволяет вам переключаться между разными версиями Ruby. chruby может управлять версиями Ruby, которые установлены с помощью ruby-install или даже собранными из исходников.
rbenv
rbenv позволяет вам управлять несколькими установленными версиями Ruby. Он не поддерживает установку Ruby, но для этого существует популярный плагин ruby-build. Оба инструмента доступны для macOS, Linux и других UNIX-подобных операционных систем.
RVM (“Ruby Version Manager”)
RVM позволяет вам устанавливать и управлять несколькими установленными версиями Ruby в вашей системе. Также он может управлять разными наборами гемов. Доступен для macOS, Linux и других UNIX-подобных операционных систем.
Uru — это легковесная, кросс-платформенная командная утилита, которая помогает вам использовать несколько версий Ruby на macOS, Linux или Windows.
Сборка из исходников
Конечно, вы можете установить Ruby из исходников. Скачайте и распакуйте архив, затем просто выполните:
По умолчанию, это установит Ruby в /usr/local . Для изменения, передайте опцию —prefix=DIR в скрипт ./configure .
Использование сторонних инструментов или пакетных менеджеров может быть лучше, хотя бы потому, что установленные Ruby не будут управляться любыми инструментами.
Ethical hacking and penetration testing
InfoSec, IT, Kali Linux, BlackArch
How to install and use Ruby on Windows
Why install Ruby
Ruby is a scripting language, that is, pre-compilation is not required to run programs. In this sense, Ruby is an analogue of PHP, Python, PERL and others.
Ruby is a fairly popular language and many interesting programs are written on it; in scope of InfoSec, the well-known WPScan, WhatWeb, Wayback Machine Downloader and others can be cited as examples.
By installing Ruby on Windows, you can run programs written in this language, as well as learn this programming language and write your own scripts.
By the way, Ruby, like PHP, Python and PERL, can be a web server module, and scripts written in this language can be used as backend of a website or service.
How to install Ruby on Windows
There you will see many installer options that differ not only in versions, but also in the composition of the downloaded files. Executable files are self-contained installers for Windows that include the Ruby language, runtime, important documentation, and more. If you do not know which version to install in order to get started with Ruby, the Ruby+Devkit 2.6.X (x64) is recommended. It provides the largest number of compatible gem (Ruby packages) and installs MSYS2-Devkit along with Ruby, so gem with C-extensions can be compiled immediately after installation.
Run the downloaded file. In this window we can select the settings:
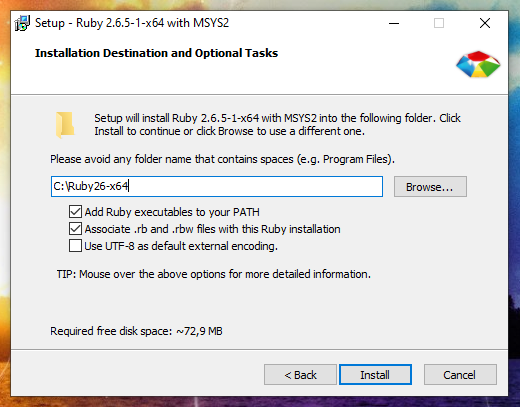
The installation folder can be left unchanged.
Add Ruby executables to your PATH – means adding a directory with Ruby executables to the system variable. This is recommended to do for in future to avoid specifying the full path to the script interpreter each time the Ruby script is run.
Associate .rb and .rbw files with Ruby installation. Thanks to this, Ruby files can be launched by double-clicking or by typing the name of the script on the command line.
Use UTF-8 as default external encoding.
I selected all three checkmarks and entered C:\Ruby26 as the installation folder:
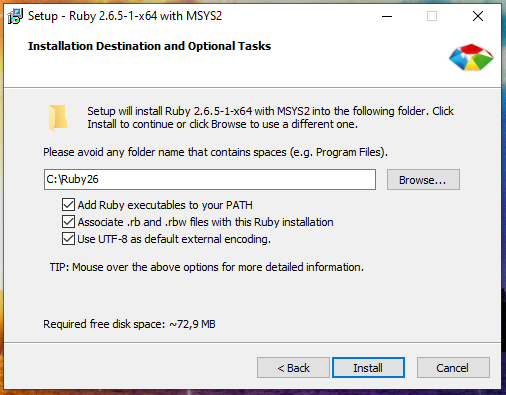
As you can see on the next page, the Ruby package itself takes up a bit of space, but the MSYS2 development toolkit offered for installation takes up a lot of space. I highly recommend installing MSYS2 because, in addition to the ability to compile packages for Ruby mentioned above, MSYS2 provides a console environment with Linux features (something like Cygwin does, but with additional features).
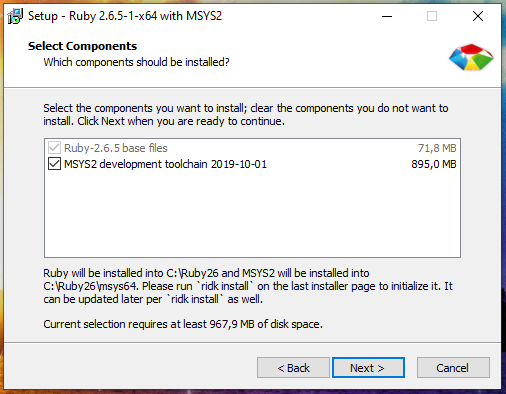
Leave a checkmark on the last window to configure the MSYS2 developer tools and click Finish.
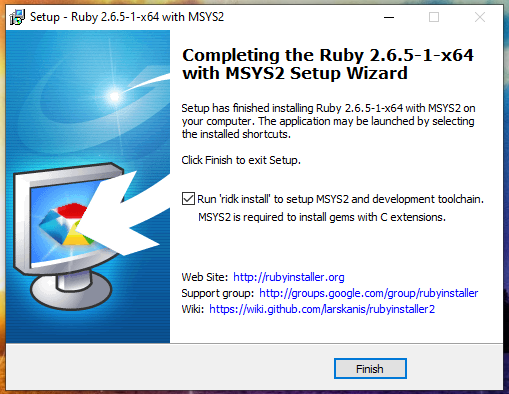
Further we are offered:
Just press ENTER to complete all three actions:
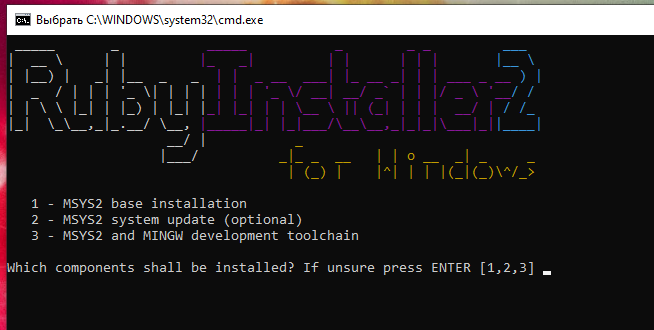
Everything is completed, to exit, press ENTER:
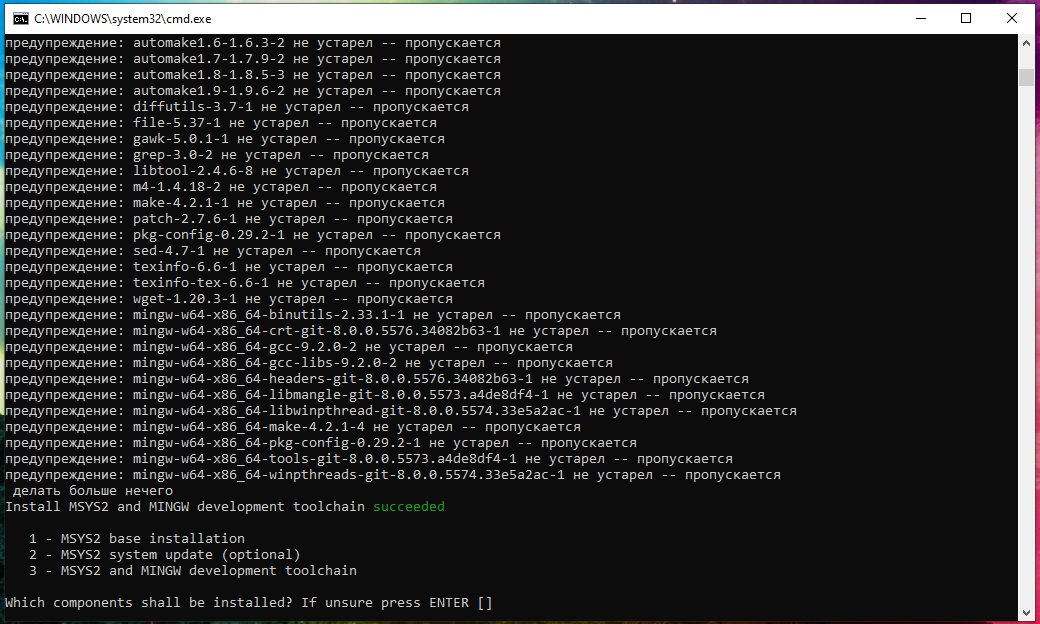
By the way, if you carefully watched what was happening on the screen, you might notice pacman. There really is a pacman package manager in this console environment. We will return to other functions of MSYS2 a bit later.
How to update Ruby on Windows
To upgrade to the latest patch (that is, the minor version, for example from 2.5.1 to 2.5.4), it is enough to launch a new version of the installer. Installed gem (packages from the Ruby repository) are not overwritten and will work with the new version without reinstalling. To upgrade the installation, just use RubyInstaller without Devkit. You can update Devkit separately by running the following command at the Windows command prompt:
When a new major version is released, it cannot be updated by installing it in the same directory as the previous one. For example, if the previous version of the installation is RubyInstaller-2.5.x, and the new version is RubyInstaller-2.6.x, then you need to install it either in a new directory or delete the old version and install a new one instead, since gem (programs) with C extensions are not compatible between ruby-2.5 and 2.6.
How to install and use gem on Windows
RubyGems is a package manager for Ruby. Using it, you can install various programs and their dependencies, installation can be done both from the source code on the local system, and from remote application sources.
The Ruby installation shown above also installs gem:
You should see gem help.
To display all available gem commands, run:
To install the package, run a command of the form:
More examples of installing packages will follow.
To show help about the installation command:
For example, to install the ‘rake’ program from a local directory or a remote server:
Installing the ‘rake’ package only from a remote server:
Installing ‘rake’, but only version 0.3.1, even if there are unsatisfied dependencies, do the installation in the user directory:
List gem (packages) whose name begins with ‘D’:
List local and remote gem whose name contains ‘log’:
The previous command is used to search for packages by name.
List only remote (non-local) gem whose name contains ‘log’:
View information about RubyGems:
Update all gem programs in the system:
Update local version of RubyGems:
How to install bundler
bundler is a Ruby dependency manager. This manager is useful when installing other programs written in Ruby.
To install bundler on Windows, run:
To upgrade bundle, run the command:
If you install the program from the source code and there is a Gemfile file, then go to the folder with this program and run the command in it:
This command will install all the dependencies listed in the Gemfile.
To see where gem packages are installed using bundle, use the command:
How to install the Ruby program on Windows. How to run a Ruby program on Windows
The following are a few examples of installing and using Ruby programs on Windows.
Recovering sites from the Internet Archive in Windows
Let’s start with the Wayback Machine Downloader program, which completely restores sites from the web archive.
To install Wayback Machine Downloader, just do:
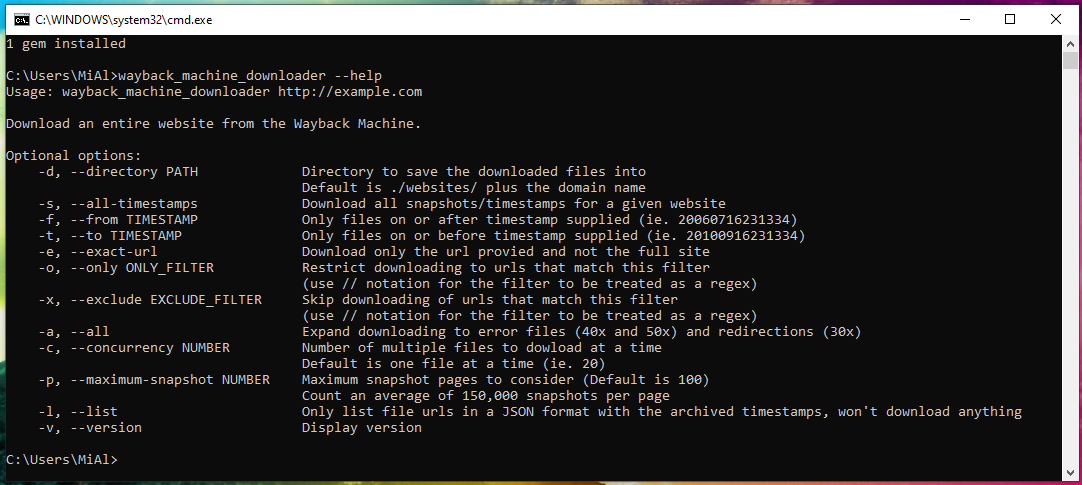
To check the operability of the program, run site restoration from the Internet Archive:
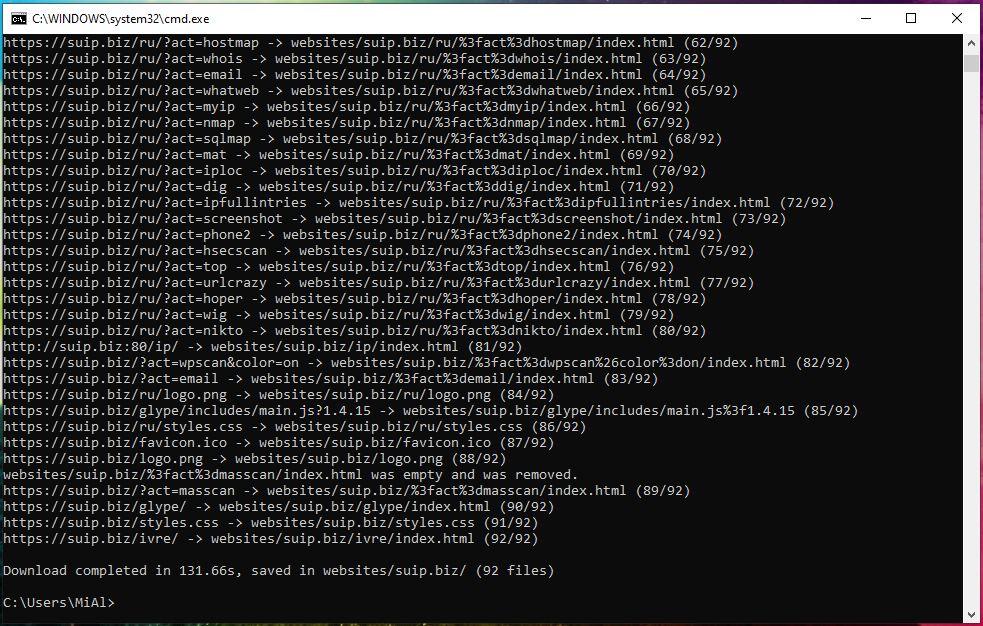
The program successfully completed the work:

How to Install WhatWeb on Windows
WhatWeb identifies websites. The purpose of this program is to answer the question “What is this website?”. WhatWeb recognizes web technologies, including a content management system (CMS), blogging platforms, statistics/analytics packages, JavaScript libraries, a web server and embedded devices. WhatWeb has over 1700 plugins, each of which is for recognizing one or the other. WhatWeb also identifies version numbers, email addresses, account IDs, web platform modules, SQL errors and more.
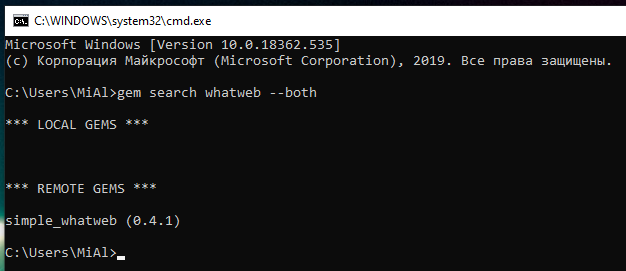
Let’s start by searching WhatWeb in the Ruby package repository:
Only simple_whatweb found (0.4.1).
Even if it’s WhatWeb, the version is very old. Therefore, on Windows, install WhatWeb from the source code.
Unzip this folder. Open a command prompt and navigate to this folder:
The following command will show the help for the program:
Run the site check:
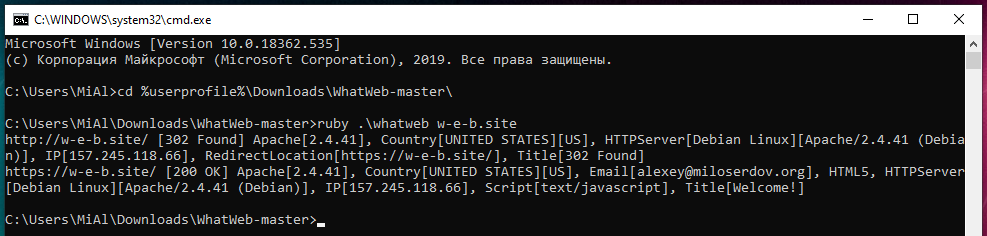
How to install WPScan on Windows
To install and run WPScan on Windows is tricky a bit, so the tutorial was divided in separate article “How to Install and Run WPScan on Windows”.
What is MSYS2. How to use MSYS2
We have already installed MSYS2 in order to gain access to compilation tools, thanks to which we can install any Ruby package. In fact, MSYS2 is based on Cygwin and contains a large number of Linux utilities.
MSYS2 provides a shell for bash, Autotools, make, gcc, pacman, sh, and many other packages. Of particular note is the pacman package manager.
To activate the MSYS2 working environment, open a command prompt or powershell console and run there:
As a result, many Linux utilities will immediately become available for work, as well as the Pacman package manager, with which you can install new packages or update existing ones. When installing packages, Pacman monitors the dependencies and installs them.
To update all packages:
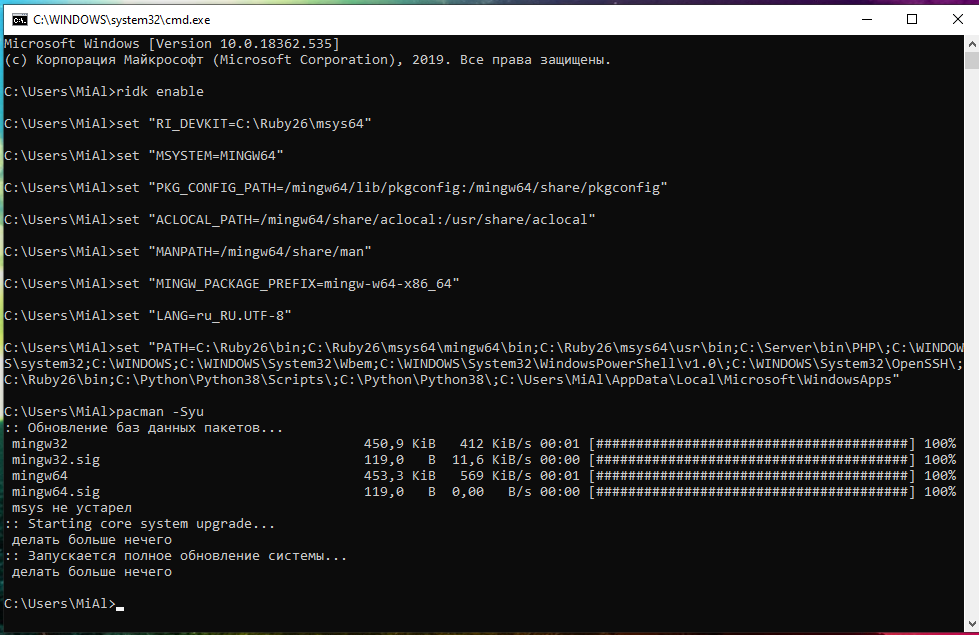
To search for a package:
To list all available packages:
How to configure Ruby as an Apache module on Windows
Ruby scripts can be run in an Apache environment similar to running PHP scripts. To do this, you need to make a little configuration.
I installed the web server according to this tutorial, if you installed according to another manual, then edit the paths to fit your environment.
Open the httpd.conf file for editing, I have it located on the path C:\Server\bin\Apache24\conf\httpd.conf.
Find the line there
and add ExecCGI to it. You should get the following line (ATTENTION: you may have different the set of options):
