Как добавить пользователя в группу Linux
Операционная система Linux изначально планировалась как многопользовательская система. Для управления правами доступа для каждого из пользователей используется три флага: чтение, запись и выполнение. Но этого было недостаточно, поэтому были придуманы группы пользователей Linux. С помощью групп можно дать нескольким пользователям доступ к одному ресурсу.
Файлу присваивается группа, для нее описываются права, затем в эту группу вступают пользователи, чтобы получить доступ к файлу. Читайте подробнее про все это в статье группы Linux. А в этой статье мы рассмотрим как добавить пользователя в группу linux.
Как добавить пользователя в группу Linux
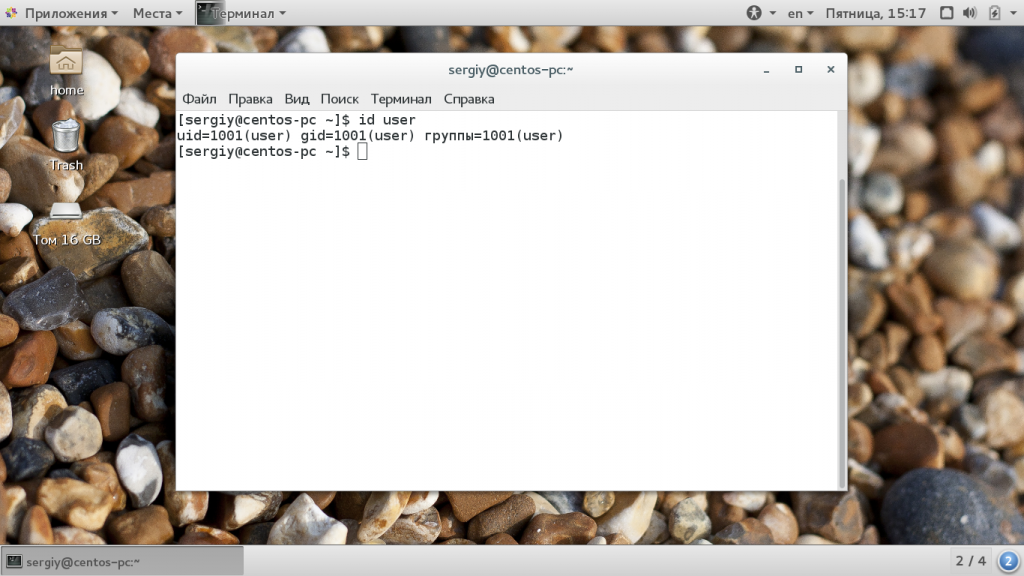
Как я уже сказал, для каждого пользователя существует два типа групп, это первичная, основная для него группа и дополнительные.
- Первичная группа — создается автоматически, когда пользователь регистрируется в системе, в большинстве случаев имеет такое же имя, как и имя пользователя. Пользователь может иметь только одну основную группу;
- Вторичные группы — это дополнительные группы, к которым пользователь может быть добавлен в процессе работы, максимальное количество таких групп для пользователя — 32;
Как обычно, лучше всего будет добавлять пользователя в группу через терминал, поскольку это даст вам больше гибкости и возможностей. Для изменения параметров пользователя используется команда usermod. Рассмотрим ее опции и синтаксис:
$ usermod опции синтаксис
Здесь нас будут интересовать только несколько опций с помощью которых можно добавить пользователя в группу root linux. Вот они:
- -G — дополнительные группы для пользователя;
- -a — добавить пользователя в дополнительные группы из параметра -G, а не заменять им текущее значение;
- -g — установить новую основную группу для пользователя, такая группа уже должна существовать, и все файлы в домашнем каталоге теперь будут принадлежать именно этой группе.
У команды намного больше опций, но нам понадобятся только эти для решения нашей задачи. Теперь рассмотрим несколько примеров. Например, чтобы добавить пользователя в группу sudo linux используйте такую комбинацию:
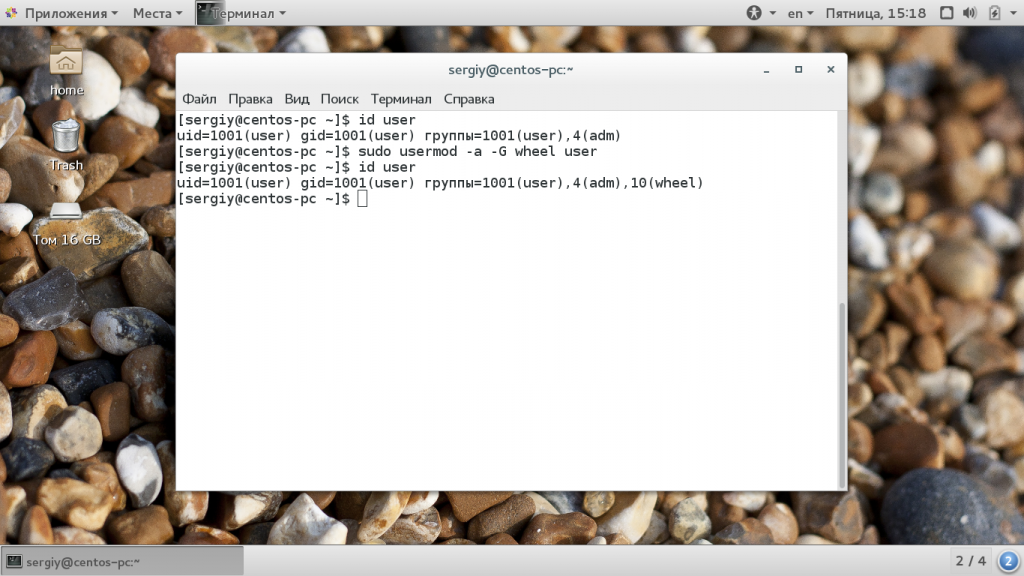
sudo usermod -a -G wheel user
Если вы не будете использовать опцию -a, и укажите только -G, то утилита затрет все группы, которые были заданы ранее, что может вызвать серьезные проблемы. Например, вы хотите добавить пользователя в группу disk и стираете wheel, тогда вы больше не сможете пользоваться правами суперпользователя и вам придется сбрасывать пароль. Теперь смотрим информацию о пользователе:
Мы можем видеть, что была добавлена указанная нами дополнительная группа и все группы, которые были раньше остались. Если вы хотите указать несколько групп, это можно сделать разделив их запятой:
sudo usermod -a -G disks,vboxusers user
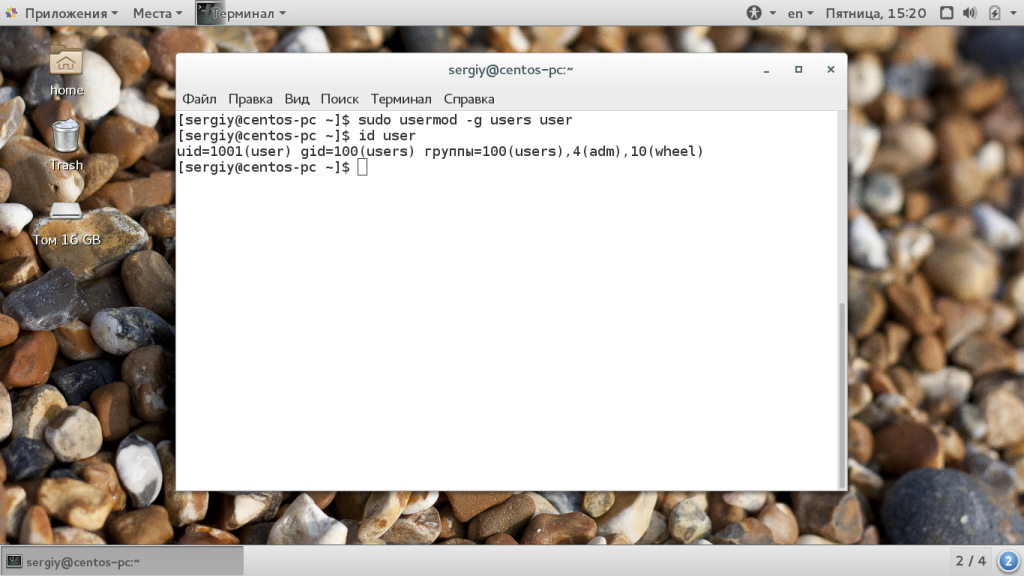
Основная группа пользователя соответствует его имени, но мы можем изменить ее на другую, например users:
sudo usermod -g users user
Теперь основная группа была изменена. Точно такие же опции вы можете использовать для добавления пользователя в группу sudo linux во время его создания с помощью команды useradd.
Добавление пользователя в группу через GUI
В графическом интерфейсе все немного сложнее. В KDE добавление пользователя в группу linux выполняется с помощью утилиты Kuser. Мы не будем ее рассматривать. В Gnome 3 возможность управления группами была удалена, но в разных системах существуют свои утилиты для решения такой задачи, например, это system-config-users в CentOS и Users & Groups в Ubuntu.
Для установки инструмента в CentOS выполните:
sudo yum install system-config-users
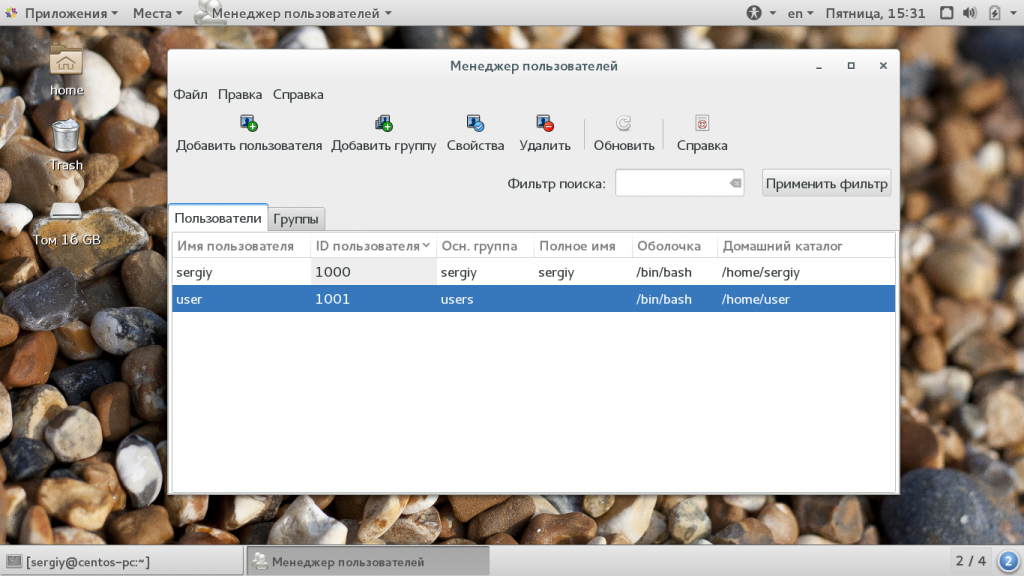
Дальше вы можете запустить утилиту через терминал или из главного меню системы. Главное окно утилиты выглядит вот так:
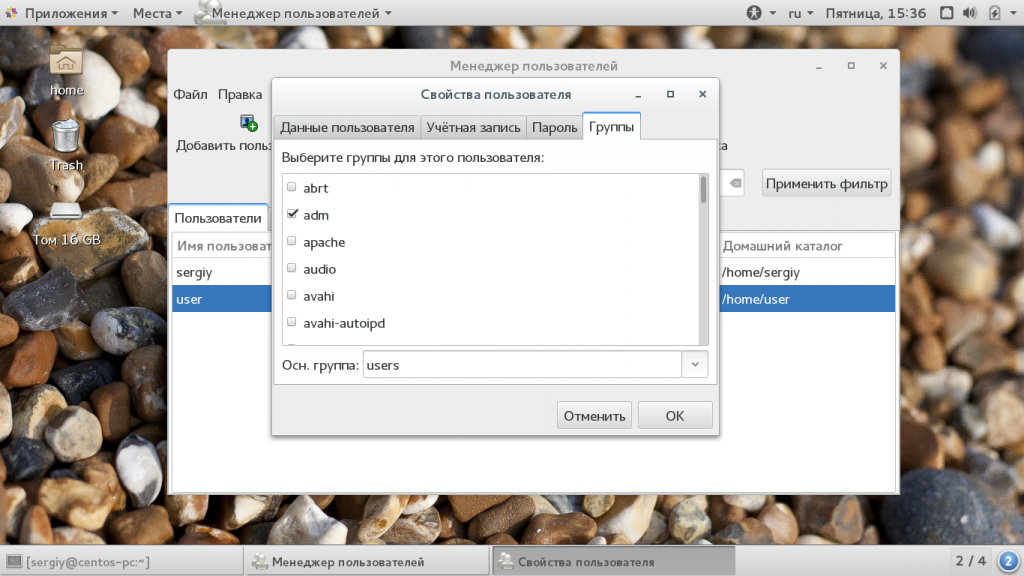
Выполните двойной клик по имени пользователя, затем перейдите на вкладку «группы». Здесь вы можете выбрать отметить галочками нужные дополнительные группы, а также изменить основную группу:
Для установки утилиты в Ubuntu запустите такую команду:
sudo apt install gnome-system-tools
Здесь интерфейс будет немного отличаться, утилита будет выглядеть так же, как и системная программа настройки пользователей только появится возможность управления группами Linux.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели как добавить пользователя в группу linux. Это может быть очень полезно для предоставления пользователю дополнительных полномочий и разграничения привилегий между пользователями. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
HowTo: Grant Root Access to User – Root Privileges – Linux
From this article you’ll learn how to create a user in Linux and grant root access to him or how to grant root privileges to already existent user.
This can be easily done by changing UID (user id) and GID (group id) in /etc/passwd file.
Also you will learn how to just add user to root group and i will explain how to delete user with root privileges.
Actually it is not a good idea to give all the privileges of root to a non-root user and outside the test environment i would not recommend to have multiply superusers.
Warning: Giving a non-root user all the permissions of root is very dangerous, because the non-root user will be able to do literally anything that could cause a big trouble if account is hijacked.
Check SSH Server Settings: If you have disabled root access in SSH server settings, by setting PermitRootLogin no in /etc/ssh/sshd_config – you won’t be able to login if your user has UID 0 .
Warning: Before moving forward, read the comments below and DON’T FOLLOW THE STEPS FROM THIS ARTICLE if you don’t understand of what you are doing and what impact this may have!
Grant Root Privileges To New User
To create a user with exactly the same privileges as root user, we have to assign him the same user ID as the root user has ( UID 0 ) and the same group ID ( GID 0 ).
Use the following commands to create a user john , grand him the same privileges as root and set him a password:
Grant Root Privileges To Existent User
Cool Tip: Dot the i’s and cross the t’s on file and folder permissions in Linux! Make it more clear! Read more →
Perhaps you already have a user john and you want to grant him root privileges (make him a second root user):
For this, it is required to edit the file /etc/passwd and just change UID and GID to 0 :
Add User To Root Group
If you just want to add john to root group, without granting him all root privileges, run the following command:
Delete User With Root Privileges
Cool Tip: Log in to a remote Linux server without entering password! Set up password-less SSH login! Read more →
You won’t be able to delete a user with UID 0 using userdel command:
To delete him, firstly open the /etc/passwd file and change his UID .
For example, change the line:
After this, you’ll be able to delete user john with userdel command:
36 Replies to “HowTo: Grant Root Access to User – Root Privileges – Linux”
“For this, it is required to edit the file /etc/passwd and just change UID and GID to 0”
WRONG.
Baaaad idea. Much regret. Undo, undo.
$ ssh 192.168.88.16 -l pi
pi@192.168.88.16‘s password:
Permission denied, please try again.
pi@192.168.88.16‘s password:
Permission denied, please try again.
– – –
Nice explanation?)
Since noone elaborate how to undo this broken way of adding users, I will. The only way is to successful login to the linux machine, if you login via ssh or tty.
If you add a user with uid 0 to group uid 0, and you set in sshd_config AllowRootLogin NO, you`re access will be denied. So you will have to login to the linux machine via tty (this is the only way if you don`t have a correctly added backup user on the linux machine). Via tty you can login with any of the users, even root.
The correct way to add a user with root privileges is adding the user the normal way, useradd -m user, and then add privileges with visudo to the user.
So if you have a backup user that haves root privileges in visudo. you will be able to login to the linux machine via ssh, and you will be able to change the uid and group to the “broken” user.
I think this article explains more likely how to add a user with root privileges “the hacker way (which is a broken way)”, and repair the broken way after.
Also if you don`t have access to a tty console, and you want to test the commands of this article and be sure you did not broke something, STAY LOGGED in current session and open another one and test if all things are OK. If you can`t login in the new session, you still have opened the previous session and you can repair what have you broken.
Hope it helps to repair further mistakes.
Linux Add User To Group
H ow can I add a user to a group under Linux operating system using command line options? How to add an existing user into a group in Linux using command line options?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Intermediate (rss) |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | usermod/useradd |
| Time | 5 minutes |
You can use the useradd or usermod commands to add a user to a group. The useradd command creates a new user or updates default new user information. The usermod command modifies a user account, and it is useful to add a user to existing groups. There are two types of groups on Linux operating systems:
- Primary user group. – It is the group that applied to you when login. Typically it is same as your login name. All of your process and files (including directories/folders) would have your primary group as the group membership. The primary group allows private group membership and security features. Your files or process cannot access by other group members or users on the Linux system.
- Secondary or supplementary user group – Users can be a member of other groups on the Linux system. It is useful for file sharing and other purposes. A sysadmin can fine-tune security too. For example, if you are a member of a secondary group called cdrom, you can mount and unmout cd-rom drive.
All user account related information are stored in the following files:
- /etc/passwd – Contains one line for each user account.
- /etc/shadow – Contains the password information in encrypted formatfor the system’s accounts and optional account aging information.
- /etc/group – Defines the groups on the system.
- /etc/default/useradd – This file contains a value for the default group, if none is specified by the useradd command.
- /etc/login.defs – This file defines the site-specific configuration for the shadow password suite stored in /etc/shadow file.
Linux command to add user to group
- Add a new user called jerry to secondary group named cartoons on Linux:
sudo useradd -G cartoons jerry - Add a new user called tom to primary group called cartoons:
useradd -g cartoons tom - Linux add a existing user named spike to existing group named cartoons:
useradd -g cartoons spike
How to become a root user
You must run all command as root user. To become a root user run:
su —
Alternatively use sudo command:
sudo -i
Add a new user to secondary group using useradd
You need to the useradd command to add new users to existing group (or create a new group and then add user). If group does not exist, create it. The syntax is as follows:
useradd -G < group-name >username
In this example, create a new user called vivek and add it to group called developers. First, make sure group developers exists using grep command:
# grep «^developers» /etc/group
Sample outputs:
If you do not see any output then you need to add group developers using the groupadd command:
# sudo groupadd developers
Verify that user vivek does not exists:
# grep «^vivek» /etc/passwd
You should not see any outputs from above command. Finally, add a new user called vivek to group developers:
# useradd -G developers vivek
Setup password for user vivek:
# passwd vivek
Ensure that user added properly to group developers:
# id vivek
Sample outputs:
Please note that capital G ( -G ) option add user to a list of supplementary groups. Each group is separated from the next by a comma, with no intervening whitespace. For example, add user jerry to groups admins, ftp, www, and developers, enter:
# useradd -G admins,ftp,www,developers jerry
How to add a new user to primary group using useradd
To add a user tony to group developers use the following command:
# useradd -g developers tony
# id tony 
Please note that small g ( -g ) option add user to initial login group (primary group). The group name must exist. A group number must refer to an already existing group.
How to add a existing user to existing group using usermod
Add existing user tony to ftp supplementary/secondary group with the usermod command using the -a option
i.e. add the user to the supplemental group(s). Use only with -G option:
# usermod -a -G ftp tony
In this example, change tony user’s primary group to www, enter:
# usermod -g www tony
usermod command options summary
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
| -a —append | Add the user to the supplementary group(s). Use only with the -G option. |
| -g GROUP —gid GROUP | Use this GROUP as the default group. |
| -G GRP1,GRP2 —groups GRP1,GRP2 | Add the user to GRP1,GRP2 secondary group. |
A note about security
If you add or delete user to existing group, you must change the owner of any crontab files or at jobs manually. You must make any changes involving NIS on the NIS server too.
A note about GUI tool
You will probably find the use of the GUI tool easy. KDE user can use KUser tool and the GNOME user can use users-admin:
users-admin is part of the GNOME system tools, a set of tools to easily access and manage system configuration
See also
For more information type the following command at the shell prompt:
$ man usermod
$ man useradd