Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon (Gen 7)
The Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon, 7th generation is an ultrabook introduced in early 2019. It features a 14″ screen, 8th-gen or 10th-gen Intel Core processors and integrated Intel UHD 620 graphics.
To ensure you have this version, install the package dmidecode and run:
| Device | Working | Modules |
| Intel graphics | Yes | i915, (intel_agp) |
| Wireless network | Yes | iwlmvm |
| Native Ethernet with dongle | Yes | ? |
| Mobile broadband Fibocom | Yes¹ | ? |
| Audio | Yes | snd_hda_intel |
| Microphone | Yes⁴ | snd_sof |
| Touchpad | Yes | psmouse, rmi_smbus, i2c_i801 |
| TrackPoint | Yes | psmouse, rmi_smbus, i2c_i801 |
| Camera | Yes | uvcvideo |
| Fingerprint reader | Yes² | ? |
| Power management | Yes³ | ? |
| Bluetooth | Yes | btusb |
| Keyboard backlight | Yes | thinkpad_acpi |
| Function/Multimedia keys | Yes | ? |
| ||
Contents
The most convenient way to install Arch Linux is by disabling «Secure Boot» Security -> Secure Boot — Set to «Disabled» . However it is possible to self-sign your kernel and boot with it enabled. For further information have a look at the Secure Boot article.
In case your efivars are not properly set it is most likely due to you not being booted into UEFI. Should the problem persist be sure to consult the UEFI#UEFI variables section.
Updates
Automatic (Linux Vendor Firmware Service)
In August of 2018 Lenovo has joined the Linux Vendor Firmware Service (LVFS) project, which enables firmware updates from within the OS. BIOS updates (and possibly other firmware such as the Thunderbolt controller) can be queried for and installed through fwupd.
Manual (fwupdmgr)
Lenovo may in the future provide cabinet files that can be directly installed with fwupdmgr. Check for Linux .cab files from the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon (Gen 7) driver website.
- Make sure the AC adapter is firmly connected to the target computer.
- Launch Terminal.
- Move to the directory where the cabinet file was placed.
- Run fwupdmgr install xxxxxxxx.cab to schedule firmware update.
- Restart the system.
- The computer will be restarted and the UEFI BIOS will be updated.
Sleep/Suspend
The BIOS has two «Sleep State» options, Windows and Linux, which you can find in at Config -> Power -> Sleep State . The Linux option is the traditional S3 power state where all hardware components are turned off except for the RAM, and it should work normally. The Windows option is a newer software-based «modern standby» which works on Linux (despite the name). One possible benefit to the Windows sleep state is faster wake up time, and one possible drawback is increased power usage.
S3 Suspend Bug with Bluetooth Devices
Occasionally your Thinkpad will wake up immediately after suspending with certain bluetooth devices added. To prevent this, remove the devices or disable bluetooth before suspending.
BIOS configurations
- Config -> Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode — Set to «Enabled» . When disabled, on Linux, power usage appears to be significantly higher because of a substantial number of CPU wakeups during s2idle.
Firmware issues
The following issues can all be resolved by upgrading the firmware with fwupdmgr (see #BIOS Updates), but there may be alternative manual/temporary fixes.
Touchpad issues
Due to a bug in a touchpad firmware, the touchpad might not work with following logs in dmesg:
Freeze when suspending
There are reports of the system freezing after initiating a suspend or hibernate. A temporary fix is to add snd_hda_intel.dmic_detect=0 to your kernel parameters. see [3]. This temporary fix is somehow disable the microphone, use this at your own risk
Power management/Throttling issues
A bug causes the CPU to consume less power than under Windows and throttle at 80°C instead of 97°.
The alternative fix is to install throttled , then run
Audio
To get it working with PulseAudio 13 and older, follow those steps:
1. Install sof-firmware (tested with 1.4.2-1)
2. Configure PulseAudio’s to load Alsa modules with the correct device and channel settings, by adding these two lines to /etc/pulse/default.pa :
Note that Alsa card numbers can change when adding more audio devices (like, connecting a USB headset or a docking station). To ensure that index ‘0’ always maps to internal audio, add snd slots=snd_soc_skl_hda_dsp to your module loading options.
3. Reboot, then use alsamixer to increase the «master» channel level of the sof-hda-dsp sound card (use the key to switch cards). If you do not see sof-hda-dsp in alsamixer , you may need to add blacklist snd_hda_intel and blacklist snd_soc_skl to /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf and reboot again.
4. If the output sounds tinny, try muting the «speaker» item in alsamixer.
Fingerprint sensor
An official Lenovo firmware with Linux support is available from fwupd. After installing fwupd, you can update the Synaptics Prometheus driver for the fingerprint sensor:
To use the fingerprint sensor, follow the instructions from Fprint.
If you had previously installed the testing version of this driver from lvfs-testing, there should be no issues updating to this driver version from the main repository.
Disabling red LED in ThinkPad logo
You can temporarily disable the red LED in the ThinkPad logo on the cover:
1. Enable writing to the embedded controller registers by adding the kernel parameter ec_sys.write_support=1 . If you use UEFI boot, you can add this parameter in /boot/efi/loader/entries/arch.conf under «options».
2. Disable the LED with this command:
This would need to be run after each suspend/reboot to be permanent.
Lenovo начала перевод флагманских ноутбуков на Linux. Первый пошел
Lenovo начала реализацию своего плана по переводу современных мобильных и настольных ПК на Linux. Она выпустила бизнес-ноутбук ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8 с предустановленным дистрибутивом Fedora, и вслед за ним эту ОС получат ноутбуки ThinkPad P1 Gen 2 и ThinkPad P53. Также в планы компании входит распространение всех устройств серий ThinkStation и ThinkPad P с RHEL и Ubuntu.
Бизнес-ноутбук без Windows
Компания Lenovo начала поставки ноутбука ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8 с предустановленным дистрибутивом Linux, хотя изначально он выпускался исключительно с Windows 10. Выбор китайского производителя пал на ОС Fedora.
Fedora – это форк дистрибутива Red Hat Enterprise Linux, разрабатываемого компанией Red Hat, которую в 2019 г. купила IBM. Сама IBM определенным образом связана с Lenovo – в 2004 г. она продала ей свой бизнес по производству настольных и мобильных компьютеров, а в 2014 г. та же участь постигла и ее серверный бизнес. В отличие от Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Fedora распространяется бесплатно.
На ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8, поставляющийся в корпусе с отделкой из карбона, установлен дистрибутив версии 32, вышедший в последних числах апреля 2020 г. В настоящее время ведется разработка Fedora 33, но дата ее выхода пока не определена.
Свои планы по переводу некоторых моделей ноутбуков на Fedora, как сообщал CNews, Lenovo озвучила еще в апреле 2020 г. На тот момент она собиралась выпустить Linux-версии лэптопов ThinkPad P1 Gen 2 и ThinkPad P53, оба 2019 модельного года, и ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8, вышедший в январе 2020 г., притом именно в такой последовательности. В итоге самый современный ноутбук получил Fedora раньше других.
Характеристики лэптопа с Fedora
Lenovo позиционирует 14-дюймовый ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8 как бизнес-ноутбук, но его могут приобрести и обычные потребители, не только корпоративные. На сайте производителя его версия с Fedora может быть кастомизирована – пользователь получает возможность выбора модели процессора, объема оперативной памяти и SSD-накопителя, разрешения и формата экрана (сенсорный или обычный) и рядя других менее значимых параметров, включая предустановленное лицензионное ПО.
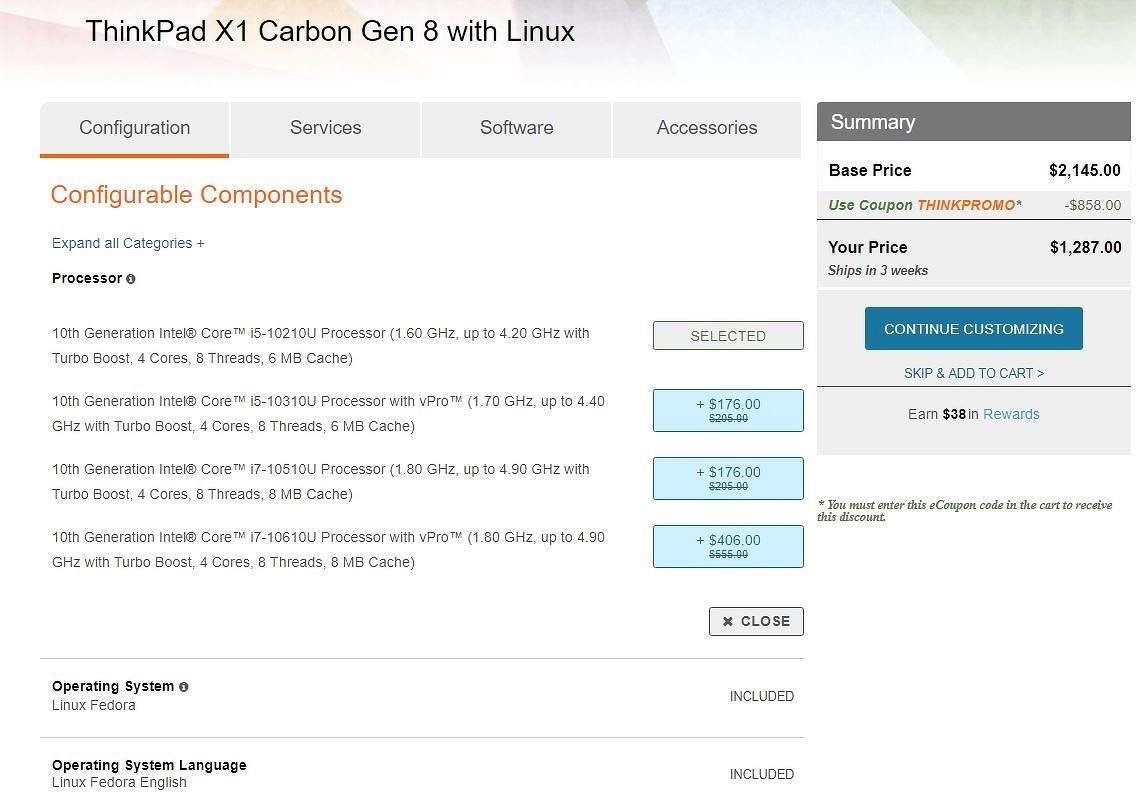
Базовая модификация Linux-версии ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8 стоит $2145 (160,1 тыс. руб. по курсу ЦБ на 31 августа 2020 г.), но Lenovo сразу позволяет снизить цену до $1287 (96,1 тыс. руб.) при помощи промокода. Цена включает процессор Intel Core i5-10210U (4 ядра, 8 потоков, частота от 1,6 до 4,2 ГГц, 6 МБ кэша третьего уровня), 8 ГБ оперативной памяти LPDDR3-2133 (распаяны на системной плате), и SSD PCI-E на 256 ГБ. Экран в такой конфигурации несенсорный, он имеет яркость 400 кд/м2, разрешение Full HD (1920×1080 точек), матрицу IPS и антибликовое покрытие.
Список опций включает процессоры Core i5-10310U, Core i7-10510U и Core i7-10510U, 16 ГБ оперативной памяти того же класса, и SSD на 512 ГБ или 1 ТБ. Экран ноутбука при том же разрешении может быть сенсорным, плюс пользователь может выбрать комплектацию с разрешением дисплея 2560х1440 точек (Quad HD, 2К) и яркостью 300 кд/м2. В самой топовой версии будет установлена несенсорная панель 4К (3840х2160 точек, Ultra HD) с яркостью 500 кд/м2, но при этом с глянцевым покрытием.
Стоимость лэптопа включает HD-камеру (можно заменить на ИК-камеру с аналогичным разрешением), сканер отпечатков пальцев, подсветку клавиатуры, 4-ячеечную батарею на 51 ВТч, модуль безопасности TPM2.0 и 65-ваттный блок питания. Список беспроводных модулей состоит из Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) и Bluetooth 5.0. Базовый срок гарантии – один год.
Программное обеспечение
По умолчанию ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 8 поставляется только с Fedora 32, без дополнительного программного обеспечения. Его пользователю придется устанавливать самостоятельно.
Также при покупке можно выбрать ряд лицензионных программ, но их наличие существенно повлияет на итоговую стоимость мобильного ПК. В первую очередь это софт для защиты информации – Norton Internet Security и McAfee Internet Security. Также можно приобрести лицензию на ПО компании Adobe – в списке есть Photoshop Elements 2020 (отдельно и в наборе с Premiere Elements 2020), Acrobat Standard 2017, Acrobat Pro 2017. Помимо этого, при покупке ноутбука можно заказать годовую подписку на облако Adobe Creative Cloud.
Lenovo заинтересована в Linux
Lenovo планирует выпускать различные ПК на базе дистрибутивов Linux, притом не только Fedora. В начале июня 2020 г. CNews писал, что она собирается адаптировать под свою технику упомянутый RHEL, а вместе с ним и Ubuntu – один из наиболее популярных пользовательских дистрибутивов.
Lenovo хочет полностью сертифицировать все устройства серий ThinkStation и ThinkPad P для работы с RHEL и Ubuntu. Это означает, что специалисты компании протестируют все имеющиеся модели на стабильность работы, и что сами ПК будут поставляться с набором необходимых драйверов (вероятно, в виде архивов с возможностью загрузки с официального сайта Lenovo).
Покупателей техники с предустановленным Linux Lenovo обеспечит полноценной поддержкой. В нее входят, помимо прочего, распространение патчей и обновлений для операционной системы, а также подготовка драйверов для устройств, оптимизированных под требуемые дистрибутивы Linux. Вместе с этим Lenovo обеспечит поставку требуемых прошивок BIOS.
В дополнение к перечисленному Lenovo планирует сотрудничать непосредственно с разработчиками ядра Linux, в рамках которого она будет передавать им свои драйверы для включения в основной состав ядра. В случае успеха этого предприятия компьютеры Lenovo получат совместимость с любыми обновляемыми дистрибутивами Linux.