Как узнать MAC-адрес в Linux
В те времена, когда только проектировался Ethernet, предусматривалось применение уникального номера каждой сетевой карте, подключённой к нему. Назначался он при изготовлении платы. MAC-адрес используется для определения получателя и отправителя информации в Сети. И в этой статье речь пойдёт о том, как узнать MAC адрес в Linux.
Практически во всех операционных системах на основе ядра Linux используется две консольные утилиты, с помощью которых можно узнать аппаратный адрес карты: ifconfig и ip. Различные графические приложения этого типа используют их данные.
Как узнать MAC-адрес с помощью ifconfig
Одной из первых сетевых программ в истории Linux является ifconfig. В некоторых дистрибутивах она запускается только от имени администратора, а где-то вообще не установлена. Рассмотрим её инсталляцию и использование в Manjaro Linux.
Пакет, содержащий в себе некоторые сетевые утилиты (в том числе и ifconfig), в Manjaro- и Arch-подобных системах называется net-tools. Установим его.
sudo pacman -S net-tools
А в Ubuntu- и Debian-подобных системах:
sudo apt install net-tools
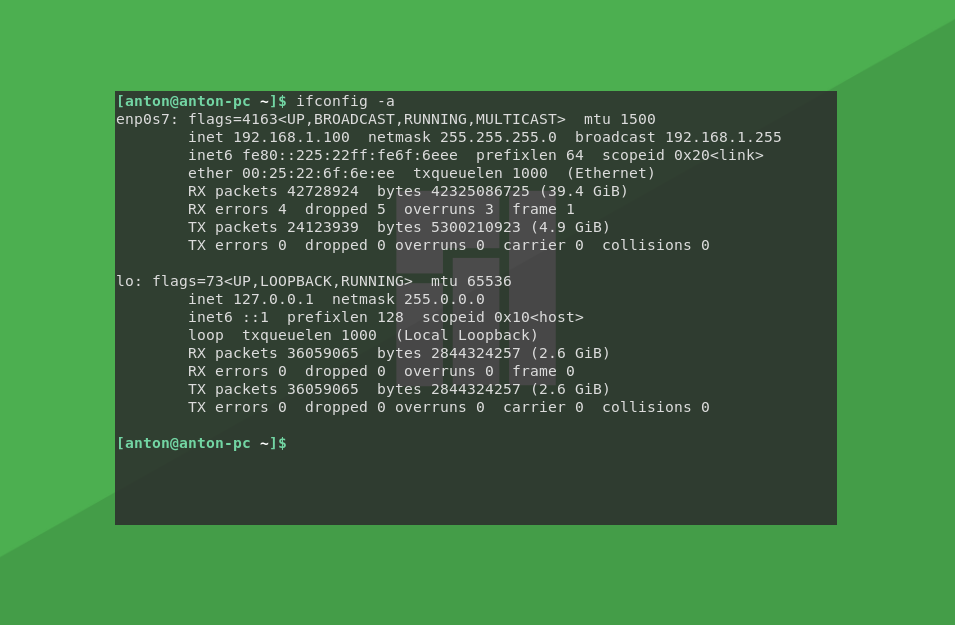
Чтобы узнать MAC-адрес Linux, сначала смотрим список интерфейсов:
Доступных интерфейсов два: enp0s7 (в вашем случае он может называться по другому) и lo (он же локальный хост, который одинаков практически для всех компьютеров). Нам нужен enp0s7.
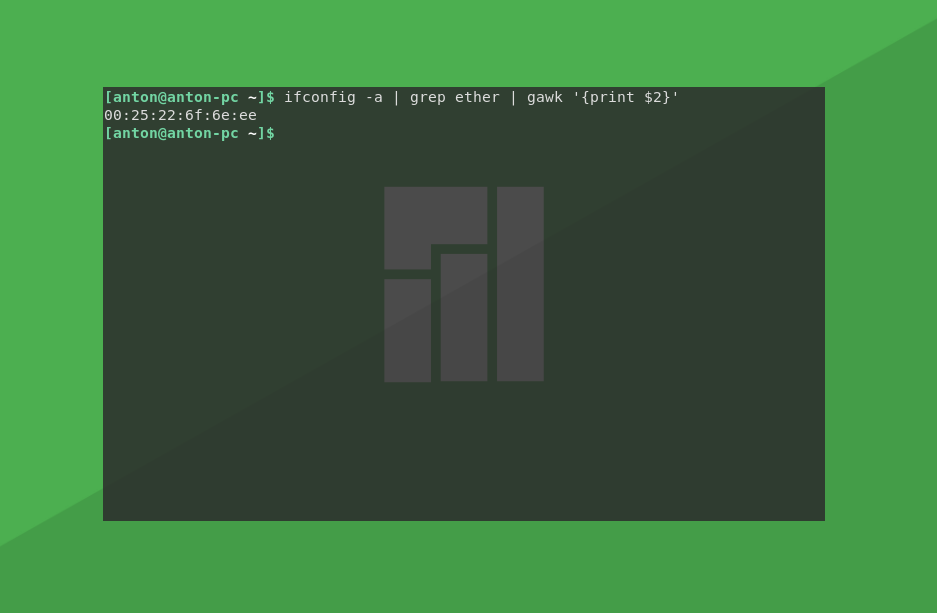
MAC-адрес устройства виден уже сейчас в поле ether, но чтобы отобразить только его, воспользуемся такой командой:
ifconfig -a | grep ether | gawk ‘
Здесь grep принимает на вход то, что вывела команда ifconfig -a, находит строку, где есть ether, и передаёт на вход команде gawk, которая выбирает второе слово в принятой строке.
Как посмотреть MAC-адрес с помощью ip
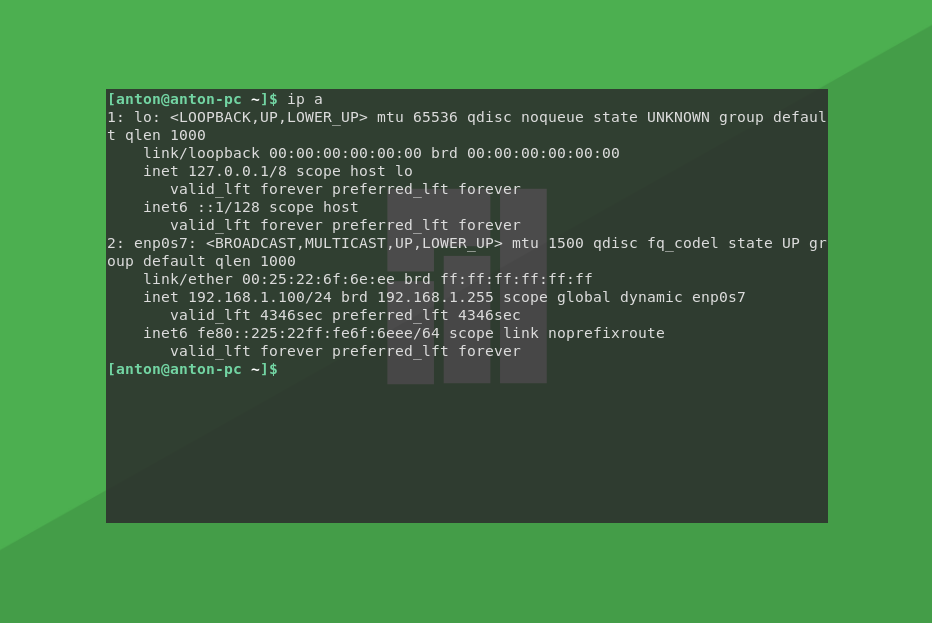
Более новой в системах GNU/Linux (относительно ifconfig) является программа ip. Её принцип работы практически такой же. Отличается синтаксисом и выводимой информацией. И она установлена по умолчанию для всех систем. Для отображения сетевых интерфейсов нужно ввести команду:
Здесь lo и enp0s7 расположены в обратном порядке.
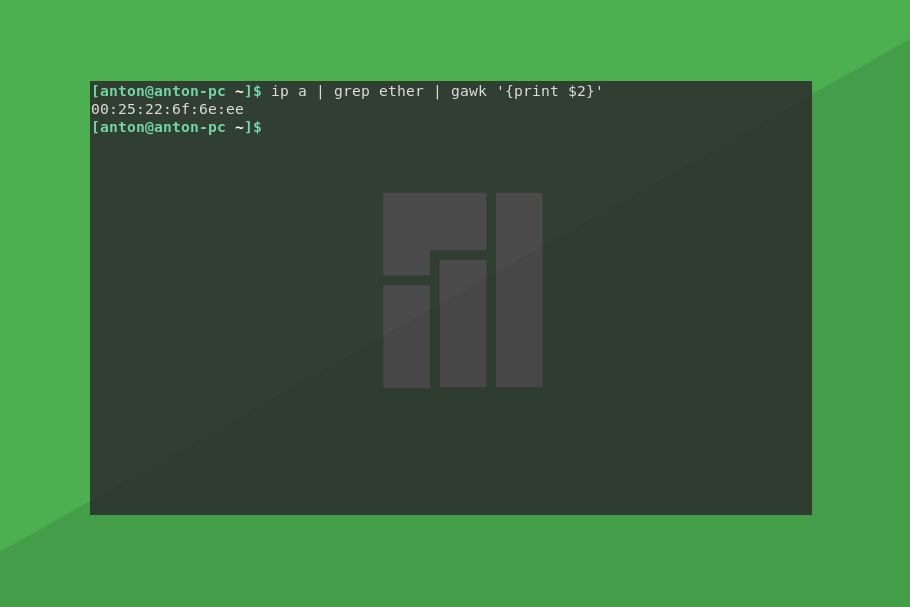
Чтобы узнать MAC адрес сетевой карты Linux, вводим ту же самую конструкцию, только для этой команды:
ip a | grep ether | gawk ‘
Выводы
За то, как узнать MAC адрес в Linux, отвечают две консольные утилиты — ifconfig и ip. Первая может запускаться от имени администратора в некоторых дистрибутивах (например в Debian), а где-то вообще не быть установленной (Manjaro). Это связано с её отходом на второй план, поскольку ip является более новой программой и устанавливается по умолчанию во всех системах.
Get MAC address using shell script
Currently all the solution mentioned for getting the MAC address always use eth0. But what if instead of eth0 my interfaces start with eth1. Also on OS X the interface names are different.
Also the interface eth0 may be present but is unused. i.e. not active, it doesn’t have an IP.
So is there a way I could get the MAC address for the first available interface that is Active.(i.e. it has an inet address, I even don’t want one having inet6).
NOTE : I have changed the values of the output.
So in this case I want the HWaddr for eth1 and not eth0. How do I find it ? Also it should work on all the Linux flavours.
12 Answers 12
Observe that the interface name and the MAC address are the first and last fields on a line with no leading whitespace.
If one of the indented lines contains inet addr: the latest interface name and MAC address should be printed.
Note that multiple interfaces could meet your criteria. Then, the script will print multiple lines. (You can add ; exit just before the final closing brace if you always only want to print the first match.)
You can do as follows
Also you can get MAC for all interface as follows
For particular interface like for eth0
The best Linux-specific solution is to use sysfs:
This method is extremely clean compared to the others and spawns no additional processes since read is a builtin command for POSIX shells, including non-BASH shells. However, if you need portability to OS X, then you’ll have to use ifconfig and sed methods, since OS X does not have a virtual filesystem interface like sysfs.
return: eth0 (my online interface)
return: ec:a8:6b:bd:55:05 (macaddress of the eth0, my online interface)
On a modern GNU/Linux system you can see the available network interfaces listing the content of /sys/class/net/ , for example:
You can check if an interface is up looking at operstate in the device directory. For example, here’s how you can see if enp0s25 is up:
You can then get the MAC address of that interface with:
For example, here’s a simple bash script that prints MAC addresses for active interfaces:
And here’s its output on a system with an ethernet and a wifi interface:
Remember also that from 2015 most GNU/Linux distributions switched to systemd , and don’t use ethX interface naming scheme any more — now they use a more robust naming convention based on the hardware topology, see:
Linux «show mac-address-table» analogue
Few days ago I could see a user question about Linux analogue for Cisco «show mac-address-table» command. He wo'nt use the «arp»or «arp -a» command for some hidden reasons. And I think it may be interesting for other users.
The «arp» or «arp -a» command shows you mac-address table (MAC-interface maping) and ARP table (MAC-IP mapping) all-in-one. Cisco IOS devices, as networking equipment, show some more information and it contains VLAN id and entry type (static or dynamic).
Cisco output are below:
#sh mac address-table
Mac Address Table
——————————————-
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
—- ———— ——— ——
All 0100.0ccc.cccc STATIC CPU
All 0100.0ccc.cccd STATIC CPU
All ffff.ffff.ffff STATIC CPU
10 0000.0c07.abcd DYNAMIC Gi0/1
20 000b.be68.bcde DYNAMIC Gi0/2
30 0013.6016.cdef DYNAMIC Gi0/3
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 67
#sh ip arp
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 10.100.10.11 0 3c4a.92b2.abcd ARPA Vlan10
Internet 10.100.20.28 162 b4b5.2fab.bcde ARPA Vlan20
But Linux «arp» and «arp -a» commands show us some another information:
# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
192.168.10.1 ether 00:50:56:c0:00:08 C eth0
192.168.10.2 ether 00:50:56:f2:83:0a C eth0
# arp -a
? (192.168.10.1) at 00:50:56:c0:00:08 [ether] on eth0
? (192.168.10.2) at 00:50:56:f2:83:0a [ether] on eth0
So you can see both ARP and MAC-address table in one output. It is not so rich as Cisco output but it is good enough.
But if you think that the «arp» output contains a lot of extra information you may parse it with «awk» command:
# arp | grep -v Address | awk ' < print $3,$5 >'
00:50:56:c0:00:08 eth0
00:50:56:f2:83:0a eth0
If you hate the «arp» or «awk» command you must
- install bridge-utils,
- set the bridge,
- add interfaces to the bridge
- use «brctl showmacs» command
# brctl addbr 1
# brctl addif 1 eth0
# brctl showmacs 1
port no mac addr is local? ageing timer
1 00:0c:29:1f:cf:5a yes 0.00
1 00:50:56:c0:00:08 no 0.00
So I hope this information may be interesting and useful.
Подписывайтесь на каналы «SecurityLab» в 

How to Find MAC Address on Linux
If you need to find MAC address numbers for any network interface attached to your computer, then Linux makes this quite easy. Each computer network interface receives a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address, which explains what device it belongs to. No two MAC addresses are alike. Users with multiple networking interfaces will end up with more than one address to take a look at.
You’ll need to be working on a command line interface to find MAC address information, but you won’t need to be logged in as root. Graphical desktop environment users can usually hold down Ctrl+Alt+T to open up a terminal. Ubuntu Unity users can search for the word terminal on the Dash. Those using Xfce4 can find it on the Whisker Menu in System Tools, and LXDE, KDE and GNOME Shell users should find it on the menu in the same place. You can work from whatever prompt you’re given.
Method 1: Find MAC Address Numbers with ip link
At the prompt, simply type ip link and push enter. You’ll be given a list of MAC address figures and you simply need to look for the name that GNU/Linux gives to your network adapter. For instance, you might see wls1:, which probably indicates a Wi-Fi connection that you’re working with. A reference to link/ether would point to your Ethernet connection. You’ll quite possibly see more than one of these references if you’re on a beefier modern desktop computer or a laptop that you’ve personally upgraded.
You’ll also find link/loopback more than likely, which will consist of all zeros. This just points back to your own host. For security reasons, our screenshots were taken in a virtual machine, so we only had this adapter. You don’t want to share your MAC address with people!
There really isn’t anything to do, though. This one single command is enough to find the answer to your question without any further playing around.
Method 2: Find MAC Address with the ifconfig Command
Like with almost everything on the Linux command line, there is more than one way to find MAC address data. At the prompt, type ifconfig -a | grep HWaddr and then push enter. If this command is long and you’d like to copy it from this article, then remember that you’ll need to paste from the Edit menu in your terminal window. You might instead want to hold down Shift+Ctrl+V, but the normal Ctrl+V keyboard shortcut won’t work.
Once again, you won’t have to be root to run this command. As soon as you’ve run it, you’ll receive the MAC hardware address for each networking device attached to the system. You might have only a few on a laptop, while connected routers could ultimately list dozens of different connections if they’re sending packets in many different places.
There’s nothing else to do; you can find MAC address data with a single command. If you don’t see anything returned, then you’re probably not connected to a network. You’ll want to check to make sure that you didn’t disable networking, loose a Wi-Fi connection by moving around or unplug an Ethernet cord. You’ll probably also want to make sure you didn’t run the command in an unconnected virtual machine without a network like we did for the purposes of demonstration.