The History of Windows Operating Systems
Related Terms
Microsoft Windows is a family of operating systems. We look at the history of Microsoft’s Windows operating systems (Windows OS) from 1985 to present day.
The Windows operating system (Windows OS) for desktop PCs are more formally called Microsoft Windows and is actually a family of operating systems for personal computers. Windows dominates the personal computer world, running, by some estimates, more than 90 percent of all personal computers – the remainder running Linux and Mac operating systems.
Windows provides a graphical user interface (GUI), virtual memory management, multitasking, and support for many peripheral devices. In addition to Windows operating systems for personal computers, Microsoft also offers operating systems for servers and mobile devices.
The following image indicates the total market share of all desktop operating systems (November, 2017).
Windows OS Quick Links
Microsoft Windows Operating Systems for PCs
The following details the history of MS-DOS and Windows operating systems designed for personal computers (PCs).
MS-DOS — Microsoft Disk Operating System (1981)
Originally developed by Microsoft for IBM, MS-DOS was the standard operating system for IBM-compatible personal computers. The initial versions of DOS were very simple and resembled another operating system called CP/M. Subsequent versions have become increasingly sophisticated as they incorporated features of minicomputer operating systems.
Windows 1.0 – 2.0 (1985-1992)
Introduced in 1985, Microsoft Windows 1.0 was named due to the computing boxes, or «windows» that represented a fundamental aspect of the operating system. Instead of typing MS-DOS commands, windows 1.0 allowed users to point and click to access the windows.
In 1987 Microsoft released Windows 2.0, which was designed for the designed for the Intel 286 processor. This version added desktop icons, keyboard shortcuts and improved graphics support.
Windows 3.0 – 3.1 (1990–1994)
Windows 3.0 was released in May, 1900 offering better icons, performance and advanced graphics with 16 colors designed for Intel 386 processors. This version is the first release that provides the standard «look and feel» of Microsoft Windows for many years to come. Windows 3.0 included Program Manager, File Manager and Print Manager and games (Hearts, Minesweeper and Solitaire). Microsoft released Windows 3.1 in 1992.
Windows 95 (August 1995)
Windows 95 was released in 1995 and was a major upgrade to the Windows operating system. This OS was a significant advancement over its precursor, Windows 3.1. In addition to sporting a new user interface, Windows 95 also includes a number of important internal improvements. Perhaps most important, it supports 32-bit applications, which means that applications written specifically for this operating system should run much faster.
Although Windows 95 can run older Windows and DOS applications, it has essentially removed DOS as the underlying platform. This has meant removal of many of the old DOS limitations, such as 640K of main memory and 8-character filenames. Other important features in this operating system are the ability to automatically detect and configure installed hardware (plug and play).
Windows 98 (June 1998)
Windows 98 offers support for a number of new technologies, including FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD, and ACPI. Its most visible feature, though, is the Active Desktop, which integrates the Web browser (Internet Explorer) with the operating system. From the user’s point of view, there is no difference between accessing a document residing locally on the user’s hard disk or on a Web server halfway around the world.
Windows ME — Millennium Edition (September 2000)
The Windows Millennium Edition, called «Windows Me» was an update to the Windows 98 core and included some features of the Windows 2000 operating system. This version also removed the «boot in DOS» option.
Windows NT 31. — 4.0 (1993-1996)
A version of the Windows operating system. Windows NT (New Technology) is a 32-bit operating system that supports preemptive multitasking. There are actually two versions of Windows NT: Windows NT Server, designed to act as a server in networks, and Windows NT Workstation for stand-alone or client workstations.
Windows 2000 (February 2000)
Often abbreviated as «W2K,» Windows 2000 is an operating system for business desktop and laptop systems to run software applications, connect to Internet and intranet sites, and access files, printers, and network resources. Microsoft released four versions of Windows 2000: Professional (for business desktop and laptop systems), Server (both a Web server and an office server), Advanced Server (for line-of-business applications) and Datacenter Server (for high-traffic computer networks).
Windows XP (October 2001)
Windows XP was released in 2001. Along with a redesigned look and feel to the user interface, the new operating system is built on the Windows 2000 kernel, giving the user a more stable and reliable environment than previous versions of Windows. Windows XP comes in two versions, Home and Professional. Microsoft focused on mobility for both editions, including plug and play features for connecting to wireless networks. The operating system also utilizes the 802.11x wireless security standard. Windows XP is one of Microsoft’s best-selling products.
Windows Vista (November 2006)
Windows Vista offered an advancement in reliability, security, ease of deployment, performance and manageability over Windows XP. New in this version was capabilities to detect hardware problems before they occur, security features to protect against the latest generation of threats, faster start-up time and low power consumption of the new sleep state. In many cases, Windows Vista is noticeably more responsive than Windows XP on identical hardware. Windows Vista simplifies and centralizes desktop configuration management, reducing the cost of keeping systems updated.
Windows 7 (October, 2009)
Windows 7 was released by Microsoft on October 22, 2009 as the latest in the 25-year-old line of Windows operating systems and as the successor to Windows Vista (which itself had followed Windows XP). Windows 7 was released in conjunction with Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7’s server counterpart. Enhancements and new features in Windows 7 include multi-touch support, Internet Explorer 8, improved performance and start-up time, Aero Snap, Aero Shake, support for virtual hard disks, a new and improved Windows Media Center, and improved security.
Windows 8
Windows 8 was released on August. 1, 2012 and is a completely redesigned operating system that’s been developed from the ground up with touchscreen use in mind as well as near-instant-on capabilities that enable a Windows 8 PC to load and start up in a matter of seconds rather than in minutes.
Windows 8 will replace the more traditional Microsoft Windows OS look and feel with a new «Metro» design system interface that first debuted in the Windows Phone 7 mobile operating system. The Metro user interface primarily consists of a «Start screen» made up of «Live Tiles,» which are links to applications and features that are dynamic and update in real time. Windows 8 supports both x86 PCs and ARM processors.
Windows 10
Windows 10 is Microsoft’s Windows successor to Windows 8. Windows 10 debuted on July 29, 2015, following a «technical preview» beta release of the new operating system that arrived in Fall 2014 and a «consumer preview» beta in early 2015. Microsoft claims Windows 10 features fast start up and resume, built-in security and the return of the Start Menu in an expanded form. This version of Windows will also feature Microsoft Edge, Microsoft’s new browser. Any qualified device (such as tablets, PCs, smartphones and Xbox consoles) can upgrade to Windows 10, including those with pirated copies of Windows.
Windows 11
As of Sept. 2020, Microsoft had no plans for Windows 11 and planned to continue to update and support Windows 10 (see Microsoft’s Windows lifecycle fact sheet).
Microsoft Operating Systems for Servers and Mobile Devices
Aside from operating systems designed for use on personal computers (PCs) and laptops, Microsoft has also developed operating systems for services, handheld devices, and mobile phones.
Windows Server (March 2003)
Windows Server is a series of Microsoft server operating systems. Windows servers are more powerful versions of their desktop operating system counterparts and are designed to more efficiently handle corporate networking, Internet/intranet hosting, databases, enterprise-scale messaging and similar functions. The Windows Server name made its debut with the release of Windows Server 2003 and continues with the current release, Windows Server 2008 R2, which shares its codebase with Windows 7. Windows Server 2008 R2 debuted in October 2009.
Windows Home Server (January 2007)
Announced in January 2007, Windows Home Server (WHS) is a «consumer server» designed to use with multiple computers connected in the home. Home Server allows you to share files such as digital photos and media files, and also allows you to automatically backup your home networked computers. Through Windows Media Connect, Windows Home Server lets you share any media located on your WHS with compatible devices.
Windows CE (November 2006)
A version of the Windows operating system designed for small devices such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) (or Handheld PCs in the Microsoft vernacular). The Windows CE graphical user interface (GUI) is very similar to Windows 95 so devices running Windows CE should be easy to operate for anyone familiar with Windows 95.
Windows Mobile (April 2000)
A mobile operating system for smartphones and mobile devices from Microsoft based on the Windows CE kernel and designed to look and operate similar to desktop versions of Microsoft Windows. Windows Mobile has largely been supplanted by Windows Phone 7, although Microsoft did release, in 2011, Windows Embedded Handheld 6.5, a mobile OS compatible with Windows Mobile 6.5 that’s designed for enterprise mobile and handheld computing devices.
Windows Phone (November 2010)
A mobile operating system for smartphones and mobile devices that serves as the successor to Microsoft’s initial mobile OS platform system, Windows Mobile. Unlike Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 (also referred to as WinPhone7) is targeted more to the consumer market than the enterprise market, and it replaces the more traditional Microsoft Windows OS look and feel with a new «Metro» design system user interface.
Windows Phone 7 features a multi-tab Internet Explorer Mobile Web browser that uses a rendering engine based on Internet Explorer 9 as well Microsoft Office Mobile, a version of Microsoft Office that’s tailored for mobile devices. Its successors include Windows Phone 8 and Windows 10 Mobile.
Webopedia’s Top 5
Study Guides
This article was last updated on August 02, 2018
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a family of operating systems are developed by Microsoft Corporation since 1983. The latest version as of 2017-07 is Windows 10 Creators Update (Version 1703), It currently uses the Windows Explorer shell.
The first versions of Windows were an operating environment for DOS. Later versions (9x) used DOS as a bootstrapper. Any version of Windows that uses the NT Kernel does not rely on MS-DOS.
History
Windows for DOS (Classic Windows)
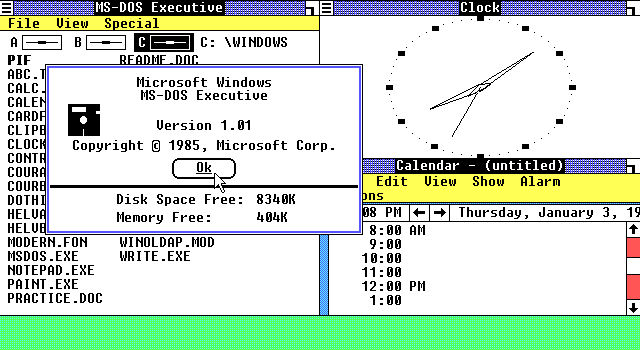
Windows 1.01, the very first public version of Windows released
Microsoft Windows debuted to the world on the Fall COMDEX 1983 computer expo as an operating environment running on top MS-DOS. The final version of the product with the version number of 1.01 was later released on 1985-11-20 and did not gain much popularity. Windows 1.0 was a cooperative multitasking desktop environment with a tiling window manager. Applications included in the first version of Windows included Calculator, Cardfile, Clipboard Viewer, Clock, Control Panel, MS-DOS Executive, Notepad, Reversi, Spooler, Terminal, and Microsoft Write. Three minor updates were released in the two following years adding support for more hardware.
A major update called Windows 2.0 was released in 1987 adding features such as overlapping windows. This version also introduced support for the Video Graphics Array and PS/2 mouse. A separate edition called Windows/386 was introduced taking advantage of the new abilities of the 386 processor. In later revisions of the Windows 2.0 environment the original edition was renamed Windows/286.
Windows 3.0 was released in 1990 and it became the first widely successful version of Windows. The new features included a completely reworked Setup program, and a new 3D user interface centered around a new shell called the Program Manager. The previously separate 286 and 386 editions of Windows were unified into one. This version of Windows was able to operate in three modes: Real mode intended for computers with the original 8088/8086 processor, Standard mode using the protected mode feature of the 286 processor, and 386 Enhanced mode combining the improved protected mode of the 386 with its ability to create and manage virtual 8086 machines for MS-DOS applications.
A major update dubbed Windows 3.1 followed in 1992 with the brand new red-green-blue-yellow Windows logo resembling a flag. The user interface was refreshed in this release, including new colorful icons. This version of Windows removed the real mode of operation and the MS-DOS Executive application. It was accompanied with a variant called Windows for Workgroups (WfW) 3.1 with an integrated networking capability, which later received a larger update bringing its version number up to 3.11, introducing 32-bit disk access and also removing the Standard mode of operation. The regular variant of Windows also received the 3.11 update, however it only contained small bug fixes.
A 32-bit TCP/IP stack was ported from an early version of Windows 95 and released in 1994 as a downloadable plugin for WfW 3.11, providing early testing for the 16/32-bit compability features of the next version of Windows.
Windows 9x
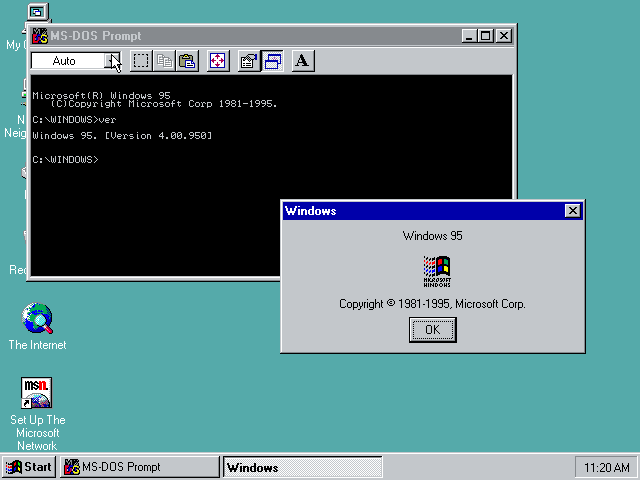
Windows 95, the first version with the Start menu and taskbar
On 1995-08-24 Microsoft released Windows 95 also known under its codename «Chicago» with a brand new user interface with a Start menu, taskbar and the desktop. Its hybrid 16/32-bit architecture made it possible to make and run 32-bit Windows applications and drivers while keeping a great degree of compatibility with already existing 16-bit ones. Among other improvements in this version was the support for long filenames through an extension to the FAT16 file system.
Windows 95 was the first release of Windows to be packed together with a specific MS-DOS version, however, the old operating system was used only as a boot loader and a compatibility layer for ancient device drivers. Most MS-DOS user applications were either extended with Windows code or entirely replaced with a Windows version, keeping only the ones that were required to run without Windows, e.g. during the OS installation, such as FDISK and FORMAT .
During its lifetime Windows 95 saw several larger updates dubbed the OEM Service Releases (OSR) that were released only to computer manufacturers, specifically OSR 1.0, OSR 2.0, OSR 2.1, and OSR 2.5. A Service Pack was also released that updated a RTM copy of Windows 95 to the OSR 1.0 level. In 1997 a USB Supplement was released for OSR 2.x that added support for the then new Universal Serial Bus interface.
The classic Windows line received a major update on 1998-06-25 with the release of Windows 98 codenamed «Memphis». It was the first version to integrate Internet Explorer deeply to the operating system’s user interface as a part of the Windows Desktop Update. Many parts of the UI started using HTML and Internet Explorer’s rendering engine to present a web-like user interface. A feature called Active Desktop made it even possible to set a webpage as the desktop background. Under the hood Windows 98 introduced the Windows Driver Model, which enabled the use of the same drivers on Windows 9x as well as on the radically different Windows NT based operating systems.
A year later, Windows 98 received an update which was called the Second Edition, which included a new version of Internet Explorer, added Internet Connection Sharing and improved USB support.
In 2000 Windows Millenium Edition, the last release of the classic Windows line saw the light of the world. It included the improvements to the user interface from Windows 2000. Windows Me is based on Windows 98, however, access to the real mode MS-DOS was restricted in order to decrease boot time among other changes to the kernel. It was infamously known for its stability problems partially caused by the rushing of its release following the cancellation of the Neptune project. It was replaced by the NT-based Windows XP a year later.
Windows NT
Windows NT (New Technology) is the current iteration of Windows. It is built on the NT hybrid kernel (hence the name), which was originally intended for use in OS/2 3.0 but was rewritten after the Microsoft — IBM split. The first release based on the new kernel was Windows NT 3.1, the version number of which was chosen to not be 1.0 to ensure eventual customers wouldn’t consider it inferior to Windows 3.1, its DOS-based counterpart. All NT-based releases up until Windows 2000 were intended primarily for business use. With Windows XP, the NT series merged with Windows 9x, creating a single operating system for consumers and businesses. Windows Phone 8 is the first Windows Phone release to be based on the NT kernel. The most recent version of Windows based on the NT kernel is Windows 10. Following the release of Windows 10, Microsoft have switched to a periodical release system.
Timeline
The Timeline shows that included while if is Released in future, There are many Unreleased timeline that has been already cancelled.
| «Classic» Windows family | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Version | Codename | Notes |
| Windows 1.0 | 1.0x | Interface Manager | First version of Windows, Released in 1985 |
| Windows 2.0 | 2.x | None | Released in 1987 |
| Windows 3.0 | 3.0 | None | Introduced Program Manager; released in 1990 |
| Windows 3.1x | 3.1x | Janus, Sparta, Snowball | Released in 1991 |
| Windows 9x family | |||
| Name | Version | Codename | Notes |
| Windows 95 | 4.0 | Chicago | Introduced Start Menu and Taskbar; released in 1995 |
| Windows ‘Nashville’ | 4.1 | Nashville | Never released |
| Windows 98 | 4.1 | Memphis | Released in 1998 |
| Windows Me | 4.9 | Millennium | Released in 2000 |
| Windows NT family | |||
| Name | Version | Codename | Notes |
| Windows NT 3.1 | NT 3.1 | NT OS/2 | Released in 1993 |
| Windows NT 3.5x | NT 3.5x | Daytona | Released in 1994 |
| Windows Cairo | NT 4.0 | Cairo | Never released |
| Windows NT 4 | NT 4.0 | Cairo, Hydra | Released in 1996 |
| Windows 2000 | NT 5.0 | Memphis NT, NT 5 | Released in 2000, Also known as Memphis NT. |
| Windows Neptune | NT 5.5 | Neptune | 1 build leaked, Never released; merged to form Whistler. |
| Windows XP | NT 5.1 | Whistler | First NT for home users; released in 2001 |
| Windows Embedded 2009 | Quebec | Released in 2008 | |
| Windows Server 2003 | NT 5.2 | Whistler Server, .NET Server | Released in 2003, Previous Codenames : «Whistler Server» |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | Bobcat | Released in 2003 | |
| Windows Home Server | Quattro | Released in 2007 | |
| Windows FLP | NT 5.1 | Eiger, Monch | Released in 2006 |
| Windows Longhorn | NT 6.0 | Longhorn | Reset as Vista |
| Windows Vista | Longhorn Omega-13 | Code Reset, .NET Server RC1 > 2003 SP1 RC, Released in 2006 | |
| Windows Server 2008 | Longhorn Server | Released in 2008 | |
| Windows 7 | NT 6.1 | Blackcomb, Vienna, ‘7’ | Released in 2009 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Server ‘7’ | Released in 2009 | |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Vail | Released in 2011 | |
| Windows Thin PC | Thin PC | Released in 2011 | |
| Windows Multipoint Server 2010 | Solution Server | Released in 2010 | |
| Windows 8 | NT 6.2 | ‘8’ | Released in 2012-10, Start menu removed, replaced with start screen |
| Windows Server 2012 | Server ‘8’ | Released in 2012 | |
| Windows 8.1 | NT 6.3 | Blue | Released in 2013 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Server Blue | Released in 2013 | |
| Windows 10 | NT 6.4 NT 10.0 | Threshold | Released in 2015-07 |
| Windows Server 2016 | Redstone Server | Released in 2016, Previous Codenames: Threshold Server, vNext Server. | |
| Windows 10 v1511 | Threshold 2 | Released in 2015-11 | |
| Windows 10 v1607 | Redstone 1 | Released in 2016-07 | |
| Windows 10 v1703 | Redstone 2/RS2 (Feature Update) | Released in 2017-03 | |
| Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (Version 1709) | Redstone 3 | In finalization, To be Released in late 2017 | |
| Windows 10 RS4 | Redstone 4 | To be released in toward 2018 | |
Unreleased Timeline
The Following for Unreleased Timeline, Which sometime it included Windows Odyssey.
- Windows Odyssey — The Unreleased Build which it was skipped, despite it uses Windows Neptune.
- Windows Triton — There is a Calendar for Planning Service pack, however it skipped this build.
- Windows Cairo — The Windows Cairo was known as Windows NT 4.0, it is a Codenamed by Cairo, There is One Leaked Build is 1175, presumably, it was Never Released.
Unofficial Timeline
Every some Projects has been started, only the Reason for Windows Longhorn has been Ported to Windows Shorthorn.
- Windows Shorthorn — A Project made by Samuka, which is why creating Project to working Windows XP Build 3790 x86.
- It is similar as Windows XP x64 Edition.
Updates
Microsoft also includes Updates that has served to get Protecting PC, enabling Automatic Updates. it also uses Knowledge Base (KB) to fix Major Bugs and improvements.
In Windows 2000, the Update string uses «Windows 2000 Hotfix», some lot Updates string other websites is «Security Update» or «Update».
In Windows XP, the String has changed similar as Windows 2000 Hotfix, as it called «Security Update for Windows XP», «Hotfix for Windows XP» and «Update for Windows XP».
In Windows Server 2003, it is Same as Windows XP, so there are nothing changed String.
In Windows Vista, 7, 8/8.1, and 10, The String has changed since It no longer uses «Vista or 7 or 8/8.1 or 10» it uses String has using «Hotfix for Microsoft Windows», «Security Update for Microsoft Windows» and «Update for Microsoft Windows».
Depending Newer OS has included by string Operating System, Despite, some Updates are included for Betas, and can be founded on Microsoft Update Catalog.