Программы и VST-плагины для Mac OSX
Stochas — это революционно новый тип пошагового секвенсора с уникальным механизмом рандомизации. Разработанный для работы в монофоническом или полифоническом режимах, движок будет выбирать из набора введённых пользователем нот и принимает во внимание вероятность, установленную для каждой, это означает, что Stochas можно использовать для создания развивающихся мелодий, богато звучащих струнных и синтезаторных секций, уникальных басов. линии и даже хаотичные, но повторяющиеся барабанные паттерны,
Giada — это бесплатный, аудио-инструмент для ди-джеев и тех, кто выступает вживую. Как он работает? Просто возьмите ваш канал, наполните его сэмплами или MIDI-событиями и начинайте шоу, используя эту компактную программу как луп-процессор, драм-машину, секвенсор, живой сэмплер и даже как хост-программу (VST) эффектов. Цель Giada — быть компактным и портативным виртуальным устройством для Linux, Mac OS X и Windows, для создания аудио и проведения живых сетов.
Elsita — это эмуляция советского аналогового автомата RMIF Elsita, выпускавшегося с 1989 по 1991 год. Несмотря на то, что Elsita была выпущена в довольно поздний период, она была построена по старым стандартам середины 70-х — начала 80-х годов: полностью аналоговая (как вы можете видеть на рисунке), только триггерная, с большими ручками.С помощью эмуляции добавлена папка, содержащая различные звуки, которые сделаны на оригинальной машине, чтобы вы могли играть с оригинальными звуками или с более
Бесплатный плагин эффекта реверберации в форматах AU и VST. Это плагин реализует алгоритм «классичекой» стерео-реверберации, который является простым, но и оптимальным. Он также создаёт очень чистую пространственную картину, которая хорошо вписывается в микс. OldSkoolVerb даёт вам всеобъемлющий набор параметров, позволяющих достигнать различных ревербераций в диапазоне от plate reverb до реверберации комнаты или холла. OldSkoolVerb лучше всего подойдёт для неперкуссионных звуков и звуков с мягкой
SPAN — анализатор спектра, работающий в реальном времени и использующий алгоритм «fast Fourier transform»(быстрое преобразование Фурье — алгоритм сокращения времени спектрального анализа). В основном сделан на базе плагина «Voxengo GlissEQ» (динамического параметрического эквалайзера), собственно из которого и был взят сам анализатор спектра.
VSTi сэмплер с профессиональными возможностями и простым графическим интерфейсом, который кстати можно настроить. Это бесплатный плагин. Полностью функциональный и без какой-либо оплаты.
Look-Ahead Brickwall — лимитр с автоматическим выравниванием уровня громкости.Максимальная громкость регулируется слайдером «Drive». Максимальная громкость звука на выходе — слайдером «Output». Особенности: Поддержка частоты дискретизации от 2 kHz до 384kHz. Возможность овердрайва без искажения звука: 730dB. Никакого увеличение частоты дискретизации сигнала, никаких измерителей. Задержка и время атаки: 1 Sample – 1.25ms. Время спада (Release Time): автоматическое. Зависит от громкости звука
ToneLib-GFX — это набор гитарных усилителей, акустических систем и эффектов, реализованных в программном обеспечении для использования с вашим компьютером. Программное обеспечение поставляется в виде отдельного приложения и в качестве плагинов для использования с наиболее популярным программным обеспечением для записи DAW (цифровое аудио рабочее место). Tonelib-GFX также поддерживает сторонние импульсные характеристики (IR), предлагая ещё большую гибкость звука.
Tonelib JAM — это программное обеспечение для создания, редактирования, печати и прослушивания табулатур и нот для гитары и других инструментов с лаконичным исполнением. Вы можете использовать Tonelib JAM для регулярных занятий на гитаре, для изучения песен или для продвижения своих навыков исполнения на следующий уровень. Tonelib JAM позволяет легко создавать минусовки практически из любой песни. Внутренний проигрыватель позволяет вам изменять темп воспроизведения, сохраняя ту же высоту, и имеет
Анализатор аудиофайлов. При большом количестве функций для полного исследования аудиоданных, у Sonic Visualiser также есть возможности написания аннотаций для описания данных, которые вы нашли, и возможность запуска плагина Vamp для автокомментирования и анализа, а также применения стандартных аудиоэффектов.
Quick Tip: How to Manage VST and AudioUnits Plugins in Mac OS X
VST and AudioUnits (AU) are the two native plugin formats for Mac OS X. Although there are other DAW specific formats for plugins, VST and AudioUnits are more common and compatible across various DAWs like Cubase, Logic, etc. There is an abundance of VST and AU plugins for expanding your DAW and building your collection of effects. However, it can be difficult to know how to get those plugins running on your computer. Especially if they are free and do not come with installers or instructions. I’ll help you get those files in the right places and make them appear in your plugin stacks.
Finding the Audio Plugins folder
The plugin folder is nested in the Macintosh HD Library. There are usually a minimum of two Libraries on your Mac, one in Macintosh HD and another in your user account. You should only place the plugins in the Macintosh HD Library so that it can be accessed by all users on the computer. The usual location of the folder should be:
Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/
How to Install VST Plugins
- Unzip the downloaded file if it is an archive like .zip or .rar. You should only see a file with a .vst extension. This is the actual file required for the plugin.
- Move the .vst file to the VST folder in your audio plugins folder.
- If your DAW is running, close it and restart it. When your DAW starts up, it will rescan your plugins folder and detect your recently installed plugin.
How to Install AudioUnits Plugins
- Unzip the downloaded file if it is an archive like .zip or .rar. You should only see a file with a .component extension. This is the actual file required for the plugin.
- Move the .component file to the Components folder in your audio plugins folder.
- If your DAW is running, close it and restart it. When your DAW starts up, it will rescan your plugins folder and detect your recently installed plugin.
Other Plugin Formats
You might come across another folder labelled VST3, this is for VST3 plugins which are not as common as of yet. They can be identified with the .vst3 file extension. MAS is used for MOTU Audio System. HAL is Hardware Abstraction Layer and you should not be needing to change anything there.
Tips and Tricks
There some things that you can do to make managing plugins easier. If you have a huge collection of plugins but you do not use them all at the same time, you can waste a lot of time waiting for your DAW/host to scan all of them.
- Create a folder as seen in the picture above labelled Components (Disabled) or VST (Disabled).
- Simply drag the associated plugin to the respective ‘Disabled’ folder if you do not wish to load the plugin or have problems loading it.
- Restart your DAW if it is running. Your DAW will rescan and load the plugins in your Components or VST folder, and ignore the ones in the «Disabled» folders.
Remember to check for updates for your plugin first if they are giving you problems. Updates could provide compatibility fixes for newer DAWs or operating systems. Keeping your plugins in check and trimming it down can make your music making experience more responsive and trouble-free.
Using AU and VST plug-ins on Mac
- Live Versions: All
- Operating System: Mac
AU or VST?
Live on Mac supports both the Audio Unit (AU) and VST2 and VST3 (10.1 and later) formats. Which format you choose to use is up to you, bearing in mind the following tips:
- If sharing projects with Windows users, it’s better to use VST. The VST format is cross platform. Provided the other user is using the same version of the plug-in, they’ll be able to open the set and the plug-ins will be available. See our recommendations for transferring Live projects.
- Some AU plug-ins may have different preset handling than the VST, or vice versa. See our article on AU preset handling.
- AU plug-ins do not support a direct MIDI out. If you wish to route MIDI from a plug-in you need to use the VST version instead. See this article for info on how to access the MIDI outputs of a plug-in.
- Avoid using the AU and VST versions of the same plug-in in a Live set.
How to install VST or AU plug-ins on Mac
1. Download the latest installer file from the plug-in manufacturer’s website and run it.
2. Most plug-ins will install themselves to the default system folders, others might simply need to be moved to the correct folder. Here are the default system folders:
- Macintosh HD:/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/Components/ (AU .component file extension)
- Macintosh HD:/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/VST/ (VST 2 .vst file extension)
- Macintosh HD:/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/VST3/ (VST 3 .vst3 file extension)
Certain plug-ins may install themselves to the folder. This folder is hidden by default, here’s how to access hidden folders.
- Macintosh HD:/Users/[Your Username]/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/Components/ (AU)
- Macintosh HD:/Users/[Your Username]/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/VST/ (VST 2)
- Macintosh HD:/Users/[Your Username]/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/VST3/ (VST 3)
3. You can instead install your plug-ins to a custom folder if you prefer (VST 2 and VST 3 only)
4. Once installed, launch Live.
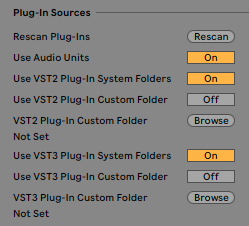
5. Open Live’s Preferences → Plug-ins (Live 10.1 and later)/File Folder (all Live versions until 10.1) → Plug-In Sources.
6. Activate the Audio units folder, and/or VST2/VST3 folders as required.
7. If you’ve installed the plug-in correctly but it’s still not appearing in Live, see our dedicated article: VST/AU plug-in doesn’t appear in Live.