Network Policy and Access Services Overview
Applies To: Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This topic provides an overview of Network Policy and Access Services in Windows ServerВ® 2012, including the specific role services of Network Policy Server (NPS), Health Registration Authority (HRA), and Host Credential Authorization Protocol (HCAP). Use the Network Policy and Access Services server role to deploy and configure Network Access Protection (NAP), secure wired and wireless access points, and RADIUS servers and proxies.
Did you mean…
Role description
Network Policy and Access Services provides the following network connectivity solutions:
Network Access Protection (NAP)
NAP is a client health policy creation, enforcement, and remediation technology. With NAP, system administrators can establish and automatically enforce health policies, which can include software requirements, security update requirements, and other settings. Client computers that are not in compliance with health policy can be provided restricted network access until their configuration is updated and brought into compliance with policy.
802.1X authenticated wired and wireless access
When you deploy 802.1X-capable wireless access points and Ethernet switches, you can use Network Policy Server (NPS) to deploy certificate-based authentication methods that are more secure than password-based authentication. Deploying 802.1X-capable hardware with NPS allows you to ensure that intranet users are authenticated before they can connect to the network or obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.
Central network policy management with RADIUS server and proxy
Rather than configuring network access policy at each network access server, you can create policies in a single location that specify all aspects of network connection requests, including who is allowed to connect, when they can connect, and the level of security they must use to connect to your network.
Network Policy and Access Services can be run in Windows Azure VMs.
New and changed functionality
The following table lists the primary differences in the Network Policy and Access Services server role by operating system:
Windows Server® 2008 R2 and Windows Server® 2008
Windows Server 2012
Support for Windows PowerShellВ®
Support for Windows PowerShell
You can now use Windows PowerShell to automate the installation of the Network Policy and Access Services server role. You can also deploy and configure some aspects of Network Policy Server by using Windows PowerShell. For more information, see Windows PowerShell for Network Policy and Access Services.
Removed functionality
In Windows Server® 2008 R2 and Windows Server® 2008, Network Policy and Access Services included the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) role service. In Windows Server 2012, RRAS is now a role service in the Remote Access server role.
Deprecated functionality
With the release of Windows Server 2012 R2, NAP is deprecated. NAP is fully supported in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1. For more information about support lifecycles, see Microsoft Support Lifecycle.
Central network policy management with RADIUS server and proxy, and 802.1X authenticated wired and wireless access are not deprecated
For the health policy creation, enforcement, and remediation features provided by NAP, as well as for monitoring, consider using System Center Configuration Manager to replace and enhance NAP’s monitoring functionality:
Windows Update status—System Center Configuration Manager integrates with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and has its own software updates feature. See Software Updates in Configuration Manager, in particular Monitor software updates.
Computer settings: registry settings, files, custom scripts—System Center Configuration Manager can help assess, track, and remediate the configuration compliance of client computers in the enterprise, see Compliance Settings in Configuration Manager.
Reporting—System Center Configuration Manager also provides a set of tools and resources that help you use the advanced reporting capabilities of Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services in the Configuration Manager console. See Reporting in Configuration Manager.
Bitlocker—Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring (MBAM) lets you manage Bitlocker drive encryption throughout your enterprise, see Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring 2 Administrator’s Guide.
To provide an always managed and always compliant experience for remote devices, you can use Remote Access, see Manage DirectAccess Clients Remotely. This way you can ensure the clients are always healthy, not only when they try to access resources in the corporate network.
NAP enables you to provide full internal network access to your users. However, if you only require the ability to provide access to specific applications and services in your internal network, you can use Web Application Proxy. Web Application Proxy enables you to provide this type of specific access to end users with domain-joined laptops or using their own devices; home computers, tablets, or personal smartphones. See Web Application Proxy Walkthrough Guide.
Server Manager information
The following role services can be installed with this role.
Network Policy Server (NPS)
You can use NPS to centrally manage network access through a variety of network access servers, including RADIUS-compliant 802.1X-capable wireless access points, VPN servers, dial-up servers, and 802.1X-capable Ethernet switches. In addition, you can use NPS to deploy secure password authentication with Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)-MS-CHAP v2 for wireless connections. NPS also contains key components for deploying NAP on your network.
Health Registration Authority (HRA)
HRA is a NAP component that issues health certificates to clients that pass the health policy verification that is performed by NPS using the client SoH. HRA is used only with the NAP IPsec enforcement method.
Host Credential Authorization Protocol (HCAP)
HCAP allows you to integrate your Microsoft NAP solution with Cisco Network Access Control Server. When you deploy HCAP with NPS and NAP, NPS can perform client health evaluation and the authorization of Cisco 802.1X access clients.
Running Network Policy and Access Services
How do I deploy and configure Network Policy and Access Services using Windows PowerShell?
You can use to deploy and configure some aspects of Network Policy and Access Services. For more information about Windows PowerShellВ® cmdlets and scripts that you can use to deploy and manage Network Policy and Access Services, see Windows PowerShell for Network Policy and Access Services.
How do I deploy and configure this role in a multi-server environment?
You can deploy NPS servers for different functions. For example, you can deploy one NPS server as a RADIUS server for authentication, another as a RADIUS proxy, in order to distribute policy evaluation between servers with different roles, and another as a NAP policy server. For more information about multi-server management of Network Policy and Access Services, see Network Policy Server Overview.
Can I run this role on virtual machines?
Yes, you can run Network Policy and Access Services on Hyper-V virtual machines.
Can I run this role in a clustered environment?
No, Network Policy and Access Services cannot be run in a server cluster.
Special considerations for managing this role remotely
You can manage Network Policy and Access Services remotely. For more information about running Network Policy and Access Services from a remote computer, see Administer NPS by Using Tools.
Special considerations for managing the role on the Server Core installation option
You cannot install or run Network Policy and Access Services on the Server Core installation option of Windows Server 2012.
See also
The following table provides links to more content about Network Policy and Access Services.
Настраиваем доменную аутентификацию на сетевом оборудовании
При обслуживании больших сетей системные администраторы часто сталкиваются с проблемами аутентификации на сетевом оборудовании. В частности, довольно сложно организовать нормальную работу нескольких сетевых администраторов под индивидуальными учетными записями на большом количестве оборудования (приходится вести и поддерживать в актуальном состоянии базу локальных учетных записей на каждом устройстве). Логичным решение было бы использовать для авторизации уже существующей базы учетных записей — Active Directory. В этой статье мы разберемся, как настроить доменную (Active Directory) аутентификацию на активном сетевом оборудовании (коммутаторы, маршрутизаторы).
Не все сетевое оборудование популярных вендоров (CISCO, HP, Huawei) поддерживает функционал для непосредственного обращения к каталогу LDAP, и такое решение не будет универсальным. Для решения нашей задачи подойдет протокол AAA (Authentication Authorization and Accounting), фактически ставший стандартом де-факто для сетевого оборудования. Клиент AAA (сетевое устройство) отправляет данные авторизующегося пользователя на сервер RADIUS и на основе его ответа принимает решение о предоставлении / отказе доступа.
Протокол Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) в Windows Server 2012 R2 включен в роль NPS (Network Policy Server). В первой части статьи мы установим и настроим роль Network Policy Server, а во второй покажем типовые конфигурации сетевого устройств с поддержкой RADUIS на примере коммутаторов HP Procurve и оборудования Cisco.
Установка и настройка сервера с ролью Network Policy Server
Как правило, сервер с ролью NPS рекомендуется устанавливать на выделенном сервере (не рекомендуется размещать эту роль на контроллере домена). В данном примере роль NPS мы будем устанавливать на сервере с Windows Server 2012 R2.
Откройте консоль Server Manager и установите роль Network Policy Server (находится в разделе Network Policy and Access Services).
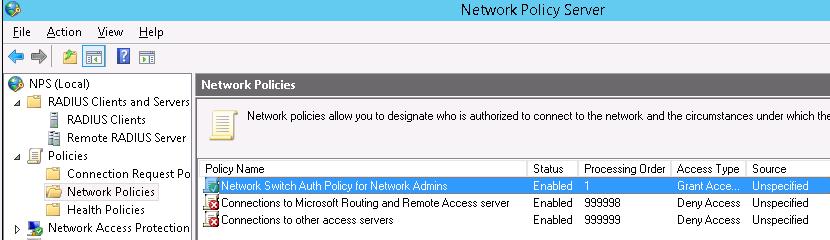
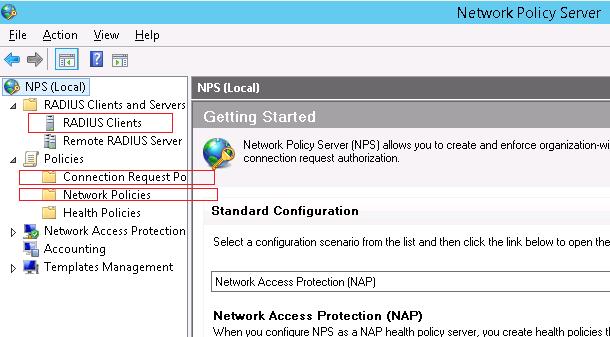
- RADIUS Clients — содержит список устройств, которые могут аутентифицироваться на сервере
- Connection Request Policies – определяет типы устройств, которые могут аутентифицироваться
- Network Polices – правила аутентификации
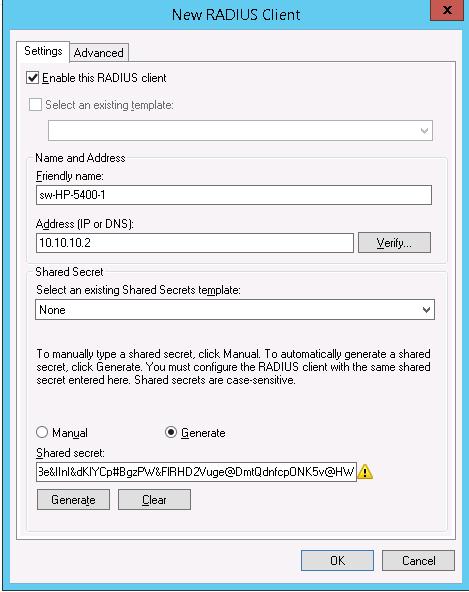
- Friendly Name:sw-HP-5400-1
- Address (IP or DNS): 10.10.10.2
- Shared secret (пароль/секретный ключ): пароль можно указать вручную (он должен быть достаточно сложным), либо сгенерировать с помощью специальной кнопки (сгенерированный пароль необходимо скопировать, т.к. в дальнейшем его придется указать на сетевом устройстве).
Создадим новую политику с именем Network-Switches-AAA и нажимаем далее. В разделе Сondition создадим новое условие. Ищем раздел RADIUS Client Properites и выбираем Client Friendly Name.
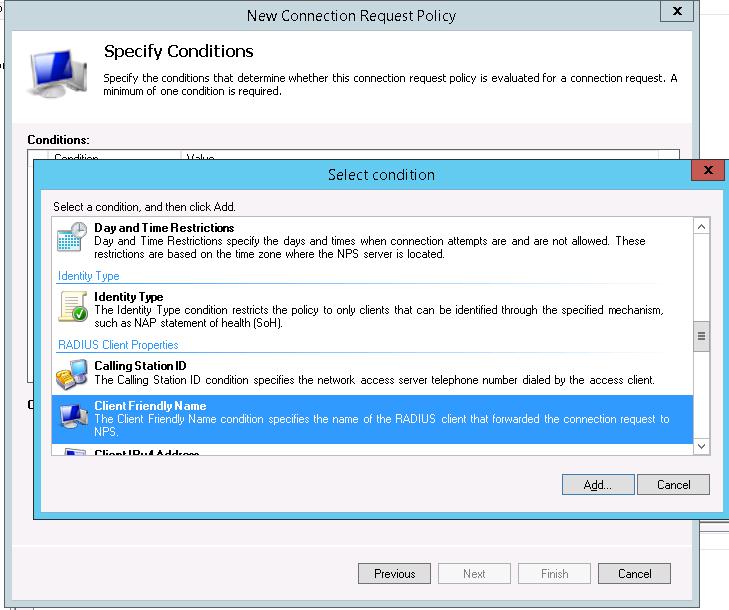
Далее в разделе Network Policies создадим новую политику аутентификации. Укажите ее имя, например Network Switch Auth Policy for Network Admins. Создадим два условия: в первом условии Windows Groups, укажем доменную группу, члены которой могут аутентифицироваться (учетные записи сетевых администраторов в нашем примере включены в группу AD Network Admins) Второе условие Authentication Type, выбрав в качестве протокола аутентификации PAP.
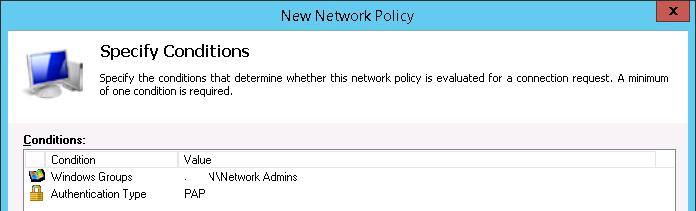
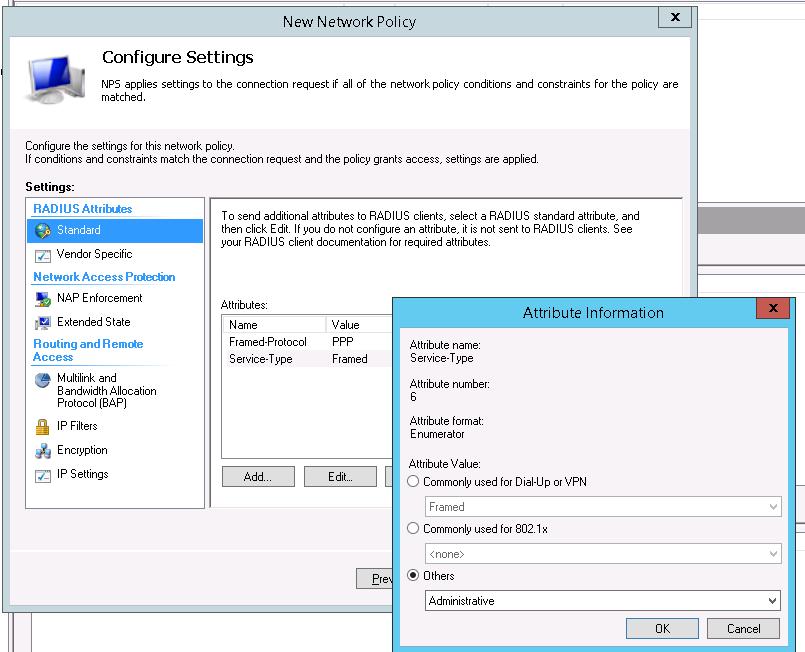
В окне Configure Settings изменим значение атрибута Service-Type на Administrative.
И, напоследок, переместим новую политику на первое место в списке политик.
Настройка сетевого оборудования для работы с сервером RADUIS
Осталось настроить наше сетевое оборудование для работы с сервером Radius. Подключимся к нашему коммутатору HP ProCurve Switch 5400 и внесем следующе изменение в его конфигурацию (измените ip адрес сервера Raduis и пароль на свои).
Совет. Если в целях безопасности вы запретили подключаться к сетевому оборудованию через telnet, эти строки нужно удалить из конфига:
Не закрывая консольное окно коммутатора (это важно!, иначе, если что-то пойдет не так, вы более не сможете подключиться к своему коммутатору), откройте вторую telnet-сессию. Должно появиться новое окно авторизации, в котором будет предложено указать имя и пароль учетной записи. Попробуйте указать данные своей учетной записи в AD (она должна входить в группу Network Admins ). Если подключение установлено – вы все сделали правильно!
Для Cisco ASA конфигурация будет выглядеть так:
Совет. Если что то-не работает, проверьте:
- Совпадают ли секретные ключи на сервере NPS и коммутаторе (для теста можно использоваться простой пароль).
- Указан ли правильный адрес NPS сервера в конфигурации. Пингуется ли он?
- Не блокируют ли межсетевые экраны порты 1645 и 1646 между коммутатором и сервером?
- Внимательно изучите логи NPS сервера