Windows Server: версии, редакции, лицензирование
Задаваясь вопросом, какую версию Windows Server выбрать для своего бизнеса, пользователи, как правило, сталкиваются с большим разнообразием, и далеко не всегда понятно как выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант. У операционной системы Windows Server существуют не только разные версии, но и разные редакции. Давайте разберемcя в чем же отличия между ними.
Что такое версия Windows Server?
В 90-е годы, во времена Windows NT, каждая версия Windows Server имела уникальный номер. Например, у Windows NT были номера 3.1, 3.51 и 4.0. Но начиная с 2000 года Microsoft вместо номера начала добавлять после названия год запуска операционной системы: Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, 2008 (которая также имела версию R2), 2012 (также с R2), 2016 и 2019, и т.д.
Каждая новая версия Microsoft Windows Server представляет новые функциональные возможности. Например, виртуализация Hyper-V, Server Core и BitLocker были представлены в Windows Server 2008, контейнеры Windows и Nano Server были представлены в Windows Server 2016, а Windows Server 2019 принес с собой Windows Admin Center — новый способ удаленного администрирования серверной инфраструктуры, улучшения гиперконвергентной инфраструктуры и глубокую поддержку подсистемы Linux.
Что такое завершение поддержки?
Как говорится, ничто не вечно. И в определенный момент Microsoft прекращает выпуск патчей для устаревшего программного обеспечения. Дата, до которой Microsoft выпускает обновления для продукта, называется датой окончания поддержки. И после того, как эта дата пройдет, устаревшая версия ОС станет легкой мишенью для вредоносных программ, поскольку она больше не будет получать обновления безопасности и, следовательно, будет уязвима для новых эксплоитов.
Операционные системы Microsoft обычно поддерживаются не менее 10 лет. Например, популярный Windows Server 2003, выпущенный в апреле 2003 года, имел расширенную поддержку, которая закончились в 2015 году. Расширенная поддержка Windows Server 2008 R2 должна закончиться в январе 2020 года, а Windows Server 2012 R2 продолжит получать обновления по крайней мере до октября 2023 года. Версии Server 2016 и 2019 будут получать обновления по 2027 и 2029 год соответственно. Поэтому в целях безопасности организациям на самом деле следует использовать только свежие версии Windows Server.
Что такое редакция Windows Server?
Когда вы покупаете автомобиль, вам доступно, как минимум, несколько комплектаций одной и той же модели. Например, базовый экономичный вариант, роскошный вариант с кожаными сиденьями и люком на крыше, а также спортивный вариант с большими колесами и более мощным двигателем. Другими словами, каждая версия автомобиля имеет свою цену и набор функций для групп клиентов с разными бюджетами и потребностями.
То же самое касается выпусков Windows Server. Каждый вариант включает в себя функциональность, которая подходит для разных компаний, в зависимости от их размера и бюджета. Например, разные редакции могут поддерживать разное количество пользователей.
Различия между редакциями Windows Server 2012 R2
Чтобы помочь понять некоторые различия между редакциями ОС, давайте разберем их на примере Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Foundation — серверная ОС общего назначения, лучше всего подходящая для серверов нижнего уровня. ОС поддерживает только один процессор и 32 ГБ RAM. Редакция Foundation (недоступная в Windows Server 2016) ограничена 15 пользователями, что делает ее пригодной только для небольших офисов. Foundation доступен только через OEM-производителей, что обычно означает, что он предустановлен на компьютерах, которые вы покупаете у таких компаний, как Dell и HPE.
- Essentials (ранее SBS или Small Business Server) — это простое в настройке серверное решение, которое поддерживает до 25 пользователей и 50 устройств, что делает его подходящим для небольших офисов. Essentials поддерживает более мощное оборудование с объемом оперативной памяти до 64 ГБ и двумя процессорами. В отличие от других выпусков Windows Server, в Essentials предварительно настроены роли, такие как Active Directory, DNS, файловые службы, IIS и удаленный рабочий стол, что делает его идеальным для организаций с менее развитым ИТ-направлением или менее опытным ИТ-персоналом.
- Standard не ограничивает пользователей, но в отличие от Foundation и Essentials вам придется отдельно приобретать клиентские лицензии (CAL) в зависимости от того, сколько людей вам нужно поддерживать. Standard поддерживает максимум 4 ТБ RAM, а каждая приобретаемая лицензия распространяется на два процессора. Если вы заинтересованы в виртуализации, этот выпуск позволит вам использовать гипервизор Hyper-V для запуска до двух виртуальных экземпляров операционной системы (дополнительные виртуальные экземпляры Windows Server потребуют дополнительных затрат) на одном физическом оборудовании, что делает редакцию Standard подходящей для легкой виртуализированной среды.
- Datacenter — это самая лучшая и самая дорогая редакция Windows Server. Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter практически идентичен стандартной версии с одним большим исключением. С лицензией Datacenter вы можете запускать неограниченное количество виртуальных экземпляров с Windows Server в качестве гостевой ОС на одном двухпроцессорном компьютере. Эта небольшая разница имеет большое влияние, так как компании могут сэкономить, запустив десятки экземпляров ОС на одном сервере.
Различия между редакциями Windows Server 2016 и 2019
- Hyper-V — это бесплатная редакция Windows Server, предназначенная только для запуска роли гипервизора Hyper-V. Его цель — быть гипервизором для вашей виртуальной среды. У него нет графического интерфейса. По сути, это урезанная версия Server Core. Вы будете использовать sconfig.cmd, чтобы включить гипервизор, а затем управлять средой с помощью диспетчера Hyper-V (как часть RSAT) с рабочей станции Windows 10 в вашей сети. Рекомендуется использовать именно эту редакцию для вашего гипервизора, чтобы сохранить чистоту и простоту лицензирования.
- Essentials — идеально подходит как для малого и среднего бизнеса, так и для людей с потребностями в базовых функциях сервера. Графический интерфейс в значительной степени такой же, как и в Standard, за исключением мастера настройки Essentials.
Права на виртуализацию
Вам разрешено запускать один физический экземпляр Essentials в качестве хоста Hyper-V, на котором размещен один виртуальный экземпляр Essentials. Вам нужно удалить все роли, кроме роли Hyper-V, из физического экземпляра Essentials для обеспечения соответствия. Essentials также подходит для одного виртуального экземпляра на любом другом гипервизоре.
Модель лицензирования
На базе процессора. Клиентские лицензии не требуются, но вы ограничены 25 пользователями и 50 устройствами, подключающимися к серверу.
Аппаратные ограничения
Essentials ограничен до 64 ГБ RAM и 2 CPU на компьютере, на котором он установлен.
- Standard — идеально подходит для любой компании или для лиц, которым требуются расширенные функции, но при этом они не будут интенсивно виртуализироваться.
Права на виртуализацию
Разрешено запускать до двух виртуальных машин или контейнеров Hyper-V или один физический экземпляр со стандартной лицензией. Если вы используете роль Hyper-V только на физическом экземпляре, то можете использовать ее в качестве хоста Hyper-V, а затем разместить на этом хосте две виртуальные машины Hyper-V. Если вы хотите использовать несколько ролей на физическом экземпляре, вы не можете запускать виртуальную машину поверх с одной и той же лицензией.
Модель лицензирования
Основанная на ядре. Клиентские лицензии необходимы для каждого пользователя или устройства, которые подключаются косвенно или напрямую к серверу. Например, если вы используете сервер в качестве файлового сервера, вам потребуется лицензия CAL для каждой учетной записи пользователя или компьютера, которые обращаются к этому файловому серверу в сети.
Аппаратные ограничения
Стандарт ограничен максимум 24 ТБ оперативной памяти и 512 ядрами.
- Datacenter — идеально подходит для любой компании с высокой степенью виртуализации. Вы приобретаете лицензию в зависимости от того, сколько ядер есть у ваших хостов, на которых может жить любая виртуальная машина с версией Datacenter (запускаться или потенциально запускаться после Vmotion). Это лицензирование, на первый взгляд, кажется дорогим, но оно позволяет создавать неограниченное количество виртуальных машин, работающих под управлением Datacenter на хостах, которые вы учитывали. Если у вас небольшое количество хостов (а впоследствии и ядер) и большое количество потенциальных виртуальных машин, тогда эта лицензия не представляет никакой сложности.
Права на виртуализацию
Неограниченное количество виртуальных машин или контейнеров Hyper-V. Как было озвучено выше, вы будете покупать лицензии в зависимости от того, сколько ядер у вас на хостах. На этом этапе вы можете запустить на хостах столько угодно виртуальных машин, используя любые роли.
Модель лицензирования
Основанная на ядрах. Убедитесь, что вы случайно не выбрали этот выпуск при установке на физический сервер, на котором не размещаются виртуальные машины. Клиентские лицензии необходимы для каждого пользователя или устройства, которые подключаются косвенно или напрямую к серверам в вашей среде.
Различия в лицензировании Windows Server 2016 и новее
Хотя цены на Windows Server 2012 R2, 2016, 2019 одинаковы, если вы используете стандартную лицензию или лицензию Datacenter на Windows Server 2016 или новее, есть некоторые ключевые изменения, о которых вам необходимо знать. Прежде всего, в то время как лицензии Windows Server исторически продавались для каждого процессора / сокета, в Windows Server 2016 модель лицензирования переключалась на каждое ядро.
Таким образом, если у вас есть сервер, содержащий 2 процессора с 24 ядрами , в Windows Server 2012 вам нужно будет купить только одну лицензию Standard или Datacenter. В Windows Server 2016 вам придется покупать лицензии на все 24 ядра. Это становится довольно сложно, так как есть много правил, но главное — если у вас есть 16-ядерный сервер, затраты будут примерно такими же. Однако лицензирование ОС может быть более дорогим на серверах с более высокой плотностью ядра.
Несмотря на изменение лицензии на ядро, правила виртуализации остаются такими же в Windows Server 2016 и новее. После того, как вы лицензировали все свои ядра на сервере, со стандартной версией вы получаете 2 лицензии гостевой ОС Windows Server по сравнению с неограниченным количеством в версии Datacenter.
Кроме того, набор функций в Windows Server 2012 Standard и Datacenter был одинаковым. Но некоторые функции Windows Server 2016, например, такие, как Storage Spaces Direct или экранированные виртуальные машины, доступны только в выпуске Datacenter.
Сравнение параметров установки Windows Server 2016 и 2019
В редакциях Standard и Datacenter можно выбрать различные варианты установки. Эти варианты влияют на то, какие функции будут доступны после установки, такие как наличие графического интерфейса пользователя и набор сервисов. Присутствуют следующие варианты установки:
- Desktop Experience (с графическим интерфейсом);
- Core;
- Nano.
Desktop Experience — это вариант установки, с которым знакомо большинство людей. Этот параметр устанавливает большинство функций и ролей из коробки, включая интерфейс графического интерфейса рабочего стола. Вы получите Диспетчер серверов, который позволяет добавлять и удалять роли и компоненты. Преимущество в том, что система может быть проще в управлении для людей, привыкших использовать графический интерфейс. Недостаток в том, что у вас появляется больше обновлений, перезагрузок и открытых портов с которыми предстоит иметь дело.
Узнайте больше от Microsoft здесь.
В Server Core отсутствует графический интерфейс и несколько ролей, которые устанавливаются по умолчанию под опцией Desktop Experience. Серверное ядро имеет меньший объем занимаемого дискового пространства и, следовательно, меньшую область атаки из-за меньшей кодовой базы. Здесь также меньше обновлений, перезагрузок и открытых портов для работы. Это отличный вариант для серверов инфраструктуры, таких как контроллеры домена Active Directory и DNS-серверы.
В этой редакции отсутствуют инструменты специальных возможностей, встроенные инструменты настройки сервера и поддержка звука. Эта версия без излишеств. Не лишним будет убедиться, что вы знакомы с администрированием на основе командной строки.
Подробнее об этом можно прочитать на сайте Microsoft.
Nano
Начиная с Windows Server 2019, Nano доступен только как контейнеризированный образ операционной системы. Он предназначен для запуска в качестве контейнера внутри хоста контейнеров, такого как Server Core, упомянутого выше. Если вы опираетесь на контейнерные приложения, предназначенные для серверных ОС, то эту версию вы будете использовать для компиляции этих приложений.
Nano можно развернуть с помощью версий Standard или Datacenter, но у вас должна быть прикреплена Software Assurance к лицензированию хост-сервера. Узнать об этом подробнее можно на сайте Microsoft.
Windows Server 2019 Standard, Datacenter, Essentials & Hyper-V Server: Features, Editions, Options and Versions Explained + Comparison
Real Network Labs
Oct 9, 2018 · 19 min read
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 family has just been announced, and despite general availability, finding clear information regarding the variety of editions, options and versions may be quite puzzling. Perhaps more challenging than ever before. We thought now is a great time to do exactly that: provide straight forward information regarding Windows Server 2019 as well as compare it with previous versions: Windows Server 2016, 2012 R2 and even 2008 R2.
It may not be clear: which editions or versions of Windows Server 2019 are there? How do they differ from one another? for example, how does Hyper-V Server 2019 (a free product) differ in virtualization from Windows Server 2019 Datacenter with Hyper-V role? Are they using the exact same hypervisor? And does Windows Server 2019 Essentials (RIP?) provide hypervisor at all?
As we look for answers, more and more q u estions may arise: Can I install the newly introduced Windows Server Features On Demand on the Windows Server 2019 with the Desktop Experience (GUI)? (no); Can Windows Server 2019 Server Core be converted to Desktop Experience and vice versa? (no); Can Windows Server 2019 Datacenter be converted to Standard and vice versa? (yes); Can I activate an evaluation version at the end of the 180-day evaluation (or perhaps extend it)? (yes); Can I use Windows Admin Center on Opera browser or on Windows 7, to remotely manage a Windows Server 2019 Server Core or other servers? (yes); Oh, and what about Windows Storage Server 2019 Workgroup? (no such a thing).
Finding answers to some questions lead to more questions being asked. All of which ended with conducting this little research of ours. Now we can confirm: it’s not always trivial to understand which products are out there, how do they differ from one another, what are their prerequisites, which product is right for me, and what is it capable of? Why would I, or should I, upgrade to Windows Server 2019 (either Datacenter or Standard or Essentials or Hyper-V)? Or perhaps I’d better stick to the good old versions I currently hold onto, e.g. Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2012 R2 or even 2008 R2?
Oh, one last thing, just before we jump in: If you are interested in downloading Windows Server 2019 Datacenter (other editions of the Server product family), for 180-day evaluation period for free, please feel free to refer to our blog from last week, where direct links to Windows Server 2019 product family are provided, via Microsoft Evaluation Center.
What’s New in Windows Server 2019?
Microsoft focuses its marketing efforts (regarding Server 2019 product family) on promoting innovation and new capabilities in 4 categories: Hybrid capabilities with Azure, HCI (Hyper-converged Infrastructure), Security, and “faster innovation for application”. Though we get more accustomed to marginal Windows Updates, Windows 2019 does bring more than just a service pack. For instance, in security we can find Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) which previously was (and still is) an independent product. ATP can be downloaded for free for 90-days evaluation here (direct download link here). ATP was initially developed by an Israeli startup company named Aorato, which was acquired by Microsoft in 2014. An in-depth comparison between version 2019 and older Windows versions is available down below: “ Windows Server Feature Comparison 2008 R2–2019”
Windows Server 2019 Datacenter and Standard
Windows Server 2019 Server Core vs Desktop Experience (GUI)
- In similar with past versions of Windows Server, also in version 2019 either Standard or Datacenter editions come with two installation options (each): To be installed in the form of Server Core or Desktop Experience (GUI).
- This is not to say that a Server Core should be transformed into a Desktop Experience. But yes, it can be used to manage Hyper-V machines; Of file management could become easier with WinRar or Explorer++. Server Core can be stretched a little, in order to find a better middle, somewhere between Powershell and a complete “Desktop Experience” server installation.
- The same applies to Hyper-V Server 2019 (a free product) just as well. It might be even more meaningful in the case of Hyper-V Server, due to the fact that such a setting allows to manage VMs from within the Hyper-V Server, rather than being dependent on another Windows license and machine. Thus, reducing complexity and costs. More about Hyper-V Server below.
- Regardless of its GUI capabilities and in similar with other servers, Server Core is designed to be managed remotely either via PowerShell or via proprietary remote management tools such as Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT), Server Manager, MMC snap-in, Remote Desktop Services and last but not least: Windows Admin Center (WAC).
- Advantages of the Server Core version include a smaller footprint (lower consumption of CPU, RAM and disk space), less vulnerabilities and more resistency to cyber attack as it contains a smaller attack surface, less updates and patches (less to update and patch) and less restarts.
- Of course, with every installed application, we also loose some of those advantages. Though many applications today are available as Portable apps, meaning they do not change the system settings, and therefore take less of a toll on the system, causing less of a performance impact as well as reduce the risk for vulnerability. This is not the case in 100% of the incidents but given as a rule of thumb.
Server with Desktop Experience is the classic and well known form of Windows Server, which has been with us (and evolving throughout time) since the iconic Windows NT. Desktop Experience obviously contains a GUI, making it easier to manage. The GUI of Windows Server 2019 is similar to Windows 10 version 1809, though default configuration settings of Windows Server, tend to be more security conscientious, in contrast with Windows 10.
Transforming Datacenter into Standard Edition and Vice Versa
Windows Server 2019 Standard and Datacenter are basically the same product, differentiating from one another in features only due to licensing. Thus, Datacenter and Standard editions can be converted to one another, post installation. This can be done upon activation by entering an activation key which then determines and as needed converts Windows to the corresponding edition. In short: Windows Server 2019 Datacenter could be activated to Standard and vice versa. How this is done exactly, and what would happen to the Datacenter features if converted to Standard — we are unsure about. Perhaps someone could relate to it in the comments below? or perhaps that might deserve a blog of its own?
Converting Evaluation to Retail for Activation Purposes
In order to activate an evaluation version of Windows Server, it needs to be converted to “retail” first. Then it can be activated. So yes, this is possible, just required an extra step. More information about converting Windows evaluation versions to retail is available here.
Microsoft Hyper-V Server is the step sibling of the Windows Server family as it’s not even called Windows (!). It is designed to only fulfill one goal: hypervising virtual machines, i.e. being the host and run VMs. Despite that, Hyper-V Server could perform other functions such as running file services or IIS. With that said, just the fact that this is technically possible does not mean it’s eligible, as the license may not permit it. Notice that despite being a free product, Hyper-V Server license agreement must be agreed during setup. Possibly this is just as binding and committing as with paid editions.
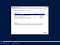
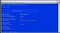
Setting up Hyper-V Server is plain and simple. Activation Key is not required, and there are less choices to make, as Hyper-V Server gives no options for GUI. It is rather installed by default as a Server Core, which cannot be later changed. Consequentially, after Hyper-V Server 2019 is installed, there is no nice GUI to work with. Rather, you are encouraged to manage your VMs remotely (or locally via command prompt/ powershell). As Hyper-V boots, it automatically loads the blue sconfig shell (sconfig.cmd), as shown below. This allows to initialize the machine via basic configuration.
Hyper-V Server is a dedicated server with stripped-down functionality. As such, it consumes the least amount of resources and is the least vulnerable to attacks. Most of the Windows features are left behind and most of the resources are left for the user. Consequentially, there are many opinions over the net, suggesting that this could and ideal enterprise-level solution. Especially as Hyper-V comes with the same hypervisor technology of the Windows Server family (i.e. same as in Windows Server 2019 Datacenter). However, this is not perfectly accurate in our opinion.
Microsoft hypervisor has not changed much since Windows 2016, though many storage-related features have been introduced for Datacenter edition only. For example: Hyper-V Server does not include software defined networking or software defined storage. Consequentially it’s lacking deduplication, remote direct memory access, storage spaces direct and more. All of which are supported by Window Server 2019 Datacenter with Hyper-V role installed. To sum it up, Hyper-V Server shall only substitute Windows Server in limited environments, where such advanced features are not required.
Hyper-V Server does allow to familiarize with, and operate in the world of virtualization. Generally speaking, Hyper-V competes with VMWare vSphere ESXi 6.7 which is a market leader and also a free hypervisor. ESXi also comes with a well-designed web-based VM management console / dashboard / GUI. In many ways, ESXi is more capable than Hyper-V Server. But at the same time, ESXi is more complex to manage and thus consumes more overhead, as it is Linux based.
Since Hyper-V Server does not provide any type of licensing for Windows products, then it may ideally be used for running already licensed Windows-based machines. Such machines can be transferred from physical to virtual, aka P2V or from other hypervisors. Hyper-V Server may also be used for running Linux or VDI workloads. However, if you are a Linux person, then perhaps ESXi should be your preferred cup of tea?
Just before we finish the discussion regarding Hyper-V Server: as need please check out “ Windows Server 2019 Server Core vs Desktop Experience (GUI)” up above. There we opportunity of using either native (integrated) GUI-based apps with Server Core, or even “transforming” it into a capable GUI-Based workstation, which can even manage VMs (via GUI-Based apps).
Windows Server Feature Comparison 2008 R2–2019
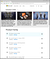
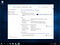
Microsoft has just released an 11-pager feature comparison between Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. Though Microsoft ignores Windows Server 2019 in their comparatively condensed comparison over their web page here, the downloadable feature comparison in PDF format is comprehensive and includes Windows server 2019 just as well. Below is a screenshot of the web-based comparison, followed by a download link to the .PDF comparison.
The 11 pager .PDF (direct download link here) compares features of Windows Server versions 2008 R2 through 2019, in multiple areas: Hybrid capabilities with Azure, HCI (Hyper-converged Infrastructure), Security and “faster innovation for application”. All of which are the areas that Microsoft currently promotes, and where the highest level of innovation is introduced, compared with previous versions.
Bonus: Windows Storage Server 2016 Standard vs. Workgroup
Whereas Windows Server 2019 Essentials just been resurrected, Windows Storage Server edition has not been that lucky. Windows Storage Server has not been released with Windows Server 2019 product family. Instead, Datacenter took over. Actually this took place a long time ago, back in version 2012. Datacenter edition contains storage features such as Software Defined Storage (SDS) (e.g. deduplication, memory access), Storage Spaces/Direct (S2D) and Storage Replica (which is available in Standard edition in a constrained manner).
Windows Storage Server 2016 seems to be the last of its breed.It was offered in two editions: Standard and Workgroup. More information about Windows Storage Server 2016 is available in the following blog by Microsoft: Announcing Windows Storage Server 2016. The link also contains feature comparison between Windows Storage Server 2016 Standard and the more limited edition Workgroup, as demonstrated in the comparison below:
Windows Multipoint Server is another server that’s not been with us for a while; and Windows Server 2016 was offered in additional editions, such as limited to specific segments (education). There are additional types of versions and licensing options (e.g. Windows Server 1809), which are not part of the Server 2019 product family.
We overviewed and discussed the differences and uniqueness of the main editions and options of the Windows Server 2019 product family: Standard vs. Datacenter, Server Core vs. Server with Desktop Experience (GUI), Essentials (RIP?), and Hyper-V Server vs. Server with Hyper-V role. We referred to an In-depth feature comparisons between different editions of the same version, as well as to comparisons between different versions of the Windows Server family (2008 R2 — 2019).
We even briefly touched Windows Storage Server 2016 Workgroup and Standard, though we’ve just excluded from this blog a comprehensive hands-on review of Windows Admin Center 1809, which would be published this coming week in a separate blog post. We intended to give WAC a paragraph here, though as WAC is a more complex than it seems at first sight (and far from being a stable, consistent and mature product), we ended spending long hours on it, leading to a full scale hands-on review with its own dedicated blog post.
If you feel it’s now time to download an evaluation version of let’s say Windows Server 2019 Datacenter or Essentials, or perhaps the unlimited free version of Hyper-V Server 2019, then feel free to refer to our blog post from earlier this week, which also contains direct download links for Windows Server 2019 product family, provided by Microsoft Evaluation Center.
- Page 10: Long-Term Servicing Channel (Windows Server 2019) vs. Semi-Annual Channel (not discussed in this article)
- Page 29: Application Compatibility: Server Core vs Server with Desktop Experience
- Page 34: Windows Server 2019 Stadnard vs Datacenter
Windows Server 2019 — Feature Comparison Summary: This 11 pager PDF compares between Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019