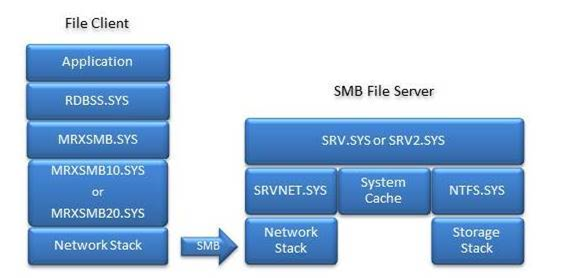
Advanced Troubleshooting Server Message Block (SMB)
Server Message Block (SMB) is a network transport protocol for file systems operations to enable a client to access resources on a server. The primary purpose of the SMB protocol is to enable remote file system access between two systems over TCP/IP.
SMB troubleshooting can be extremely complex. This article is not an exhaustive troubleshooting guide Instead, it is a short primer to understand the basics of how to effectively troubleshoot SMB.
Tools and data collection
One key aspect of quality SMB troubleshooting is communicating the correct terminology. Therefore, this article introduces basic SMB terminology to ensure accuracy of data collection and analysis.
The SMB Server (SRV) refers to the system that is hosting the file system, also known as the file server. The SMB Client (CLI) refers to the system that is trying to access the file system, regardless of the OS version or edition.
For example, if you use Windows Server 2016 to reach an SMB share that is hosted on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 is the SMB Client and Windows 10 the SMB Server.
Collect data
Before you troubleshoot SMB issues, we recommend that you first collect a network trace on both the client and server sides. The following guidelines apply:
On Windows systems, you can use netshell (netsh), Network Monitor, Message Analyser, or Wireshark to collect a network trace.
Third-party devices generally have an in-box packet capture tool, such as tcpdump (Linux/FreeBSD/Unix), or pktt (NetApp). For example, if the SMB client or SMB server is a Unix host, you can collect data by running the following command:
Stop collecting data by using Ctrl+C from keyboard.
To discover the source of the issue, you can check the two-sided traces: CLI, SRV, or somewhere in between.
Using netshell to collect data
This section provides the steps for using netshell to collect network trace.
A Netsh trace creates an ETL file. ETL files can be opened only in Message Analyzer (MA) and Network Monitor 3.4 (set the parser to Network Monitor Parsers > Windows).
On both the SMB server and SMB client, create a Temp folder on drive C. Then, run the following command:
If you are using PowerShell, run the following cmdlets:
Reproduce the issue.
Stop the trace by running the following command:
If you are using PowerShell, run the following cmdlets:
You should trace only a minimum amount of the data that’s transferred. For performance issues, always take both a good and bad trace, if the situation allows it.
Analyze the traffic
SMB is an application-level protocol that uses TCP/IP as the network transport protocol. Therefore, an SMB issue can also be caused by TCP/IP issues.
Check whether TCP/IP experiences any of these issues:
The TCP three-way handshake does not finish. This typically indicates that there is a firewall block, or that the Server service is not running.
Retransmits are occurring. These can cause slow file transfers because of compound TCP congestion throttling.
Five retransmits followed by a TCP reset could mean that the connection between systems was lost, or that one of the SMB services crashed or stopped responding.
The TCP receive window is diminishing. This can be caused by slow storage or some other issue that prevents data from being retrieved from the Ancillary Function Driver (AFD) Winsock buffer.
If there is no noticeable TCP/IP issue, look for SMB errors. To do this, follow these steps:
Always check SMB errors against the MS-SMB2 protocol specification. Many SMB errors are benign (not harmful). Refer to the following information to determine why SMB returned the error before you conclude that the error is related to any of the following issues:
The MS-SMB2 Message Syntax topic details each SMB command and its options.
The MS-SMB2 Client Processing topic details how the SMB client creates requests and responds to server messages.
The MS-SMB2 Server Processing topic details how the SMB server creates requests and responds to client requests.
Check whether a TCP reset command is sent immediately after an FSCTL_VALIDATE_NEGOTIATE_INFO (validate negotiate) command. If so, refer to the following information:
The SMB session must be terminated (TCP reset) when the Validate Negotiate process fails on either the client or the server.
This process might fail because a WAN optimizer is modifying the SMB Negotiate packet.
If the connection ended prematurely, identify the last exchange communication between the client and server.
Analyze the protocol
Look at the actual SMB protocol details in the network trace to understand the exact commands and options that are used.
Only Message Analyzer can parse SMBv3 and later version commands.
Remember that SMB does only what it is told to do.
You can learn a lot about what the application is trying to do by examining the SMB commands.
Compare the commands and operations to the protocol specification to make sure that everything is operating correctly. If it is not, collect data that is closer to or at a lower level to look for more information about the root cause. To do this, follow these steps:
Collect a standard packet capture.
Run the netsh command to trace and gather details about whether there are issues in the network stack or drops in Windows Filtering Platform (WFP) applications, such as firewall or antivirus program.
If all other options fail, collect a t.cmd if you suspect that the issue occurs within SMB itself, or if none of the other data is sufficient to identify a root cause.
You experience slow file transfers to a single file server.
The two-sided traces show that the SRV responds slowly to a READ request.
Removing an antivirus program resolves the slow file transfers.
You contact the antivirus program manufactory to resolve the issue.
Optionally, you might also temporarily uninstall the antivirus program during troubleshooting.
Event logs
Both SMB Client and SMB Server have a detailed event log structure, as shown in the following screenshot. Collect the event logs to help find the root cause of the issue.
SMB-related system files
This section lists the SMB-related system files. To keep the system files updated, make sure that the latest update rollup is installed.
SMB Client binaries that are listed under %windir%\system32\Drivers:
SMB Server binaries that are listed under %windir%\system32\Drivers:
Under %windir%\system32
Update suggestions
We recommend that you update the following components before you troubleshoot SMB issues:
A file server requires file storage. If your storage has iSCSI component, update those components.
Update the network components.
For better performance and stability, update Windows Core.
Логирование операций с файлами в Samba
Ранее я неоднократно рассказывал, как настроить файловый сервер samba для совместной работы с файлами. При совместной работе часто бывает нужно знать, кто и когда что-то сделал с тем или иным файлом, а конкретно, кто удалил файл. По-умолчанию, такой лог не ведется, нужно настраивать отдельно. Займемся настройкой логирования операций с файлами в данной статье.
Введение
У меня есть две статьи по настройке файлового сервера samba:
В обоих случаях будет не лишним настроить логирование всех обращений к файлам на сервере. Делается это штатными возможностями самой самбы. Она будет отправлять логи в syslog, а в нем мы уже настроим их хранение и ротацию с помощью logrotate. На нагруженных серверах логи будут очень объемными. Нужно обязательно позаботиться об их хранении и удалении.
Я буду настраивать логи в samba на сервере CentOS 7. В других случаях отличий почти не будет. Сами настройки самбы везде одинаковые. Syslog и Logrotate тоже примерно одинаковые во всех дистрибутивах Linux.
Включаем логирование операций в samba
Для логирования действий пользователей на файловом сервере будем использовать модуль самбы full_audit. Если вы хотите выполнять логирование операций с файлами в один лог файл по всем доступным шарам, то добавляйте настройки аудита в глобальную секцию. Если же захотите разделить по шарам, то отдельно в каждую шару с небольшими изменениями. Я рассмотрю оба варианта. Для начала, настроим аудит по всем шарам в один общий файл. Добавляем в /etc/samba/smb.conf в секцию [global] следующие строки:
Поясню каждый параметр.
| full_audit:prefix | В каком формате будет выводиться информация о подключении: %u — имя пользователя, %I — его ip адрес, %S — название шары. |
| full_audit:success | Какие удачные события будут логироваться. В приведенном примере по смыслу и так понятно, о чем речь. Полный список событий такой: chdir, chflags, chmod, chmod_acl, chown, close, closedir, connect, disconnect, disk_free, fchmod, fchmod_acl, fchown, fget_nt_acl, fgetxattr, flistxattr, fremovexattr, fset_nt_acl, fsetxattr, fstat, fsync, ftruncate, get_nt_acl, get_quota, get_shadow_copy_data, getlock, getwd, getxattr, kernel_flock, link, linux_setlease, listxattr, lock, lseek, lstat, mkdir, mknod, open, opendir, pread, pwrite, read, readdir, readlink, realpath, removexattr, rename, rewinddir, rmdir, seekdir, sendfile, set_nt_acl, set_quota, setxattr, stat, statvfs, symlink, sys_acl_delete_def_file, sys_acl_get_fd, sys_acl_get_file, sys_acl_set_fd, sys_acl_set_file, telldir, unlink, utime, write. |
| full_audit:failure | То же самое, что выше, только для ошибок. |
| full_audit:facility | Категория событий syslog, в которую будут попадать записи. |
| full_audit:priority | Приоритет записей для syslog. Для самбы будет достаточно приоритета notice, чем ее записи по сути и являются. |
Если вы хотите настроить вывод лога доступа с разных шар в отдельные файлы, то указанные выше параметры поместите не в глобальную, а отдельно в каждую секцию с шарой, изменив категории событий, сделав их в каждой шаре уникальными, например local5 и local6. Так же нужно будет в каждую шару отдельно добавить еще один параметр:
После изменения конфигурации, не забудьте перезапустить самбу. Если больше ничего не делать, то логи посещений самбы польются в стандартный поток вывода для системных логов. В Centos в /var/log/messages. Это очень неудобно, поэтому далее настроим вывод логов в отдельный файл.
Вывод лога доступа к файлам samba в отдельный файл
Нам нужно отредактировать файл конфигурации rsyslog для направления вывода лога самбы в отдельный файл. В CentOS 7 открываем файл /etc/rsyslog.conf и добавляем в самый конец такую строку:
Этим параметром мы направили вывод логов аудита посещений в отдельный файл audit.log. Если все оставить как есть, то информация о посещениях будет писаться как в отдельный файл, так и в общий системный. Чтобы в общий не писалось, редактируем еще одну строку, добавляя туда выделенный фрагмент:
Сохраняем файл и перезапускаем rsyslog.
Теперь все нормально. Все логи посещений шары на samba будут складываться в отдельный файл и только туда. Если у вас есть желание хранить логи на удаленном сервере, то воспользуйтесь моей статье на эту тему — настройка syslog-ng для удаленного сбора логов. Это сделать быстро и просто. Зачастую это может быть оправданно и удобно, особенно с точки зрения безопасности и не только логов от самбы.
Осталось малось — настроить ротацию логов. Сделать это надо обязательно, так как файл аудита будет расти очень быстро. Здесь ничего особенного, используем logrotate. Скорее всего у вас уже есть фал конфигурации logrotate для самбы. Он создается в момент установки. Отредактируем его, добавив новые параметры.
Я храню логи за последние 90 дней, ротацию делаю раз в день и складываю старые логи в отдельную папку. Если у вас в конфигурации есть параметр с маской, который захватывает сразу все файлы в директории /var/log/samba, например вот так:
То либо вынесите лог-файл с аудитом в отдельную директорию, либо измените маску.
Заключение
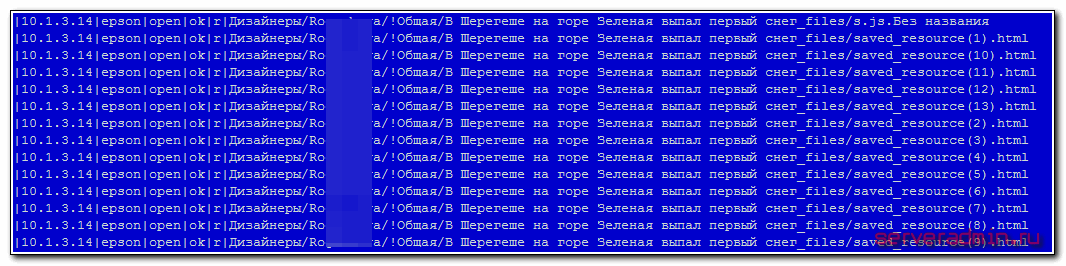
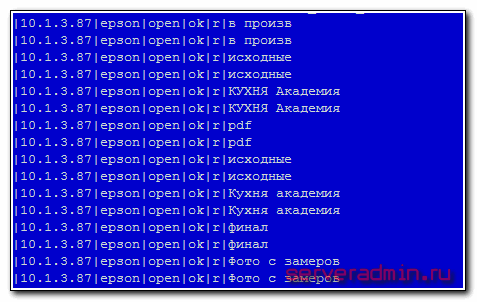
Я уже давно заметил один неприятный баг в самбе 4-й версии. Привожу пример того, как выглядит лог посещений файловой шары самбы с русскими названиями в именах на 3 и 4-й версии. В данном случае сначала версия 3.6.3, потом 4.6.2
В первом случае отображаются полные корректные пути. Во втором случае на события типа open идут только обрывки названий директорий, по которым не понятен полный путь. Делаю важный акцент — только на события open. Если идут события создания, удаления, изменения, то пути уже корректны, даже если они русские. В принципе, события на доступ лично для меня обычно не важны. Интерес представляет только создание, изменение и особенно удаление файлов. С этим все в порядке. Аудит показывает корректный лог удаления файлов. Но все равно не приятно смотреть на неинформативный лог.
Возможно, дело не в 3-1 и 4-й версии. Я не проверял различные изменения в рамках одной и той же ветки. Просто посмотрел на имеющиеся у меня сервера. Там где 3-я версия все в порядке, там где 4-я везде такой бардак в логах. Если кто-то знает, как от него избавиться, прошу поделиться.
Как обнаруживать, включать и отключать SMBv1, SMB и SMBv3 в Windows How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows
Сводка Summary
В этой статье описывается, как включить и отключить протокол SMB версии 1 (SMBv1), SMB версии 2 (SMB) и SMB версии 3 (SMBv3) на клиентских и серверных компонентах SMB. This article describes how to enable and disable Server Message Block (SMB) version 1 (SMBv1), SMB version 2 (SMBv2), and SMB version 3 (SMBv3) on the SMB client and server components.
Рекомендуется не отключать протоколы SMB или SMBv3. We recommend that you do not disable SMBv2 or SMBv3. Отключите SMB 2.0 или SMBv3 только как временную меру устранения неполадок. Disable SMBv2 or SMBv3 only as a temporary troubleshooting measure. Не оставляйте протоколы SMB или SMBv3 отключенными. Do not leave SMBv2 or SMBv3 disabled.
В Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2 отключение SMB отключает следующие функциональные возможности. In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, disabling SMBv2 deactivates the following functionality:
- Составной запрос — позволяет отправлять несколько запросов SMB 2 в виде одного сетевого запроса. Request compounding — allows for sending multiple SMB 2 requests as a single network request
- Большие операции чтения и записи — лучшее использование более быстрых сетей. Larger reads and writes — better use of faster networks
- Кэширование свойств папок и файлов — клиенты сохраняют локальные копии папок и файлов Caching of folder and file properties — clients keep local copies of folders and files
- Устойчивые дескрипторы. разрешение на прозрачное повторное подключение к серверу при наличии временного отключения Durable handles — allow for connection to transparently reconnect to the server if there is a temporary disconnection
- Улучшенная подпись сообщения — HMAC SHA-256 заменяет MD5 как алгоритм хеширования Improved message signing — HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
- Улучшенная масштабируемость общего доступа к файлам — число пользователей, общих папок и открытых файлов на сервере значительно увеличилось. Improved scalability for file sharing — number of users, shares, and open files per server greatly increased
- Поддержка символьных ссылок Support for symbolic links
- Модель нежесткой аренды клиента — ограничивает данные, передаваемые между клиентом и сервером, повышая производительность в сетях с высокой задержкой и повышая масштабируемость сервера SMB. Client oplock leasing model — limits the data transferred between the client and server, improving performance on high-latency networks and increasing SMB server scalability
- Поддержка большого MTU — для полного использования 10-гигабе (ГБ) Ethernet Large MTU support — for full use of 10-gigabye (GB) Ethernet
- Повышение эффективности энергопотребления — клиенты, которые имеют открытые файлы на сервере, могут перейти в спящий режим Improved energy efficiency — clients that have open files to a server can sleep
В Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019, отключение SMBv3 деактивирует следующие функции (а также функции 2.0, описанные в предыдущем списке): In Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2019, disabling SMBv3 deactivates the following functionality (and also the SMBv2 functionality that’s described in the previous list):
- Прозрачная отработка отказа — клиенты повторно подключаются без прерывания узлов кластера во время обслуживания или отработки отказа Transparent Failover — clients reconnect without interruption to cluster nodes during maintenance or failover
- Scale Out — одновременный доступ к общим данным на всех узлах кластеров файлов Scale Out – concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
- Многоканальное агрегирование пропускной способности сети и отказоустойчивости при наличии нескольких путей между клиентом и сервером Multichannel — aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
- SMB Direct — добавляет поддержку сети RDMA для очень высокой производительности с низкой задержкой и низкой загрузкой ЦП. SMB Direct – adds RDMA networking support for very high performance, with low latency and low CPU utilization
- Шифрование — обеспечивает сквозное шифрование и защищает от перехвата в ненадежных сетях. Encryption – Provides end-to-end encryption and protects from eavesdropping on untrustworthy networks
- Аренда каталога — улучшает время отклика приложений в филиалах за счет кэширования Directory Leasing — Improves application response times in branch offices through caching
- Оптимизация производительности — оптимизация для небольшого случайного чтения и записи ввода-вывода Performance Optimizations — optimizations for small random read/write I/O
Дополнительные сведения More Information
Протокол SMB был впервые появился в Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008. The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
Протокол SMBv3 появился в Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012. The SMBv3 protocol was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
Дополнительные сведения о возможностях протоколов SMB 2.0 и SMBv3 см. в следующих статьях: For more information about the capabilities of SMBv2 and SMBv3 capabilities, see the following articles: