Как подключиться к сетевой папке в Windows (SMB)
На компьютерах, которые должны подключаться к общей сетевой папке, перейдите в «Изменение расширенных параметров общего доступа», для этого нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на значок сетевого соединения и нажмите «Открыть параметры сети и Интернет»:
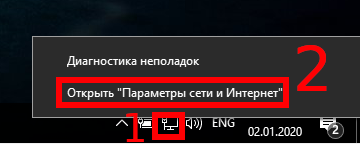
В открывшемся окне нажмите на «Параметры общего доступа»:

На компьютерах, которые должны подключаться к общей сетевой папке, перейдите в «Изменение расширенных параметров общего доступа» и выберите опцию «Включить сетевое обнаружение»:
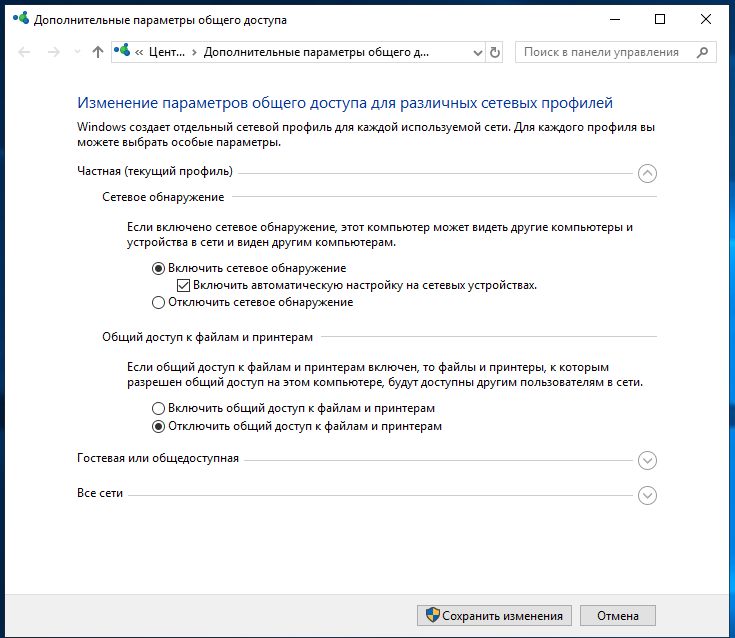
С недавнего времени, после очередного обновления Windows 10 в некоторых случаях перестали открываться сетевые папки. Дело в том, что теперь вход без ввода пароля нужно настраивать не только на компьютерах, где находится сетевая папка, но и на компьютерах, с которых выполняется подключение. Это довольно странное решение объясняется тем, чтобы вы случайно не подключились к папке злоумышленника и не скачали с неё вредоносное ПО. Вам НЕ НУЖНО делать настройку в gpedit.msc если вы подключаетесь к сетевой шаре по паролю. Если же вы настроили вход в общую папку без пароля, то для исправления ситуации нажмите Win+r (Пуск->Выполнить) и запустите:
Далее необходимо перейти по следующему пути «Конфигурация компьютера» → «Административные шаблоны» → «Сеть» → «Рабочая станция Lanmann»:
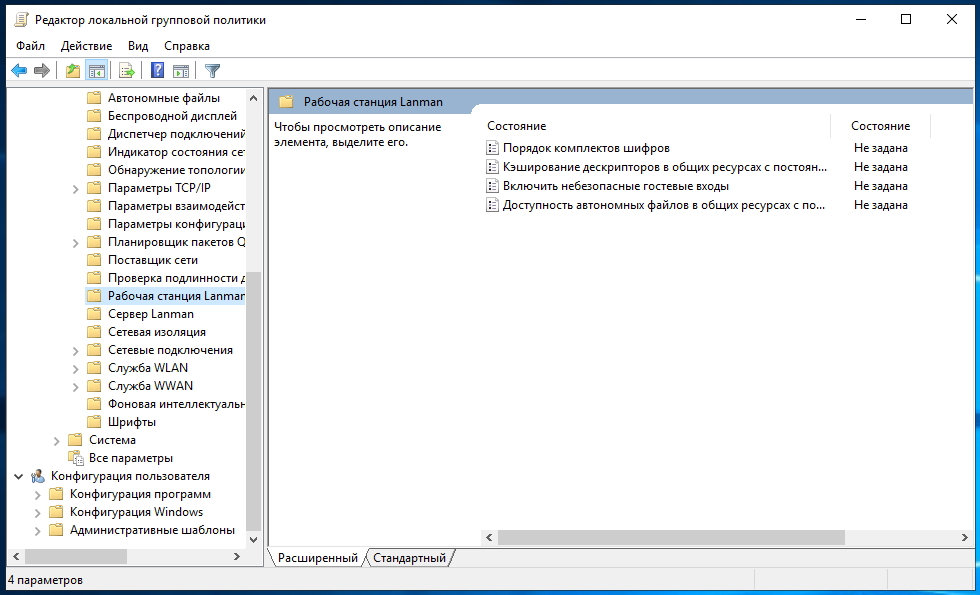
Теперь выставите параметр «Включить небезопасные гостевые входы» в положение «Включено»:

Описание в документации:
Этот параметр политики определяет, разрешит ли клиент SMB небезопасные гостевые входы на сервер SMB.
Если этот параметр политики включён или не настроен, клиент SMB разрешит небезопасные гостевые входы.
Если этот параметр политики отключён, клиент SMB будет отклонять небезопасные гостевые входы.
Небезопасные гостевые входы используются файловыми серверами для разрешения доступа без проверки подлинности к общим папкам. Небезопасные гостевые входы обычно не используются в среде предприятия, однако часто используются потребительскими запоминающими устройствами, подключёнными к сети (NAS), которые выступают в качестве файловых серверов. Для файловых серверов Windows требуется проверка подлинности, и на них по умолчанию не используются небезопасные гостевые входы. Поскольку небезопасные гостевые входы не проходят проверку подлинности, важные функции безопасности, такие как подписывание и шифрование SMB-пакетов отключены. В результате этого клиенты, которые разрешают небезопасные гостевые входы, являются уязвимыми к различным атакам с перехватом, которые могут привести к потере данных, повреждению данных и уязвимости к вредоносным программам. Кроме того, какие-либо данные, записанные на файловый сервер с использованием небезопасного гостевого входа, являются потенциально доступными для любого пользователя в сети. Майкрософт рекомендует отключить небезопасные гостевые входы и настроить файловые серверы на требование доступа с проверкой подлинности.»
Наконец-то, можно подключиться к общей папке (share) в локальной сети. Для этого откройте проводник и перейдите в раздел «Сеть»:

Обратите внимание на глючность этой службы — в левой части проводника мы видим 4 компьютера, а в главном разделе окна — только два.
Если вы не видите нужный компьютер, то попробуйте открыть его по прямой ссылке, например, у меня имя компьютера с сетевой папкой HACKWARE-MIAL, тогда я открываю его по ссылке \\HACKWARE-MIAL.
Примечание для Windows Server: в серверных версиях Windows даже когда разрешено подключаться без пароля, всё равно появляется окно запроса:
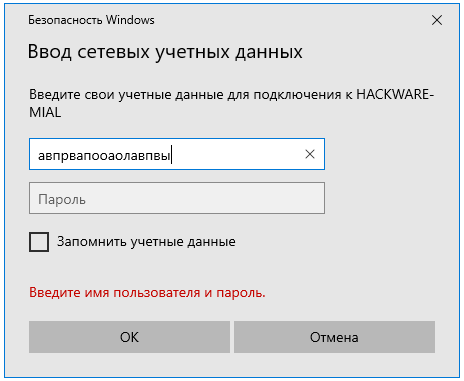
Достаточно ввести произвольные данные и, моём случае, сетевая папка успешно открывалась. При подключении к этой же папке с обычного Windows 10, запрос на ввод пароля не появлялся. Видимо, для сервера настроены какие-то более строгие политики.
При клике на имя компьютера вы увидите доступные сетевые папки. При переходе в папку вы увидите её содержимое:
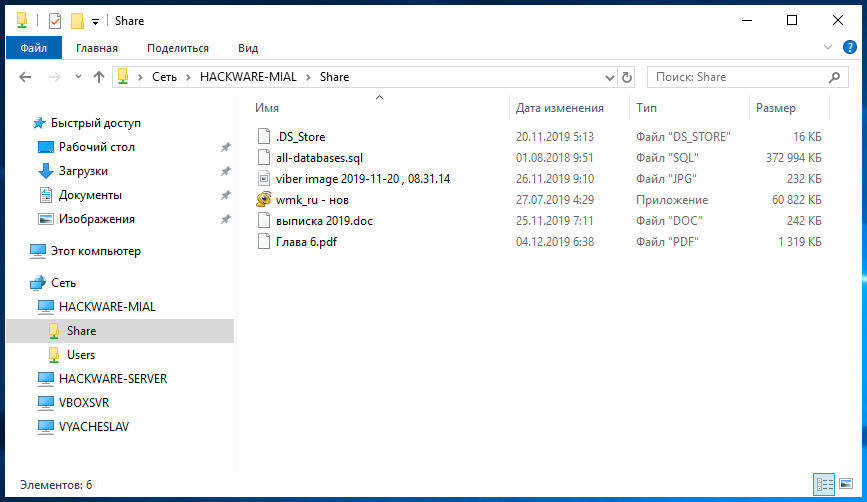
Вы можете открывать файлы по сети, то есть не нужно предварительно копировать их на свой компьютер. Можете копировать файлы из общей папки, добавлять туда новые или удалять существующие — с сетевой папкой можно работать как с обычной локальной папкой.
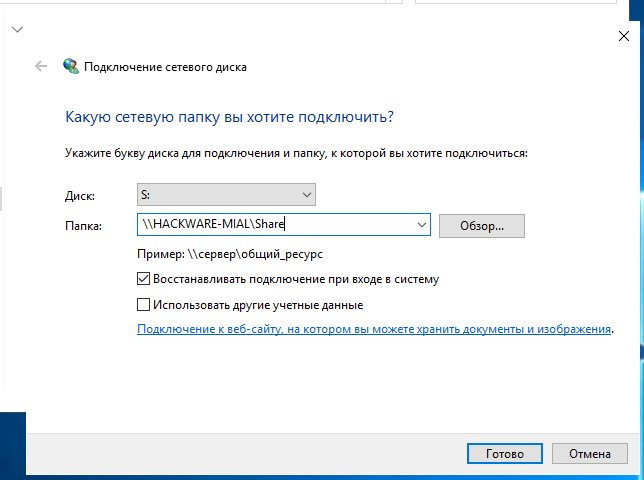
В Windows сетевые папки можно сделать доступными в качестве дисков с буквой. Для этого правой кнопкой мыши кликните по слову «Сеть» и выберите пункт «Подключить сетевой диск»:

Выберите букву для диска, введите путь до папки, поставьте галочку «Восстанавливать подключение при входе в систему»:
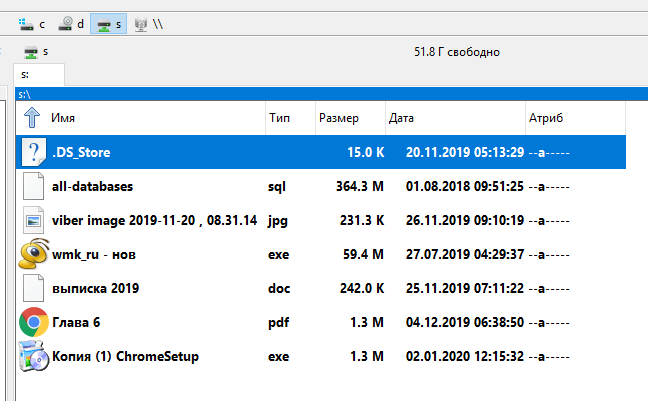
Теперь вы будете видеть сетевую папку как диск в любом файловом менеджере:
Как подключиться с общей папке на Windows, для которой требуется ввод учётных данных
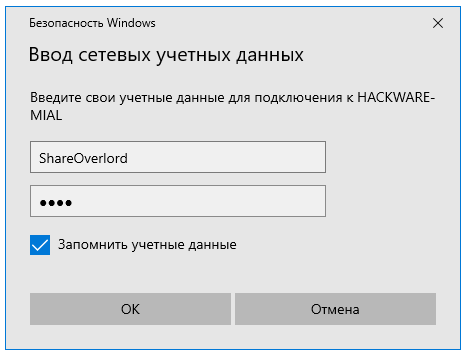
В целом процесс очень схож с подключением к незащищённой папке, но при попытке подключения появится такое окно:
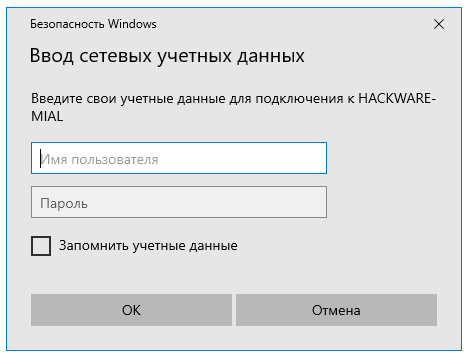
Чуть выше я создал папку, для доступа к которой нужно ввести учётные данные пользователя ShareOverlord, ссылка на эту папку: \\HACKWARE-MIAL\ShareRestricted
В это окно авторизации нужно вводить имя пользователя и пароль того пользователя, который имеет права на доступ к этой папке на УДАЛЁННОМ компьютере, то есть на том компьютере, где находится эта папка с совместным доступом.
Доступ в папку ShareRestricted получен:

Смотрите такжке полное Руководство по SMB и Samba.
Как обнаруживать, включать и отключать SMBv1, SMB и SMBv3 в Windows How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows
Сводка Summary
В этой статье описывается, как включить и отключить протокол SMB версии 1 (SMBv1), SMB версии 2 (SMB) и SMB версии 3 (SMBv3) на клиентских и серверных компонентах SMB. This article describes how to enable and disable Server Message Block (SMB) version 1 (SMBv1), SMB version 2 (SMBv2), and SMB version 3 (SMBv3) on the SMB client and server components.
Рекомендуется не отключать протоколы SMB или SMBv3. We recommend that you do not disable SMBv2 or SMBv3. Отключите SMB 2.0 или SMBv3 только как временную меру устранения неполадок. Disable SMBv2 or SMBv3 only as a temporary troubleshooting measure. Не оставляйте протоколы SMB или SMBv3 отключенными. Do not leave SMBv2 or SMBv3 disabled.
В Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2 отключение SMB отключает следующие функциональные возможности. In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, disabling SMBv2 deactivates the following functionality:
- Составной запрос — позволяет отправлять несколько запросов SMB 2 в виде одного сетевого запроса. Request compounding — allows for sending multiple SMB 2 requests as a single network request
- Большие операции чтения и записи — лучшее использование более быстрых сетей. Larger reads and writes — better use of faster networks
- Кэширование свойств папок и файлов — клиенты сохраняют локальные копии папок и файлов Caching of folder and file properties — clients keep local copies of folders and files
- Устойчивые дескрипторы. разрешение на прозрачное повторное подключение к серверу при наличии временного отключения Durable handles — allow for connection to transparently reconnect to the server if there is a temporary disconnection
- Улучшенная подпись сообщения — HMAC SHA-256 заменяет MD5 как алгоритм хеширования Improved message signing — HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
- Улучшенная масштабируемость общего доступа к файлам — число пользователей, общих папок и открытых файлов на сервере значительно увеличилось. Improved scalability for file sharing — number of users, shares, and open files per server greatly increased
- Поддержка символьных ссылок Support for symbolic links
- Модель нежесткой аренды клиента — ограничивает данные, передаваемые между клиентом и сервером, повышая производительность в сетях с высокой задержкой и повышая масштабируемость сервера SMB. Client oplock leasing model — limits the data transferred between the client and server, improving performance on high-latency networks and increasing SMB server scalability
- Поддержка большого MTU — для полного использования 10-гигабе (ГБ) Ethernet Large MTU support — for full use of 10-gigabye (GB) Ethernet
- Повышение эффективности энергопотребления — клиенты, которые имеют открытые файлы на сервере, могут перейти в спящий режим Improved energy efficiency — clients that have open files to a server can sleep
В Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019, отключение SMBv3 деактивирует следующие функции (а также функции 2.0, описанные в предыдущем списке): In Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2019, disabling SMBv3 deactivates the following functionality (and also the SMBv2 functionality that’s described in the previous list):
- Прозрачная отработка отказа — клиенты повторно подключаются без прерывания узлов кластера во время обслуживания или отработки отказа Transparent Failover — clients reconnect without interruption to cluster nodes during maintenance or failover
- Scale Out — одновременный доступ к общим данным на всех узлах кластеров файлов Scale Out – concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
- Многоканальное агрегирование пропускной способности сети и отказоустойчивости при наличии нескольких путей между клиентом и сервером Multichannel — aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
- SMB Direct — добавляет поддержку сети RDMA для очень высокой производительности с низкой задержкой и низкой загрузкой ЦП. SMB Direct – adds RDMA networking support for very high performance, with low latency and low CPU utilization
- Шифрование — обеспечивает сквозное шифрование и защищает от перехвата в ненадежных сетях. Encryption – Provides end-to-end encryption and protects from eavesdropping on untrustworthy networks
- Аренда каталога — улучшает время отклика приложений в филиалах за счет кэширования Directory Leasing — Improves application response times in branch offices through caching
- Оптимизация производительности — оптимизация для небольшого случайного чтения и записи ввода-вывода Performance Optimizations — optimizations for small random read/write I/O
Дополнительные сведения More Information
Протокол SMB был впервые появился в Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008. The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
Протокол SMBv3 появился в Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012. The SMBv3 protocol was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
Дополнительные сведения о возможностях протоколов SMB 2.0 и SMBv3 см. в следующих статьях: For more information about the capabilities of SMBv2 and SMBv3 capabilities, see the following articles:
Overview of file sharing using the SMB 3 protocol in Windows Server
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This topic describes the SMB 3 feature in Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012—practical uses for the feature, the most significant new or updated functionality in this version compared to previous versions, and the hardware requirements. SMB is also a fabric protocol used by software-defined data center (SDDC) solutions such as Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica, and others. SMB version 3.0 was introduced with Windows Server 2012 and has been incrementally improved in subsequent releases.
Feature description
The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol is a network file sharing protocol that allows applications on a computer to read and write to files and to request services from server programs in a computer network. The SMB protocol can be used on top of its TCP/IP protocol or other network protocols. Using the SMB protocol, an application (or the user of an application) can access files or other resources at a remote server. This allows applications to read, create, and update files on the remote server. SMB can also communicate with any server program that is set up to receive an SMB client request. SMB is a fabric protocol that is used by Software-defined Data Center (SDDC) computing technologies, such as Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica. For more information, see Windows Server software-defined datacenter.
Practical applications
This section discusses some new practical ways to use the new SMB 3.0 protocol.
- File storage for virtualization (Hyper-Vв„ў over SMB). Hyper-V can store virtual machine files, such as configuration, Virtual hard disk (VHD) files, and snapshots, in file shares over the SMB 3.0 protocol. This can be used for both stand-alone file servers and clustered file servers that use Hyper-V together with shared file storage for the cluster.
- Microsoft SQL Server over SMB. SQL Server can store user database files on SMB file shares. Currently, this is supported with SQL Server 2008 R2 for stand-alone SQL servers. Upcoming versions of SQL Server will add support for clustered SQL servers and system databases.
- Traditional storage for end-user data. The SMB 3.0 protocol provides enhancements to the Information Worker (or client) workloads. These enhancements include reducing the application latencies experienced by branch office users when accessing data over wide area networks (WAN) and protecting data from eavesdropping attacks.
New and changed functionality
The following sections describe functionality that was added in SMB 3 and subsequent updates.
Features added in Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10, version 1809
| Feature/functionality | New or updated | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Ability to require write-through to disk on file shares that aren’t continuously available | New | To provide some added assurance that writes to a file share make it all the way through the software and hardware stack to the physical disk prior to the write operation returning as completed, you can enable write-through on the file share using either the NET USE /WRITETHROUGH command or the New-SMBMapping -UseWriteThrough PowerShell cmdlet. There’s some amount of performance hit to using write-through; see the blog post Controlling write-through behaviors in SMB for further discussion. |
Features added in Windows Server, version 1709, and Windows 10, version 1709
| Feature/functionality | New or updated | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Guest access to file shares is disabled | New | The SMB client no longer allows the following actions: Guest account access to a remote server; Fallback to the Guest account after invalid credentials are provided. For details, see Guest access in SMB2 disabled by default in Windows. |
| SMB global mapping | New | Maps a remote SMB share to a drive letter that is accessible to all users on the local host, including containers. This is required to enable container I/O on the data volume to traverse the remote mount point. Be aware that when using SMB global mapping for containers, all users on the container host can access the remote share. Any application running on the container host also have access to the mapped remote share. For details, see Container Storage Support with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV), Storage Spaces Direct, SMB Global Mapping. |
| SMB dialect control | New | You can now set registry values to control the minimum SMB version (dialect) and maximum SMB version used. For details, see Controlling SMB Dialects. |
Features added in SMB 3.11 with Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10, version 1607
| Feature/functionality | New or updated | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| SMB Encryption | Updated | SMB 3.1.1 encryption with Advanced Encryption Standard-Galois/Counter Mode (AES-GCM) is faster than SMB Signing or previous SMB encryption using AES-CCM. |
| Directory Caching | New | SMB 3.1.1 includes enhancements to directory caching. Windows clients can now cache much larger directories, approximately 500K entries. Windows clients will attempt directory queries with 1 MB buffers to reduce round trips and improve performance. |
| Pre-Authentication Integrity | New | In SMB 3.1.1, pre-authentication integrity provides improved protection from a man-in-the-middle attacker tampering with SMB’s connection establishment and authentication messages. For details, see SMB 3.1.1 Pre-authentication integrity in Windows 10. |
| SMB Encryption Improvements | New | SMB 3.1.1 offers a mechanism to negotiate the crypto algorithm per connection, with options for AES-128-CCM and AES-128-GCM. AES-128-GCM is the default for new Windows versions, while older versions will continue to use AES-128-CCM. |
| Rolling cluster upgrade support | New | Enables rolling cluster upgrades by letting SMB appear to support different max versions of SMB for clusters in the process of being upgraded. For more details on letting SMB communicate using different versions (dialects) of the protocol, see the blog post Controlling SMB Dialects. |
| SMB Direct client support in Windows 10 | New | Windows 10 Enterprise, Windows 10 Education, and Windows 10 Pro for Workstations now include SMB Direct client support. |
| Native support for FileNormalizedNameInformation API calls | New | Adds native support for querying the normalized name of a file. For details, see FileNormalizedNameInformation. |
Features added in SMB 3.02 with Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1
| Feature/functionality | New or updated | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic rebalancing of Scale-Out File Server clients | New | Improves scalability and manageability for Scale-Out File Servers. SMB client connections are tracked per file share (instead of per server), and clients are then redirected to the cluster node with the best access to the volume used by the file share. This improves efficiency by reducing redirection traffic between file server nodes. Clients are redirected following an initial connection and when cluster storage is reconfigured. |
| Performance over WAN | Updated | Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 provide improved CopyFile SRV_COPYCHUNK over SMB support when you use File Explorer for remote copies from one location on a remote machine to another copy on the same server. You will copy only a small amount of metadata over the network (1/2KiB per 16MiB of file data is transmitted). This results in a significant performance improvement. This is an OS-level and File Explorer-level distinction for SMB. |
| SMB Direct | Updated | Improves performance for small I/O workloads by increasing efficiency when hosting workloads with small I/Os (such as an online transaction processing (OLTP) database in a virtual machine). These improvements are evident when using higher speed network interfaces, such as 40 Gbps Ethernet and 56 Gbps InfiniBand. |
| SMB bandwidth limits | New | You can now use Set-SmbBandwidthLimit to set bandwidth limits in three categories: VirtualMachine (Hyper-V over SMB traffic), LiveMigration (Hyper-V Live Migration traffic over SMB), or Default (all other types of SMB traffic). |
For more information on new and changed SMB functionality in Windows Server 2012 R2, see What’s New in SMB in Windows Server.
Features added in SMB 3.0 with Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8
| Feature/functionality | New or updated | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| SMB Transparent Failover | New | Enables administrators to perform hardware or software maintenance of nodes in a clustered file server without interrupting server applications storing data on these file shares. Also, if a hardware or software failure occurs on a cluster node, SMB clients transparently reconnect to another cluster node without interrupting server applications that are storing data on these file shares. |
| SMB Scale Out | New | Support for multiple SMB instances on a Scale-Out File Server. Using Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) version 2, administrators can create file shares that provide simultaneous access to data files, with direct I/O, through all nodes in a file server cluster. This provides better utilization of network bandwidth and load balancing of the file server clients, and optimizes performance for server applications. |
| SMB Multichannel | New | Enables aggregation of network bandwidth and network fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between the SMB client and server. This enables server applications to take full advantage of all available network bandwidth and be resilient to a network failure. |
SMB Multichannel in SMB 3 contributes to a substantial increase in performance compared to previous versions of SMB.
SMB Direct in SMB 3 contributes to a substantial increase in performance compared to previous versions of SMB.
In SMB 3, the Windows implementation of SMB has been refined to improve the caching behavior on the client as well as the ability to push higher throughputs.
SMB 3 features improvements to the CopyFile() API, as well as to associated tools such as Robocopy, to push significantly more data over the network.
Hardware requirements
SMB Transparent Failover has the following requirements:
- A failover cluster running Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2016 with at least two nodes configured. The cluster must pass the cluster validation tests included in the validation wizard.
- File shares must be created with the Continuous Availability (CA) property, which is the default.
- File shares must be created on CSV volume paths to attain SMB Scale-Out.
- Client computers must be running WindowsВ® 8 or Windows Server 2012, both of which include the updated SMB client that supports continuous availability.
Down-level clients can connect to file shares that have the CA property, but transparent failover will not be supported for these clients.
SMB Multichannel has the following requirements:
- At least two computers running Windows Server 2012 are required. No extra features need to be installed—the technology is on by default.
- For information on recommended network configurations, see the See Also section at the end of this overview topic.
SMB Direct has the following requirements:
- At least two computers running Windows Server 2012 are required. No extra features need to be installed—the technology is on by default.
- Network adapters with RDMA capability are required. Currently, these adapters are available in three different types: iWARP, Infiniband, or RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet).
More information
The following list provides additional resources on the web about SMB and related technologies in Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2016.
